Poojasingh
Posts
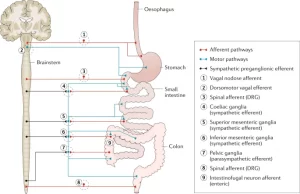
Enteric Nervous System (ENS)
Introduction The nervous system of the stomach. Types of Enteric Neurons Gastrointestinal neurons Preceptive afferent neurons Circular muscle motorneurons excitatory Circular muscle motorneurones inhibitory Motorneurons...
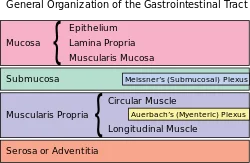
Submucosal Plexus (Meissner Plexus)
A local circuitry of neurons and ganglia that is located within the gut wall (from the esophagus to the rectum) is known as the submucosal...
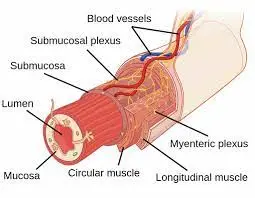
Myenteric plexus (Auerbach plexus)
Introduction The myenteric plexus, also known as Auerbach’s plexus, is a network of nerve fibers and ganglia located in the muscular layer of the gastrointestinal...
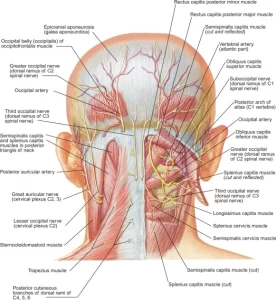
Suboccipital Nerve
Introduction The suboccipital nerve is also referred to as the dorsal ramus of the first cervical nerve since it arises from the posterior/dorsal ramus of...
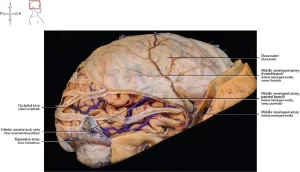
Meninges of the Brain and Spinal cord
Introduction The brain and spinal cord divide from the walls of their bony enclosures or illustrations (the skull and spinal column) by three membranes called...
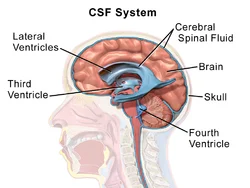
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
What is a Cerebrospinal Fluid? Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear or transparent, colorless plasma-like fluid that bathes or cleans the central nervous system (CNS)....
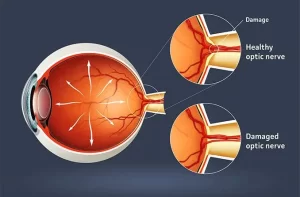
Optic nerve (CN- 2)
The optic nerve is highly important for your vision. It’s the 2nd cranial nerve out of 12 cranial nerves and part of your central nervous...
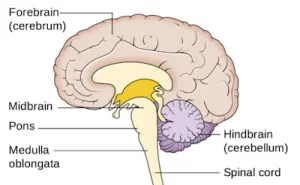
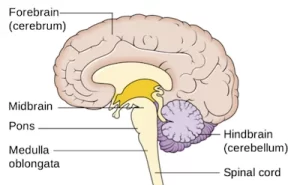
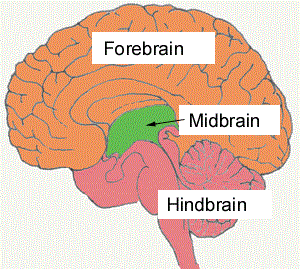
Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
The mesencephalon or midbrain is the greatest rostral (front) segment of the brainstem that joins the cerebellum and pons with the forebrain. For most of...