Snapping Pes Anserinus Syndrome
What is Snapping pes anserinus syndrome?
Snapping pes anserinus syndrome is the major extraarticular reason for snapping at the medial knee. It results from impingement of the semitendinosus and gracilis tendons against the tibial condyle at 15 extensions when returning from a bent position of the knee joint.
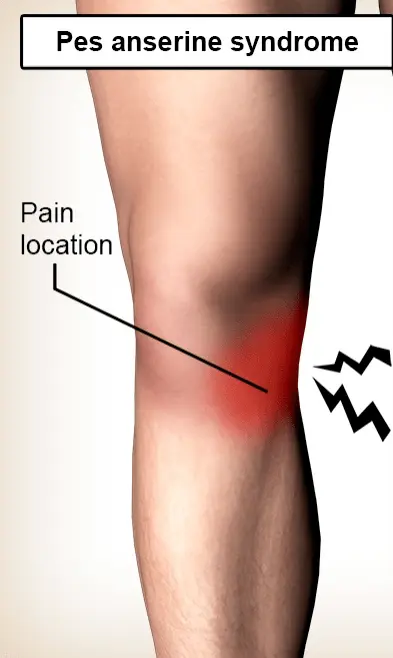
The pes anserinus is the insertion of three – 3 tendons on the medial side of the knee joint. Pes anserinus suggests “goosefoot”, due to the figure of these three tendons. An ache in the pes anserinus can be induced by inflammation of one of the tendons or by bursitis. The ache is felt on the medial side of the knee joint.
Description of the condition
The pes anserinus is created by the tendons of three different muscles: the gracilis, sartorius, and semitendinous. These tendons connect to the tibia. The role of these three muscles is especially to flex and turn the knee joint and to provide the asset to control valgus stress. Valgus stress is the inward caving of the knee joint, which is why it is also guided to as a knock knee joint. The distance between the conjoined tendon and the tibia includes a bursa. A bursa is a bag loaded with fluid that creates sure that other structures slide over one another.
The dissimilarity between tendinitis ( tendinopathy ) and bursitis is to be determined. Thus, the word pes anserinus syndrome is nodes. The difference also has no added matter because the therapy is the same in both circumstances.
What are the Causes of Snapping Pes Anserinus Syndrome?
- Female gender ( the pelvis is generally broader, evolving into knock knee joint faster ).
- Obesity ( the stress on the knees joints becomes too high and this can cause knock knee joint ).
- Arthrosis of the knee ( which can induce knock knee joint ).
- Diabetes ( decreased circulation so that tendons and bursas heal less fast ).
- Rheumatism ( decreased quality of the muscles results in a higher chance of wear and tear ).
- Repetitive sports ( cycling, running, and swimming can induce excessive pressure ).
- Flatfoot ( Which can play a function in the position of the knee joint ).
- Local trauma ( accident, fall, or making a wrong motion ).
- Osteophytic formation ( additional ossification on the medial side of the knee joint ).
Signs and symptoms of Snapping Pes Anserinus Syndrome
Usual symptoms contain aches on the medial side of the knee joint and pain when pushing on the insertion of the tendons. The insertion sits below the knee joint on the medial side of the tibia. The ache frequently obtains worse by walking up and down the stairs. The specific symptoms for everyone. Ache is frequently experienced over a larger region. As an outcome, it is hard to determine if the ache arises from the pes anserinus, medial meniscus, or medial knee joint ligament.
The set criteria for the diagnosis contain:
- Ache on the medial side of the knee joint.
- Ache when stepping up and down the stairs.
- An ache in the morning.
- Morning immobility at the site ( of the ache ) lasting at least one hour.
- A problem in reaching out of a chair or car.
- Local sensitivity.
- Local swelling.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is completed by a ( general ) practitioner or physiotherapist based on a discussion and physical examination. the above – mentioned measures play an essential role in this. Further examinations like x-ray studies or ultrasound studies have no added matter in the case of these symptoms.
An x- rays analysis can, yet, be used to select the degree of osteoarthritis in the knee joint. Osteoarthritis is a risk factor for the growth of pes anserinus symptoms.
An ultrasound study recognizes muscles, tendons, and bursas, but it is known that this is a reliable analysis when it arrives to pes anserinus symptoms.
When completing the diagnosis, other issues in this area must be ruled out. Especially meniscus issues and medial ligament impairment cause ache in the same area. This should be carried into account when completing the diagnosis.
Treatment of Snapping Pes Anserinus Syndrome
The therapy of pes anserinus syndrome concentrates on decreasing the inflammatory response. This can be performed using ( relatives) rest, icing, and anti-inflammatory medications prescribed by the ( general ) practitioner or doctor. A local injection of an anti-inflammatory may be allocated. To sleep, the help of a pillow between the knees joints is suggested to decrease pressure on the aching spot
In extra, the therapy consists of attacking the risk factors. If overweight, the person is urgently recommended to lose weight. If the person has flatfeet, these can be managed with insoles.
Physiotherapy plays an essential role during therapy. The physiotherapist can manage the muscles around the knee joint or junction via activities and specific stretching methods. Posture is functioned on too, particularly when the person has to knock the knee joint. If required, strength training is recommended and provided to control the loss of muscle strength around the knee joint or junction.
Many persons with pes anserinus syndrome begin to feel sounder within a few weeks of the damage. Your physiotherapy treatment will purpose to:
- Relieve pain and inflammation.
- Normalize joint or junction range of movement.
- Stretch tight muscles around the knee joint
- Strengthen your knee joint: specifically the quadriceps (especially VMO) and hamstrings.
- Strengthen your lower limb muscles: hip, calves, and pelvis muscles.
- Enhance patellofemoral (knee-cap) alignment
- Regularize your muscle lengths
- Enhance your proprioception, agility, and balance
- Enhance your method and function example running, walking, squatting, hopping, and landing.
- Minimize your probability of re-injury.
FAQ
What connects to the pes anserine?
From anterior to posterior, the pes anserinus contains the tendons of the sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus muscles, per of which is supplied by various lower-extremity nerves (obturator, femoral, and tibial, respectively)
Can the knee swell if the PES tendon is damaged?
A repetitious overload of the tendons generally causes this disease. This excess leads to swelling and ache. Frequently, persons document a change in the usual intensity or frequency of running or sport. Occasionally a drop onto the inside of the knee joint causes swelling and ache in the pes bursa.
How do you stop pes anserine?
Your physical therapist can suggest a home-exercise schedule to strengthen and lengthen the muscles around your upper legs, knees, and abdomen to assist to control the onset or reproduction of pes anserine bursitis. These may contain strength and flexibility activities for the knees, legs, and core muscles.
How long does pes anserine heal?
Most people with pes anserine bursitis recover in approximately six to eight weeks. It could bring longer for more severe issues. You’re probably to heal quickly if you rest and seek appropriate therapy.
How do you sleep with pes anserine?
You may be woken by an ache when you move over as you flex or straighten the knee joint. It can assist to sleep with a cushion between your knees and joints to provide some cushioning to the pes anserine bursa.

One Comment