Swollen Lymph Node in Groin Region
Swollen lymph nodes in the groin region, also known as inguinal lymphadenopathy, can be a cause for concern and may indicate an underlying medical condition. Within the body’s immune system, lymph nodes are essential for removing pathogens and clearing toxic substances.
When lymph nodes in the groin become enlarged or swollen, it often signals a response to an infection, inflammation, or other medical issues in the lower part of the body.
Introduction
Ten lymph nodes can be found in each groin region. They are a component of your body’s defense mechanism against illness. Usually, enlarged lymph nodes indicate an infection. To be certain, though, it’s important to consult your healthcare professional.
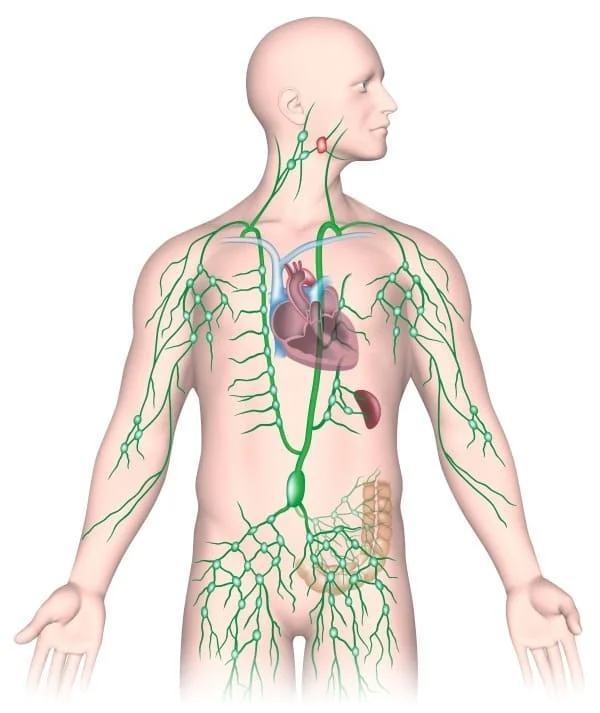
Lymph nodes: What are they?
Your immune system contains tiny, circular structures called lymph nodes, sometimes known as glands. They are fleshy and serve to filter lymph, a fluid that contains a particular kind of white blood cell that aids in the body’s defense against infection.
The body is made up of clusters of lymph nodes, which include: in back of your earlobes.
- On your neck’s sides.
- Beneath your biceps.
- In the groin, the upper inside portion of the leg.
The inguinal lymph nodes are what?
Deep in the groin are these lymph nodes. In each leg, there are ten inguinal nodes close to the upper thigh.
What does lymphadenopathy—the enlargement of the lymph nodes—mean?
Your lymph nodes may go unnoticed in regular circumstances. They swell due to increased cell activity as they attempt to remove toxic toxins from the body. Your subcutaneous tissue swells and may feel tender to the touch.
What effects do enlarged inguinal lymph nodes have on my body?
Your body is typically fighting an infection, such as an ingrown nail, an insect bite, or a dog bite when your lymph nodes are swollen. However, they might also be an indication of other lower body diseases.
Causes of Swollen Lymph Node in Groin Region
The majority of the time, lower body injuries or illnesses result in enlarged inguinal lymph nodes. This may encompass the:
groin, urinary tract, leg, and foot
A few examples of these are:
- Foot of an athlete: a fungal infection that often starts as a scaly rash in the space between the toes
- A fungal infection called jock itch can result in a red, itchy rash in the groin area.
- Yeast infections of the vagina or penile regions are frequently brought on by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida.
- Any region of the urinary tract can be affected by a common illness called a urinary tract infection.
- Cellulitis is a common, possibly serious skin illness that typically affects the lower legs and is characterized by swelling and redness.
- Balanitis: an inflammatory skin condition affecting the head of the penis and foreskin, more common in non-circumcised individuals
- Prostatitis is an enlargement of the prostate gland that may result from an injury or bacterial infection.
- Cystitis: a bladder inflammation most commonly caused by a urinary tract infection (UTI), however, it can also be caused by some drugs or irritating personal hygiene items.
- Before genital blisters appear, enlarged lymph nodes in the groin and flu-like symptoms are frequently the first signs of genital herpes.
- Gonorrhea: a very common sexually transmitted infection that frequently has no symptoms but can produce painful urine and discharge
- Syphilis is a serious sexually transmitted infection that starts as a chancre and progresses over time, offering significant risks if left untreated.
- HIV is an immune-system-compromising virus that first manifests as flu-like symptoms and swollen lymph nodes.
- When a cat bites, scratches, or licks an open wound on a human, it can cause cat scratch disease, also known as cat scratch fever, a bacterial infection.
Rarely, enlarged lymph nodes in the groin may be the result of cancer.The inguinal lymph nodes may get infected with cancer that has migrated from the back, pelvis, or lower limbs. These cancer types include, among others:
- Melanoma, and prostate cancer
- Cancer of the ovaries
Leukemia and lymphoma are two more cancers that can result in swollen lymph nodes. Multiple areas of lymph node swelling are more common in these types of cancers.
Lymph node swelling can also be caused by immune system deficiencies and diseases like chickenpox and mononucleosis.
The following are a few common symptoms of enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area:
- The most typical symptom is a lump or bump in the groin area; the lymph node may be pea-sized, grape-sized, or even larger.
- Groin tenderness or pain: The lymph node may feel tender to touch and can be painful, particularly when the legs are moved.
- Warmth or redness in the groin area: This could indicate an infection.
- Fever is a general symptom that can be present with a wide range of infections.
- Chills: An infection may also be a symptom of them.
- Fatigue: This is a prevalent sign of a wide range of illnesses, such as cancer and infections.
Diagnoses and Tests
How are groin swelling lymph nodes diagnosed?
Medical professionals will obtain a medical history and conduct a thorough physical examination, taking into account all possible causes. It consists of:
Take medical history by asking about:
- Symptoms: How do they feel and how long have they continued?
- Personal health history: A list of conditions you have previously been treated for.
- Medication: All drugs, vitamins, and dietary supplements you take.
- Social factors: Activities that can increase your chance of infection, such as unprotected sex.
- Health history in the family: includes autoimmune diseases and cancer in blood relations.
Conducting a physical examination, which includes:
- assessing each of the body’s key systems for symptoms of diseases
- Examine the size and tenderness of your inguinal lymph nodes by lightly pressing on them.
- Checking for swollen lymph nodes in other body parts.
Do I need to take any tests?
Medical professionals might advise:
- Labs: Blood testing to verify or exclude particular infections kinds.
- Imaging studies: A pelvic CT scan or ultrasound to determine the location and size of enlarged lymph nodes. These investigations might be useful in identifying abnormal growths.
- Biopsy: Medical professionals could remove a sample of tissue and analyze it in a laboratory. A biopsy helps in ruling out or confirming cancer.
Treatments of Swollen Lymph Node in Groin Region
How are groin swelling lymph nodes treated?
The cause affects the treatment:
- Immune treatment, comprising immune-system-regulating medications, is used to treat autoimmune illnesses.
- Cancer: Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery for removing abnormal growths.
- Prescription medications for infections, such as anti-fungal, antibiotics, and antivirals.
- Medication management: Your healthcare practitioner may adjust the drug or dosage to address swelling brought on by drugs.
Prevention
How can I prevent developing swollen groin lymph nodes?
steps you can do include:
- avoiding STDs through the use of safe sexual practices.
- maintaining current immunization records.
- implementing the treatment suggestions made by your healthcare physician for conditions like autoimmune diseases.
- Self-care involves maintaining proper cleanliness to reduce the risk of skin infections.
Prognosis
How much longer before the swelling goes down?
It varies. In the event that you are receiving therapy with antibiotics or antivirals, the swelling should subside in a few days, though it may take longer.
Will inguinal lymph nodes impact enlarged my health in the future?
Individuals who have infection-related swelling usually recover completely. The illness has no long-term effects on your health.
Living With
What happens if the treatment doesn’t work?
See your doctor again if, despite taking medicine, the swelling does not subside. They might advise a biopsy, more testing, or other types of treatment.
Can cancer be the cause?
Swollen inguinal lymph nodes are unlikely to be cancerous, as the disease usually presents with other symptoms.
Consult with your doctor if you have any concerns.
Which symptoms could indicate that it’s cancer?
Problems that could indicate that testing to rule out cancer is necessary include lymph nodes that:
- You won’t get better with medicine.
- Don’t make someone uncomfortable.
- Proceed to grow, reaching a size of a few inches in certain situations.
- are hard and do not move to light pressure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a number of factors, such as infections, immune system abnormalities, and specific medical problems, can produce enlarged lymph nodes. Even though common infections are frequently the cause, persistent or severe instances need to be assessed by a medical specialist in order to determine the underlying cause and treat it. Seeking timely medical consultation is essential for a precise diagnosis and the right course of action.
FAQ
When should I worry about swollen lymph nodes in the groin?
Consult your physician if your swollen lymph nodes are causing you any concern. have emerged seemingly out of nowhere. Have persisted in growing or been there for two to four weeks. Feel firm or rubbery, or remain still in response to pressure.
How do you fix swollen groin lymph nodes?
Personal hygiene
Put on a heated compress. Treat the affected region with a warm, moist compress, such as a washcloth dipped in hot water and squeezed dry.
Utilize an over-the-counter analgesic. These consist of aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol, etc.), naproxen (Aleve), or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, etc.).
Get enough rest.
How long do groin lymph nodes last?
Glands that are swollen will reduce in one to two weeks, depending on what caused them.
Where are groin lymph nodes located?
The groin region contains the superficial and deep inguinal lymph nodes. The inferior, supero lateral, and superomedial nodes are the divisions of the superficial inguinal lymph nodes, which are located beneath the inguinal ligament.
Can groin lymph nodes be removed?
Surgery to remove the lymph nodes from the groin is called an inguinal lymph node dissection. Inguinal lymph nodes are the lymph nodes located in the groin area. The fold or depression where the thigh and belly (abdomen) meet is called the groin. Another name for this procedure is a groin dissection or inguinal lymphadenectomy.
References
- Access Anytime Anywhere | Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/
- Santos-Longhurst, A. (2023, February 19). Swollen Lymph Nodes in the Groin: What Does It Mean? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/swollen-lymph-nodes-in-groin#causes