Ultrasonic therapy Machine [ Ultrasound ]
Introduction:
- Ultrasonic therapy m(Ultrasonic diathermy) Equipment are used in Physiotherapy equipment produce high-frequency sound waves that travel deep into tissue and create gentle therapeutic heat.
- Ultrasonic diathermy is intended to generate deep heat within body tissues for the treatment of selected medical conditions such as Muscles pain, muscle spasms, and joint contractures, but not for the treatment of malignancies.
- The sound waves are transmitted through a round-headed wand that the therapist applies to the skin with gentle, circular movements.
- A hypo-allergenic gel aids in the transmission of ultrasonic energy and prevents overheating at the surface of the applicator.
- Treatments usually last between five and 10 minutes.
Definition of wavelength
It is the distance between the two closet points on a wave that are performing the same motion at any instant in time.
Definition of frequency
It is the number of times a particle undergoes a complete cycle in one second.
Definition of velocity
It is a wave is the speed at which the waves moves through the medium.
It varies depending upon the physical nature of the medium.
The production of Ultrasound
- For 1 MHz machine a vibrating source with a frequency of once million cycles per second is needed.
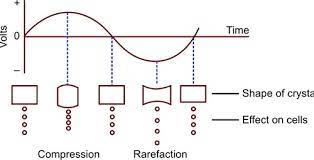
- This is achieved using either a quartz or a barium titanate crystal.
- These crystals deform when subjects to a varying potential difference = a piezo – electric – effect.
The components of Ultrasonic apparatus :
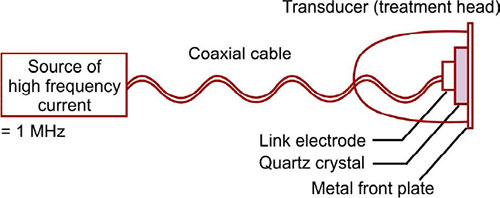
- There is a source of high-frequency current, which is conveyed by a coaxial cable to a transducer circuit or treatment head.
- Inside the transducer circuit, the high-frequency current is applied to the crystal via a linked electrode.
- the crystal being fused to the metal front plate of the treatment head.
Any change in the shape of the crystal = effect of the ultrasound is different.
Ultrasound treatment parameters :
Frequency :
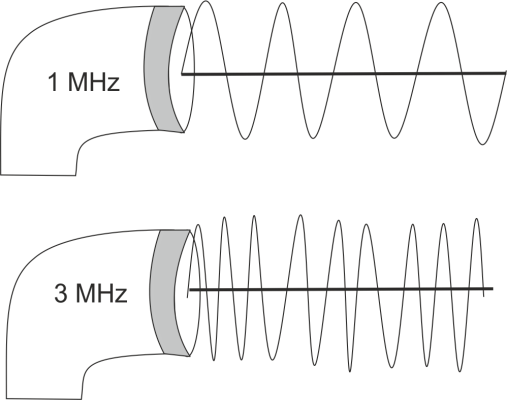
- Mostly used 1 MHz & 3 MHz
- 1 MHz = heats tissue form 2 to 5 cm
- 3 MHz = heats superficial tissue
Mode :
- Continuous = treatment head continuously produce ultrasonic energy .
- Pulsed = the period of ultrasound are separated by periods of silence.
Intensity :
- Unit of intensity = watt.
- Space averaged intensity = it is used in continuous mode [ watt per square centimetre ].
- Time averaged intensity = it is used in pulse mode and give to per second intensity [ watt per square centimetre ].
Reflection of ultrasound :
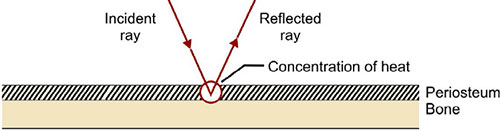
- When ultrasonic beams travelling through one medium encounters another medium which will not transmit and reflection is occurs.
- However there will always be some reflection at each interface that the ultrasound beam encounters .
- Acoustic impedance [Z] = ratio between the reflected and transmitted ultrasound at an interface.
- When acoustic impedance low = transmission is high.
- So acoustic impedance & transmission is vice versa.
Transmission of ultrasound :
- If the ultrasonic beam encounters an interface between two media and is transmitted, it may be refracted.
- When travelling low velocity medium to high velocity medium it is refracted form the normal, deflected form original path.
Attenuation of ultrasound :
- Attenuation is the term used to describe the gradual reduction in intensity of the ultrasonic beam once it has left the treatment head.
- This is reduced in intensity the deeper it passes.
- This gives rise to the expression half-value distance.
Two factor of attenuation :
- Absorption
- Scatter
Absorption :
- Ultrasound is absorbed by the tissues and converted to heat at the point.
- This is the thermal effect of ultrasound.
Scatter :
- When the normally cylindrical ultrasonic beam deflected form its path by reflection at interfaces, bubbles or particles in its path.
Ultrasonic field of ultrasound :
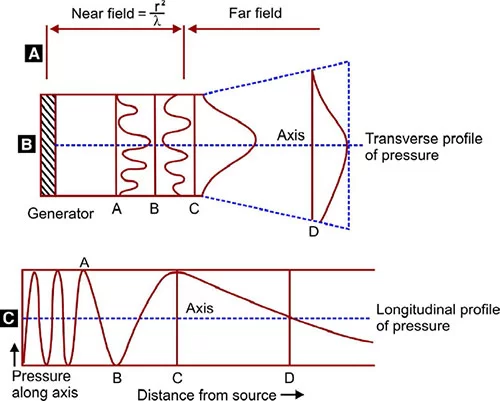
- It is relating to depth of penetration and intensity of the ultrasonic beam of the near and far field.
- the extent of the near field is depends upon the radius [r]of the transducer & wavelength (?) of the ultrasound in the medium.
- Depth of the near field = square of radius / wavelength
Depth of near field for different sizes of transducers :
| NO. | TRANSDUCER RADIUS (mm ) | FREQUENCY ( MHz ) | EXTENT OF NEAR FIELD ( cm ) |
| 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 |
| 2 | 15 | 3 | 45 |
| 3 | 10 | 1 | 6.5 |
| 4 | 20 | 1 | 26.5 |
Coupling media for ultrasound :
- Ultrasonic waves are not transmitted by air, thus some couplant which does transmit them must be interposed between head and patient’s skin.
- Unfortunately no couplant affords perfect transmission and only a % of the original intensity is transmitted to the patient.
- Air transmission is zero so it is reflect the ultrasonic beam back into the treatment head & damage to crystal.
Efficiency of transmission of ultrasound by various coupling media :
| NO. | COUPLANT | % TRANSMISSION |
| 1 | Aqua sonic gel | 72.6 |
| 2 | Glycerol | 67 |
| 3 | Distilled water | 59 |
| 4 | Liquid paraffin | 19 |
| 5 | Petroleum jelly | 0 |
| 6 | Air | 0 |
Testing of ultrasound machine :
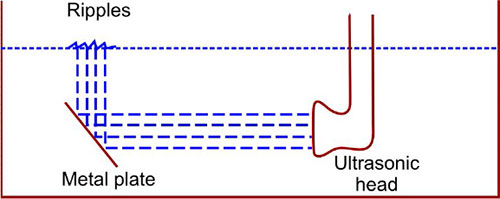
- Always before use the machine carefully check the machine.
- The simplest way of finding out whether ultrasound is in fact being produced is to use a water bath and to reflect an ultrasonic beam up to the surface where it should produce ripples .
- The apparatus is turned on and off the treatment head below the water.
Techniques of application of ultrasound :
- Direct contact
- water bath
- water bag
Direct contact :
- If the surface is regular than a coupling medium is applied on the skin in order to eliminate air between the skin and the treatment head.
- The treatment head is moved in small concentric circles over the skin.
- The machine is turned on -off while in contact with the patient.
- This technique is suitable for areas up to three times the size of the treatment head.
- For large area =divided the area and each area treated separately.
Water bath :
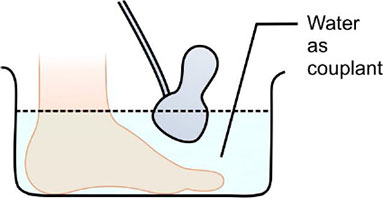
- A water bath filled de – gassed water is used.
- When used to tap water it is produce gas bubbles on the patient’s skin and treatment head.
- So if use the tap water then wiped the gas bubbles form these surface frequently.
- On this technique treatment head is held 1 cm from the skin and moved in small concentric circles.
- Keeping the front plate parallel to the skin surface to reduce reflection to a minimum.
Water bag :
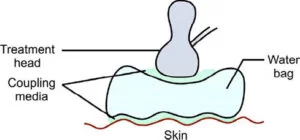
- On irregular bony surfaces a rubber bag filled with de – gassed water can be used.
- A coupling medium has to be placed both between the rubber bag and the skin and also between rubber bag and the treatment head to eliminate any air.
- It is slippery bag so that the treatment head moved in the same way as if it were the patient’s skin.
Dosage of Ultrasonic therapy Machine:
Acute conditions :
- Prevent to exacerbation of symptoms
- Initial stage = low does [ 0.25 or 0.5 W/cm2 ] is used for 2-3 minutes.
- Using pulsed beam will reduce the heating effect which could provoke symptoms.
- For progression = same dose repeated
- If failure to improve = increase to intensity 0.8 W/cm2 & 4-5 minutes.
- Aggravation of symptoms is not always a bad sign as it may indicate the repair processes are taking places
- Ratio = m:s pulse [ very acute – 1:7 , less acute – 1:1 ]
Chronic conditions:
- Pulsed or continuous beam
- For continuous = maximum intensity used – 2 W/cm2 for 8 minutes
- For progression = increase to dose
Physiological effect of Ultrasonic therapy Machine :
Effect is follow the step :
- Increased blood flow
- Reduction in muscle spasms
- Increased extensibility of collagen fibers
- A pro-inflammatory response
Thermal effect of Ultrasonic therapy Machine :
- Ultrasound is absorbed by the tissues and converted to heat at the point.
The amount of heat depends upon:
- Absorption characteristics of the tissue.
- Times of treatment.
- Efficiency of the circulation through the insonated tissue.
- Continuous ultrasound = intensity & duration of insonation.
- Pulsed = less effect than continuous.
Uses :
- Accelerate healing
- Stretching of scar and adhesion
- Reduce pain
Cavitation effect of Ultrasonic therapy Machine:
- This is the oscillatory activity of highly compressible bodies within the tissues such as gas or vapor filled voids.
- cavitation may be unstable so dangerous for tissue as the collapse of the bubbles causes a great local rise in temperature.
- It is avoid by moving the treatment head, using a low intensity, using a high frequency
- Stable cavitation = micro-streaming
Mechanical effect of Ultrasonic therapy :
- This is where the longitudinal compression waves of the ultrasonic beam produce compression/rarefaction of cells and affect the movement of tissue fluid in interstitial spaces.
- This can help reduce edema.
Biological effect of Ultrasonic therapy machine :
On this effect oh non- thermal help to healing in 3 stages :
- Inflammatory = increase the fragility of lysosomes membranes so release the contained enzymes , it is help to clear the area of debris.
- Proliferative = fibroblasts and myofibroblasts may have ca+ ions driven into them by ultrasound, they increase their mobility and encourages their movement towards the area of repair.
- Remodeling = increase the tensile strength of the scar by affecting the direction, strength and elasticity of the fibers which make up the scar.
Indications of Ultrasonic therapy machine :
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Shoulder pain, including frozen shoulder
- Tendinitis
- joint Arthritis
- Tennis elbow
- Golfer elbow
- Ganglion cyst
- Recent injuries and inflammation
- Scar tissue
- Chronic indurated edema
- Swelling
- Ligament injuries
- Wound healing
Contraindications of Ultrasonic therapy machine :
Vascular conditions :
- Condition such as thrombophlebitis, where insonation may cause emboli to be broken off.
- So that not treated with ultrasound.
Acute sepsis :
- An area which presents acute sepsis should not be treated with ultersound becausedanger to spreading the infection.
- Some time breaking off septic emboil.
Radiotherapy :
- It has a deviating effect on the tissues therefore ultrasound is not applied to a radiated area for at least six month after Irradiation.
Tumors :
- Tumors are not insonated because they may be stimulated into growth or throw off metastases.
Pregnancy :
- A pregnant uterus is not treated as the insonation might produce fetal damage.
- During pregnancy the back and abdomen should not be treated.
Cardiac disease :
- It is suggested that ultrasound may alter the electrical signals around your heart.
- If you have a pacemaker, ultrasound may interfere with its normal function.
In children :
- Ultrasound over the bone that has not fully developed may cause fractures or other problems with the part of the bones that are responsible for growth.
Over reproductive organs :
- The effect of ultrasound used over reproductive organs like the testes or ovaries is not fully explored and therefore should be avoided.
In areas with decreased temperature sensation:
- If your injury prevents you from feeling normal hot and cold temperatures, ultrasound should not be used since you would not be able to report any discomfort or burning sensations to your physical therapist.
Over body parts with total joint replacements:
- Many total joint replacements use a special cement to hold the new joint in place, and ultrasound may rapidly heat this cement and damage surrounding body parts.
Dangers of Ultrasonic therapy machine :
Burns :
- If a continuous beam is used and is allowed to remain stationary.
- Excess heat can accumulate in the tissue.
- eventually, lead to burn.
Overdose :
- Excessive treatment may cause an exacerbation of symptoms.
Damage to equipment
- When the treatment head is held in the air while switched on, a reflection of the beam back into the treatment head damages the crystal.



35 Comments