SPASTICITY TREATMENT IN CEREBRAL PALSY
INTRODUCTION
- Spastic Cerebral palsy is a chronic disability of the central nervous system origin characterized by aberrant control of the movement of posture, appearing early in life and not the result of progressive neurological disease.
- Most children with CP will have spasticity as the main motor disorder and it can be classified either according to which body area is affected: hemiplegia, diplegia, tetraplegia, or the movement disorder type: the spastic, athetoid, ataxic, and hypotonic cerebral palsy brain. Spasticity is a major challenge in the rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy.
- Spasticity can prevent or reduce function, cause pain, disturb sleep, cause unnecessary complications, and present major difficulties for care workers.
DEFINITION OF SPASTICITY
- Spasticity of Muscles is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia.
- It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual “tightness”, stiffness, or “pull” of muscles.
Which are the Causes of Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy?
- In cerebral palsy, spasticity is due to injury to the motor cortex of the brain before, during or after birth.
- Premature Delivery is more vulnerable, in part because their organs are not fully developed, increasing the risk of hypoxic injury to the brain that may manifest as cerebral palsy.
- Problems in intrauterine development (e.g. exposure to radiation, infection), asphyxia before birth, hypoxia of the brain, birth trauma during labor and delivery, and complications in the prenatal period or during childhood.
- Head Injury
- Spinal Cord Injury
- Stroke
Which are the Signs and Symptoms of Spastic Cerebral Palsy?
The signs and symptoms of spastic cerebral palsy are different for every child. Differences in symptoms depend on the severity of the child’s brain injury and any co-occurring disorders that may be present.
The most common symptoms of spastic CP are:
- Stiff, tight muscles (hypertonia) on one or both sides of the body
- Exaggerated movements
- Limited mobility
- Inhibit muscle growth
- Abnormal gait
- Crossed knees
- Joints don’t fully extend
- Walking on tiptoes
- Contractures of muscles
- Poor Posture
- Abnormal reflexes
- Insomnia.
- Co-occurring issues may also present themselves, such as hearing and vision impairment, but these aren’t directly related to cerebral palsy; they are caused by the initial birth injury.
- In the first years of a child’s life, it can be very hard to recognize the signs of cerebral palsy. This is because symptoms typically do not present themselves until a child begins missing developmental milestones.
- During toddlerhood, many children tend to exhibit some of the same jerky reflexes associated with spastic CP. It can take up to 5 years of age before a full cerebral palsy diagnosis is reached.
How to Measure Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy?
The Modified Ashworth scale (MAS) measures resistance during passive soft-tissue stretching and is used as a simple measure of spasticity.
Scoring of modified Ashworth scale:
- 0 — No increase in muscle tone
- 1 — Slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch and release or by minimal resistance at the end of the range of motion when the affected part(s) is moved in flexion or extension.
- 1+— Slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch, followed by minimal resistance throughout the remainder (less than half) of the ROM.
- 2 — a More marked increase in muscle tone through most of the ROM, but affected part(s) easily moved.
- 3 — Considerable increase in muscle tone, passive movement difficult.
- 4 — Affected part(s) rigid in flexion or extension.
What is the Treatment of Spastic Cerebral Palsy?
In Spastic Cerebral Palsy, Medicine is used to reduce spasticity with Physiotherapy Treatment to improve motor function, stretching exercises, and rarely surgery also require in severe cases. Orthoses like splints are used to reduce spasticity.
Medical Treatment
Treatment of spasticity is a major challenge for the Rehabilitation team. Mainly Physiotherapy is available to people living with cerebral palsy as well as caregivers and parents caring for someone with this disability. They can all be useful at all stages of this disability and are vital in a CP person’s ability to function and live more effectively.
- Medications to control spasticity, such as muscle relaxants. Baclofen oral medicine – pump (to help control muscle spasticity).
Anti-spasticity Medicine
Baclofen (Lioresal)
- GABA agonist
- Max. dose 180 mg daily, divided
- Side effects: sedation, incontinence, weakness, withdrawal seizures
Tizanidine (Zanaflex)
- Alpha2 adrenergic agonist
- Max. dose 24-32 mg daily
- Side effects: sedation, hypotension, weakness, hepatotoxicity
Dantrolene – a reserve for specialists
- Diazepam et al. (Valium)
- Gabapentin (Neurontin)
SPASTICITY INVASIVE TREATMENTS:
- Botulinum Toxins A & B
- Baclofen pump
- Intrathecal delivery via implanted pump (ITB)
- Surgical interventions:
- Tenotomy (Tendon Lengthening)
- Selective Rhizotomy
Physiotherapy Treatment in spastic cerebral palsy :
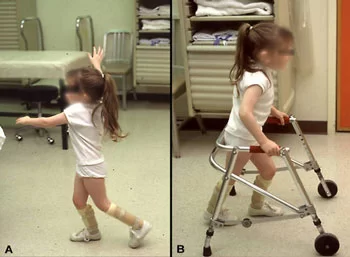
- Physiotherapy for cerebral palsy is aimed at promoting motor and developmental skills. It is used to address sensory impairments, range of motion issues, muscle tightness, and other physical disability.
- The parent or caregiver should be taught the exercises or activities that are necessary to help the child reach their full potential and improve function.
- Physiotherapy treatment also helps in improving balance, movement, and walking independently or using mobility aids. Some individuals with spasticity can experience painful contractures, joint deformities, and other complications. Physiotherapy can prevent and treat these issues.
- Daily range-of-motion (ROM) exercises are important to prevent or delay contractures caused by spasticity and to maintain the mobility of joints and soft tissues.
- Children and their parents often enjoy hippotherapy (therapeutic horseback riding; this is a type of complementary/alternative therapy). Hippotherapy uses the rhythmic gait of a horse to help improve the child’s muscle tone, ROM, strength, coordination, and balance. It offers many social, cognitive, physical, and emotional benefits.
- Physiotherapy is crucial when a child has had surgery to help correct spasticity; it helps the child obtain maximum benefit from surgery.
Stretching Exercise :
Stretching exercise is highly useful for reducing spasticity, Long and gradual stretching exercises are required daily for long periods of time 4 to 5 times a week is required.
In the Lower limb Hip adductors, Hamstring and Calf muscles are seen spasticity, and stretching of these muscles with the use of orthosis is also useful.
Position stretching is highly beneficial in spastic cerebral palsy. eg. long sitting position is useful for stretching of Hamstring and calf muscle.
Weight Bearing Exercise :

Physiotherapists regularly use static weight-bearing exercises in children with spastic cerebral palsy, which are believed to stimulate antigravity muscle strength, reduce spasticity, improve bone mineral density, improve self-esteem, improve feeding, assist bowel and urinary functions, and Balance.
Icing for Reducing Spasticity :
Ice is Highly used for reducing spasticity and is the most natural way. Ice has 2 way uses, If You use it as a quick stroke over muscles, it may increase muscle tone and so also increase spasticity, so never give a stroke of ice over spastic muscles, Icing is applied slowly over bulky muscles for 15 to 20 minutes helps in reducing spasticity.
To increase the muscle tone of the opposite group of muscles mainly flaccid muscles are applied a quick stroke of ice helps in increasing the tone of muscles.
Strengthening Exercise :
Strengthening exercise of an opposite group of muscles is highly useful for reducing spasticity. eg. if spasticity is present in the flexor group of muscles in the lower limb will create flexor deformity, to reduce spasticity and deformity, strengthening exercises of the Quadriceps are highly useful, this will help in reducing spasticity in flexor group and also reducing deformity.
Strengthening exercise of the Quadriceps stretches the Hamstring muscles and gradually helps in Indirectly reducing spasticity.
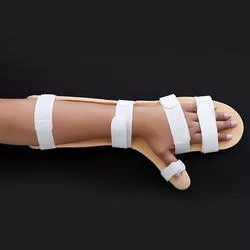
Orthosis / Splint
orthosis is a device that is used to support, align, prevent, or correct deformities or improve the function of movable parts of the body. Also known as casts, braces, or splints.
Orthoses are highly used for the treatment of spasticity, orthoses may reduce muscle tone, increase or maintain motion, and prevent skin damage such as the breakdown that would occur in your palm if your fist is continually clenched. eg. Cockup splint for forearm flexor’s muscles.