11 Best Knee Stability Exercise
What is a Knee Stability Exercise?
Knee stability exercise are a vital component of any comprehensive fitness program, particularly for individuals who engage in activities that place stress on the knees. These exercises focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee joint, enhancing balance, improving coordination, and promoting overall stability. By incorporating knee stability exercises into your routine, you can reduce the risk of knee injuries, enhance athletic performance, and support the rehabilitation and recovery process.
The knee joint is particularly susceptible to injury due to its complex structure and the forces it experiences during physical activities. Weakness or imbalance in the muscles surrounding the knee can lead to instability, increased stress on the joint, and a higher likelihood of injuries such as ligament sprains, strains, or tears. Knee stability exercises help address these issues by targeting the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and other surrounding muscles, which provide support and stability to the knee.
In addition to injury prevention, knee stability exercises offer benefits for individuals with existing knee conditions, such as patellofemoral pain syndrome or osteoarthritis. These exercises can help alleviate pain, improve joint function, and enhance overall knee health.
Knee stability exercises are important for strengthening the muscles around the knee joint and improving overall stability.
Here are some Knee Stability Exercises you can try:
Straight Leg Raises:
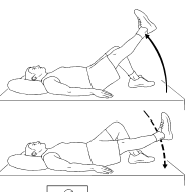
In the Supine lying position, one leg should be straight while the other leg bent. Maintaining a straight knee, raise the straight leg off the ground. Hold for a short second, then gradually bring it back down. Repeat 10 to 15 times.
Wall Squats:
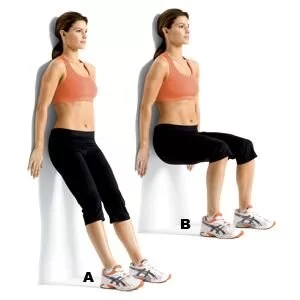
Keep your feet hip-width apart and your back supported against a wall. Keeping your back against the wall and your knees in line with your toes, slide down the wall into a squat position.
Push through your heels to get back to the starting position after holding for 10 to 15 seconds. Repeat ten to fifteen times.
Step-Ups:

Stand facing a step or elevated platform. Step up onto the platform with one foot, pushing through your heel, and bring the other foot up to join it. Step back down with the leading foot, followed by the other foot. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
Single-Leg Balance:

Stand on one leg and lift the other leg off the ground, bending it slightly at the knee. Engage your core and maintain your balance for 30 seconds to 1 minute. Switch legs and repeat.
Hamstring Curls:

Stand tall with your feet hip-width apart while keeping your hands on your hips. Lift one foot toward your glutes, bending at the knee, and hold for a second or two. Lower the foot back down and repeat with the other leg. Perform 10-15 repetitions on each leg.
Side-Lying Leg Lifts:
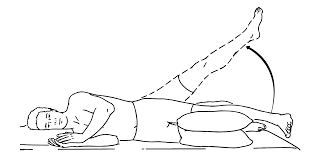
Lie on your side with your lower leg bent. Straighten your top leg and lift it upward while keeping it in line with your body. Hold for a few seconds, then lower it back down. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
Clamshells:
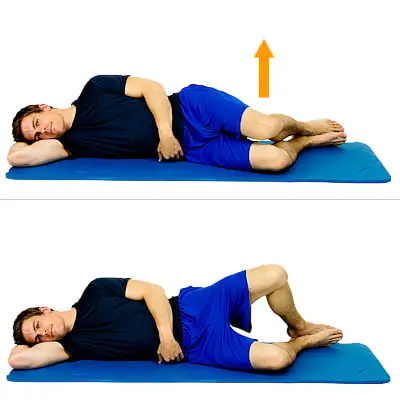
Your feet should be close together, and your knees should be bent.
Keep your feet together as you clamshell your knees open and then slowly shut them.
On each side, repeat 10 to 15 times.
Step-Ups with Knee Lift:

- Perform step-ups as described earlier, but as you step up onto the platform, drive your opposite knee up towards your chest.
- Step down and repeat on the other side. Perform 10-15 repetitions on each leg.
Calf Raises:
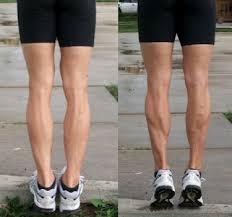
Stand with your feet hip-width apart and hold onto a sturdy surface for balance. Rise up – lifting your heels. Hold for a second or two, then lower your heels back down. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
Single-Leg Deadlifts:

Stand on one leg while the other leg slightly bends in the knee. Keeping your back straight, hinge forward at the hips while extending the other leg straight behind you. Keep your core engaged and return to the starting position. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
Quadriceps Sets:
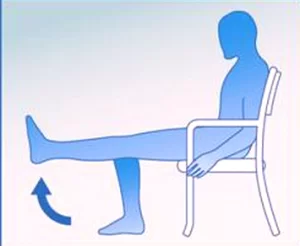
Sit on a chair while keeping your feet flat on the floor. Tighten the muscles on the front of your thigh (quadriceps) and straighten your knee as much as possible. Hold for a few seconds, then release. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
Remember to start with a weight or difficulty level that challenges you but doesn’t cause pain or excessive discomfort. If you have any existing knee conditions or injuries, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified physical therapist before starting any new exercise routine.
Benefits of Knee Stability Exercise
Knee stability exercises offer numerous benefits for individuals of all ages and fitness levels. Here are some key benefits of incorporating knee stability exercises into your workout routine:
- Injury Prevention: Knee stability exercises help strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. By improving the stability and strength of these muscles, you can reduce the risk of knee injuries, such as ligament sprains or tears, and patellofemoral pain syndrome.
- Enhanced Joint Stability: Strong and stable knee joints are essential for maintaining proper alignment and function during various physical activities. Knee stability exercises target the muscles, tendons, and ligaments that support the knee joint, helping to improve overall joint stability and reduce the risk of instability or buckling.
- Improved Performance: Athletes and individuals involved in sports or activities that require frequent knee movement, such as running, jumping, or pivoting, can benefit from knee stability exercises. These exercises help enhance proprioception (awareness of body position), balance, and coordination, leading to improved performance and reduced risk of falls or accidents.
- Rehabilitation and Recovery: Knee stability exercises are commonly used in rehabilitation programs for knee injuries or post-surgery recovery. They can help rebuild strength, range of motion, and stability in the knee joint, facilitating a smoother recovery process.
- Alleviation of Knee Pain: For individuals with chronic knee pain or conditions like patellofemoral pain syndrome or osteoarthritis, knee stability exercises can help alleviate pain and discomfort. Strengthening the muscles around the knee can provide better support to the joint, reduce stress on the affected areas, and improve overall knee function.
- Functional Movement Improvement: Knee stability exercises focus on functional movements that mimic everyday activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, or bending down. By enhancing the stability and strength of the knee joint, these exercises can improve your ability to perform daily tasks with ease and reduce the risk of knee-related limitations.
Remember, it’s essential to perform knee stability exercises correctly and gradually increase the difficulty level to avoid overexertion or injury. If you have any underlying knee conditions or concerns, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified physical therapist to develop a personalized exercise program that suits your needs.
What Precautions are Required During Knee Stability Exercise?
While exercise is generally beneficial for your health and well-being, it’s important to take certain precautions to ensure your safety and reduce the risk of injury. Here are some general precautions to keep in mind during exercise:
- Consult with a healthcare professional: If you have any underlying health conditions, injuries, or concerns, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new exercise program.
- Warm-up and cool-down: Always start your exercise session with a proper warm-up, which may include light cardiovascular activities and dynamic stretching. This helps increase blood flow, warm up your muscles, and prepare your body for exercise. Similarly, cool down with gentle stretches and low-intensity movements to gradually bring your heart rate down and prevent muscle stiffness.
- Listen to your body: If you experience pain, dizziness, or shortness of breath, it’s important to stop and rest. Pushing through severe pain or discomfort can lead to injuries. If symptoms present, consult a Doctor immediately.
- Use proper form and technique: Correct form and technique are crucial to prevent injuries and maximize the effectiveness of your exercises. If you’re unsure about the proper form, consider working with a qualified trainer or seeking professional guidance to ensure you’re performing the exercises correctly.
- Gradually progress: Avoid sudden increases in intensity, duration, or weight. Gradually progress your exercise program to allow your body time to adapt and reduce the risk of overuse injuries. Listen to your body’s limits and avoid pushing yourself too hard too quickly.
- Stay hydrated: To stay properly hydrated during and after your workouts, consume lots of water. Dehydration can affect your performance and increase the risk of heat-related illnesses.
- Wear appropriate attire and footwear: Choose comfortable, breathable clothing that allows for a full range of motion during exercise. Wear supportive athletic shoes that fit properly and provide adequate cushioning and stability for your activities.
- Modify exercises as needed: If you have specific limitations or injuries, modify exercises to accommodate your needs. Seek guidance from a healthcare professional or a qualified trainer to find suitable alternatives or modifications that work for you.
Remember, everyone’s fitness level and abilities are different, so it’s essential to listen to your body and tailor your exercise routine accordingly. By taking these precautions, you can exercise safely and reduce the risk of injuries.
Conclusion
Knee stability exercises play a crucial role in strengthening the muscles around the knee joint, improving overall stability, and reducing the risk of injuries. By incorporating these exercises into your routine, you can experience several benefits, including injury prevention, enhanced joint stability, improved performance, rehabilitation and recovery support, alleviation of knee pain, and improved functional movement.
It’s important to remember that proper form and gradual progression are key when performing knee stability exercises. If you have any underlying knee conditions or concerns, it’s advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or a qualified physical therapist to develop a personalized exercise program that suits your needs.
By prioritizing knee stability exercises, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining strong, stable knees and enjoying an active, healthy lifestyle.