Rotator Cuff Muscle Pain
When you feel a sharp and aching pain over the front or outside means the lateral part of the shoulder joint and upper arm, you may have Rotator cuff muscle pain. You also feel the loss of strength in the arm.
Anatomy of the Rotator cuff muscle
The rotator cuff is made up of the muscles and tendons which are situated in the ball means the head of the upper arm bone, in the shoulder joint socket.
This rotator cuff muscle helps you lift and rotate the arm.
The rotator cuff muscle includes 4 muscles:
- Supraspinatus muscle
- Infraspinatus muscle
- Teres Minor muscle
- Subscapularis muscle
Supraspinatus muscle – This muscle keeps the humerus bone in place and holds the upper arm stable and helps to raise the arm.
Infraspinatus muscle – This muscle is the main muscle that is led to rotate and extend the shoulder joint.
Teres Minor muscle – This muscle is the smallest rotator cuff muscle, and the main job of this muscle is to assist with the rotation of the arm away from the body.
Subscapularis muscle – This muscle is held to the upper arm bone to the shoulder blade and helps to rotate the arm, and keep the arm straight out and lower to arm.
Cause of the Rotator cuff muscle pain
Rotator Cuff Tear:
A rotator cuff tear occurs when the muscle tendon is pulled from the arm bone.
This Rotator Cuff tear is found mostly in middle-aged and older adults.
This Rotator Cuff tear is caused by trauma like a fall directly on the shoulder joint and a direct blow to the shoulder. when they do the chronic overuse of the rotator cuff muscles which is also contributing to this muscle tear.
Obesity and smoking also increase a person’s chance of tearing the rotator cuff muscle.
Rotator Cuff Tendinitis:
Rotator cuff tendinitis which is a condition in the tendons begins to weaken and thin out due to aging.
In this tendinitis reduction of the blood supply to the rotator cuff tendons.
when the tendons become too stressed and injured, it is not recovered and heal as well.
Poor posture, repetitive overhead movement, smoking, and genes also play an important role in the development of rotator cuff tendinitis.
Rotator cuff pain is also due to playing sports that involve throwing and overhead reaching, like baseball and swimming.
Other causes of muscle pain include aging and weakening of the tendons or injuries of the shoulder.
Symptoms of the Rotator Cuff muscle pain
- You feel a sharp and aching pain in the site of pain.
- Swelling is also presently located over the front or outside means the lateral side of the shoulder joint and upper arm.
- In some cases, feel the pain farther down the arm.
- You feel the problem in many activities like combing the hair and reaching behind the back.
- Loss of strength in the arm means you notice to have a difficult time putting dishes away in the upper cabinets and reaching into the refrigerator to lift a carton of milk.
- You also feel pain in sleeping on the impacted shoulder joint.
- The feeling of throbbing pain at night is also common with rotator cuff tendinitis and tears.
- You feel the swelling, redness, bruising, and warmth around the shoulder joint.
- Shoulder pain is along with trouble breathing, dizziness, and abdominal pain.
- You feel the problem in lifting the arm above the head and carrying things.
Diagnosis of the Rotator Cuff muscle pain
The doctor also examined the range of motion ( ROM ) and strength of the upper limb in the analysis part of the assessment.
The doctor is do the imaging scans, such as an X-ray or an arthrogram, which is a type of detailed X-ray which is help to identify any bone triggers.
These small bone growths are rubbed against the rotator cuff tendon which produces pain and inflammation.
MRI & ultrasound scans ( US ) are also used in the diagnosis.
These tools examine the soft tissues, including the tendons and muscles.
These tools help to identify tears and show how large and severe the tears have become.
Test for the diagnosis of Rotator Cuff muscle pain:
When you feel a rotator cuff difficulty, the healthcare provider is suggested to conduct some tests to evaluate the rotator cuff tendons injury.
Empty Can Test
This empty can test is help to check the supraspinatus, a muscle that is situated on the upper part of the shoulder.
This test is simple to test to complete.
In this test, the patient’s position is to sit or stand comfortably.
Then lift the painful arm out to the side so the arm is parallel to the ground.
Bring the arm forward to about 30-45 degrees.
Then turn the hand over so that the thumb is pointing toward the ground.
Have the other person which is applied gentle pressure on the arm down.
When the pain is produced and weakness prevents from keeping the arm in the “empty can” position, it is indicated as surpassing impetus rotator cuff injury.
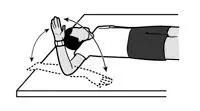
Lift-off Test
This lift-off test is a shoulder test which is help to specify the tear in the subscapularis muscle.
This test is responsible for turning the shoulder inward.
For this test, the patient’s position is in standing up and placing the back of the hand on the small of the back.
Face the palm away from the back, and then attempt to raise the hand away from the body.
If you are unable to raise the hand away from the low back, it is suggested to be a subscapularis rotator cuff injury.
Resistance Testing
This test also helps to for defining the rotator cuff tear which also leads to shoulder pain to complete the manual strength testing of the rotator cuff muscles.
For this test, the patient position sitting comfortably in a chair.
Then flex the elbow joint at 90 degrees and must keep the elbow joint tucked into the side.
Keep someone pushing the hand in toward the abdomen.
When you are unable to hold this position and produce pain, it is indicated as a rotator cuff tear.
Pain-Relief Test
This test is commonly conducted by orthopedic surgeons and sports medicine specialists.
It helps to differentiate between pain that is caused by a rotator cuff tear and pain generated by tendinitis.
The doctor injects lidocaine, which is an anesthetic medicine that does numb the site, into the shoulder joint.
When you are suffering from rotator cuff tendinitis, that lidocaine reduces the pain, and muscle strength remains normal.
Because of this test, the pain will be reduced, but the muscle becomes too weak.
When the doctor found to large tear, the primary healthcare provider is directed to the orthopedic surgeon.
Sometimes extensive tears of muscle are required for surgery and repair to tear.
Differential Diagnosis of the rotator cuff muscle pain
Not all rotator cuff muscle pain arises from the injury region.
Doctors usually want to rule out other possible reasons for a person’s symptoms to help them make the right diagnosis so which is essential to differential diagnosis for rotator cuff injury.
Some other musculoskeletal conditions which also impact the muscles and bones which is also produced similar symptoms of rotator cuff muscle injury include:
- frozen shoulder
- Osteoarthritis
- Shoulder instability and dislocation
- Labral tear
- Biceps tendonitis
- This differential diagnosis occurs with imaging tests.
- An X-ray is show symptoms of osteoarthritis.
- An MRI is used to analyze the labral tear.
Risk Factors for Rotator cuff muscle pain
The following characteristics increase the risk of rotator cuff muscle injury which is caused to rotator cuff muscle pain :
Age:
When you are older, risk of the rotator cuff damage increases.
So that Rotator cuff muscle tears are most common in people who are older than 50-60.
Construction jobs:
Some professions like carpentry and house painting which is needed repetitive arm movements in the work that applies to overhead on the muscle which causes damage to the rotator cuff muscle.
Family history:
Some hereditary component is also involved with rotator cuff injuries which appear to occur more commonly in individual families.
Treatment for the Rotator cuff muscle pain
RICE principle:
In the initial stage of pain reduction, muscle pain, and swelling are applied to the RICE principle.
Rest-(R): When you feel the pain must be avoiding to movements that provoke the pain, like overhead reaching and reaching behind the back means to do the rest someways.
Ice-(I): Use ice on the site of pain for 15 to 20 minutes which is used to relieve pain and swellings, you can also use an ice pack and frozen peas at the site of pain.
Compression-(C): Used as a compression bandage in the place of muscle pain for release to swelling by compression but not used to slings because it is the risk for the frozen shoulder.
Elevation-(E): Elevate to manufactured arm for release to swellings with the help of a pillow.

Pain medication:
For over-the-counter medicine, you are taken to the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) like Advil (ibuprofen) medication.
You also used volini gel and defense gel on the location of muscle pain for pain release.
Heat therapy:
You also used heat therapy to the site of muscle pain release to swellings and muscle pain.
You are used to a hot pack and heating pad on the site of pain for 10 minutes and do it 3 times every day.
Surgery:
Sometimes surgery is required for this muscle pain.
When this injury occurs young athletes usually require surgery.
Rotator cuff muscle repair surgery is done as an open procedure and a minimally invasive arthroscopic one.
The surgeon is recommended on which is the approach best for you.
This relies on the exact area of the rotator cuff injury and how severe to injury is.
Physiotherapy treatment of the Rotator cuff muscle pain
The physiotherapy treatment includes massage, electrotherapy, stretching, and strengthening exercises which help you release pain and swelling.
Massage:
Massage helps remove trigger points and tenderness of muscle pain.
It is also reduced muscle pain and swelling.
Massage is given by a therapist to the trigger points of the muscle for 5-10 minutes.
It is given with the help of oil.
The physiotherapist is also used to massage appliance release to spasms of muscle.
Electrotherapy:
The electrotherapy includes SWD, TENS, IFT, US, & Deep heating therapy which is used to release the pain and swellings as well as spasms.
For release to tender points and swellings, the physiotherapist advises (US) an ultrasound machine for 5-10 minutes with volini gel.
For release to pain as well as swellings therapist advised (SWD) short wave diathermy, (IFT) Inferential therapy, and (TENS): transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for 10-15 minutes.
So electrotherapy treatment is needed release to muscle pain.
Stretching Exercise:
- Doorway stretch
- Crossover arm stretch
- Two-arm wall stretch
- Sleeper Stretch
- Over-your-head stretch
- Up-the-back stretch
Stretching helps release the tightness in the muscle.
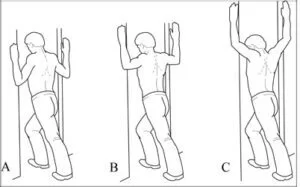
Doorway stretch:
For Warm-up, the muscles accomplish the stretching.
For this stretching exercise the patient’s position is in a standing position near to open doorway and spreading the arms out to the side.
After then grasp the sides of the doorway with each hand and below the shoulder joint height and tilt forward through the doorway till the patient feels a light stretch.
Must keep a straight back as the lean and shift the weight onto the toes.
The patient feels a stretch in the front of the shoulder joint but, and does not the overstretch of the muscle.
Crossover arm stretch
The patient’s position is to lift one arm so that it is perpendicular to the ground and extend it straight without locking it.
Take to the wrist joint of the extended and raised arm with the opposite hand.
Gently pull the arm across the front of the body, and try to hug the chest with the arm, and then maintain this stretch exercise for 5-10 seconds before slowly releasing it.
Repeat this stretching exercise on the other side.

Two-arm wall stretch
The patient’s position is in stand up straight with the back against a wall.
Lift each arm sideways into an L-shape with the upper arms parallel to the ground, and keep the arms as flat against the wall as possible.
Keep the elbow joint flexed, move the arms up the wall which brings the hands closer together, and then move the arms back down.
Then back to the starting position.

Sleeper stretch:
The patient’s position is lying on the side on a firm or flat surface with the impacted shoulder under the arm bent.
The patient also places the head on a pillow for comfort, if required.
Use the unaffected arm to push the other arm down and stop pushing down when the patient feels a stretch in the back of the impacted shoulder.
Maintain this stretching position for 20 seconds, then relax the arm for 30 seconds.
Repeat this stretching exercise and do it 3 times in 1 session every day.
Over-your-head stretch
The patient’s position is to lie flat on the ground and the bed, with arms straight at the sides.
Maintain the cane or rod with both hands near the hip joint.
Keeping the arms straight then slowly bring the cane or rod up in an arc-like trajectory, then continue the movement till the cane/rod goes over the face and touches down above the head.
Back to the starting position, repeat this stretching exercise, and do it 3 times in 1 session every day.
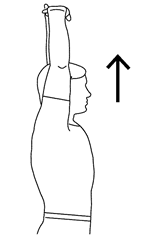
Up-the-back stretch
The patient’s starting this exercise in a standing position and with arms at the side.
Maintain the cane against the body behind you, then slowly slide the cane or rod up to the back, flexing the elbow joint as it travels up.
Go to as high as feels too relaxed, and then back to the starting position.
Repeat this stretching exercise and do it 3 times in a session every day.

Exercise for rotator cuff muscle pain
Exercise helps remove pain and also reduces the weakness of the muscle.
Side-lying external rotation
The patient’s position is lying down on the side opposite the affected arm.
Flex the elbow joint of the injured arm at 90 degrees and rest the elbow on the side, the patient’s forearm is resting across the abdomen.
After then maintain a light dumbbell in the injured side’s hand and keep the elbow joint against the side, then slowly raise the dumbbell toward the roof.
Stop rotating the arm when you feel the strain.
Maintain the dumbbell up for too few seconds before going back to the starting position with the arm down.
Repeat this stretching exercise for 3 sets of 10 up to 3 times every day.

Arm reach:
The patient’s position is lying flat on the back, and then raising the arms and legs and engaging the abdominal muscles.
One arm reaches toward the roof and raises the arm till the shoulder blade comes off the floor.
Maintain this exercise for 5 seconds, then back to the arm to the ground.
Repeat this exercise on both sides.

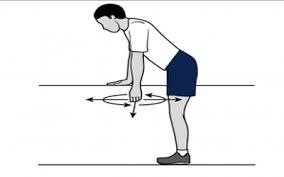
Pendulum
The patient’s position is Tilted forward with one arm hanging freely.
And then use the other arm to brace against a chair for support.
Gently swing the hanging arm from side to side, forward and back, or in a circular movement.
After then slowly back to a standing position, and then repeat this stretching exercise on the opposite side.
Lawnmower:
The patient’s position is to place one foot slightly forward then the feet are shoulder-width apart and hold a light weight in one hand.
After then keeps the hand, not holding the weight on the hip, and lean slightly forward and flex at the knee joint so that the weight is parallel to the other side knee joint.
Like starting a lawnmower, and pulling the elbow joint of the arm with the weight back across the body.
Back slowly to the starting position, and repeat by working up to 2 to 3 sets of the 8 to 10 repetitions.
Then repeat this stretching exercise on the opposite side.
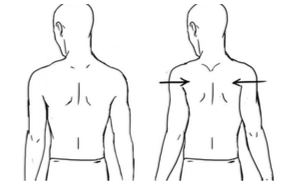
Scapula setting:
The patient’s position is lying on the stomach with the arms by the sides, and then place a pillow under the forehead for comfort.
Gently draw the shoulder blades together and down the back as far as possible, for Ease of this exercise about halfway off from this position, and maintain this exercise position for 10 seconds.
Relax and repeat this stretching exercise 10 times every day.
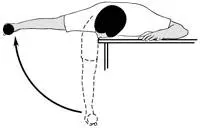
Bent-Over Horizontal Abduction
The patient’s position is lying on their stomach on a table and bed with the injured arm hanging over the side.
Maintain the arm straight and slowly lift it to eye level.
And then slowly lower to exercise and return to the starting position.
Repeat this stretching exercise 10 times in 1 session every day.
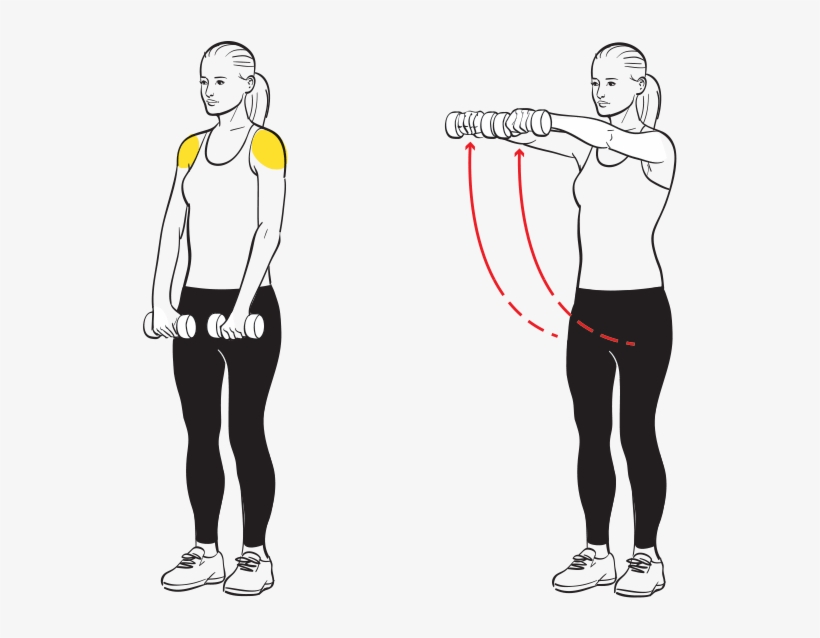
Arm raise
The patient position is in a standing position, and then stretches out the arms and brings the hands together, and creates a V shape.
Maintain the thumbs pointed up, and then slowly lift the arms to the ceiling and maintain the V shape.
Then back to the starting position.
Repeat this stretching exercise 10 times in 1 session every day.
Wing flap:
The patient’s position is lying on the side, with the undamaged shoulder joint down and the injured should up.
After the injured arm is resting on the body, the elbow joint is bent at 90 degrees.
Rotate the arm up toward the roof, and keep the elbow joint flexed.
Then back to the starting position.
Repeat this stretching exercise 10 times in 1 session every day.
Strengthening exercises
Strengthening exercise is useful to you for strengthening the muscle so that decreases the weakness of the muscle.
High-to-low rows
The patient’s position is to attach a resistance band for something sturdy at and above shoulder height.
Be sure it is safe so that it does not come to loss when you pull on the resistance band, after then get down to one knee so the knee is other side to the affected arm is raised.
Relax the other hand on the raised knee.
Maintaining the band securely with the arm outstretched and pulling the elbow joint toward the body.
Maintain the back straight and squeeze the shoulder blades together and down as they pull.
Must be sure the body should not move and twist with the arm.
Back to starting position and repeat to 3 sets of 10 every day.

Reverse fly:
The patient’s position is to stand with the feet shoulder-width apart and knees slightly flexed.
Maintain the back straight and lean forward slightly at the waist.
With a hold to lightweight in each hand, extend the arms and raise the hand away from the body, and do not lock the elbow joint.
Squeeze the shoulder blades together as you do, but do not lift the arms above shoulder height.
Then back to starting position and repeat this strengthening exercise in 3 sets of 10 every day.
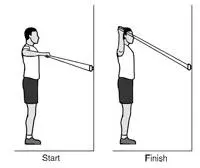
External Rotation With Arm Abducted 90°
The patient’s position is to 3-foot-long loop with an elastic band that ties the ends together.
Which is attaching the loop to a doorknob and another stable thing.
The patient is standing to maintain the band with the elbow flexed at 90° and raised to shoulder height this position is known as the starting position.
Maintain the shoulder and elbow joint at level then slowly raise the hand to line with the head.
Then slowly back to the starting position and repeat this strengthening exercise 10 times every day.
Internal Rotation:
This helps to at achieving a subscapularis stretch and also stretches the pectoralis muscle, and then will need an elastic stretch band for this particular exercise.
For this exercise, the patient it’s position is to make a 2.5 to 3-foot-long loop with the elastic band, and tying the ends together, and then attach the loop to a firm and stable object thing. Keeping the elbow bent & pressed into the side, maintain the band with your arm close to your side & bring your arm across your body, and then slowly return to the starting position & perform at least 2 sets of 10 for both arms.
standing rotation
This exercise helps the middle and lower trapezius muscles and will need an elastic stretch band for this particular exercise. For this exercise, the patient’s position is to make a 2.5 to 3-foot-long loop with the elastic band & tie the ends together, then attach the loop to a firm and stable object. Keep the elbow flexed at your side, maintain the band, and with your arm close to your side, pull your elbow straight back. Then slowly back to the starting position and repeat, Do at least two sets of 10 for both arms.
Elbow Flexion
This exercise targets strengthening the biceps.
You should use weights appropriately.
The patient’s position is standing position, and take care that weight is evenly distributed over both feet. Maintaining your elbow close to your side, and then slowly bring the weight up toward your shoulder and hold for 3 seconds.
After then slowly back to the starting position and repeat 2 sets of 10 repetitions every day.
Elbow Extension
This exercise works at strengthening the triceps.
For this exercise, the patient’s position is a standing position, taking care that your weight is evenly distributed over both feet. Lift your arm and flex your elbow with the weight behind your head and at the same time support your arm by placing your other hand on your upper arm.
Then slowly and gently straighten the elbow and bring the eight overhead and hold for 3 seconds.
Then slowly back to the starting position and repeat 2 sets of 10 repetitions every day.
Care should be taken so that your back is not arched while doing the exercise.
Scapular Retraction
This scapular retraction exercise also works to strengthen the middle trapezius & serratus musculature.
The patient’s position is to lie face down on a bed or table, keeping the injured arm hanging over the side.
Keep the elbow straight and lift the weight slowly by squeezing the shoulder blade towards the opposite side as far as possible.
Then slowly back to the starting position.

The complication of rotator cuff pain:
The most typical complication that occurs to re-tearing of the rotator cuff muscle after recovery.
The General surgical risks include blood loss and issues with the anesthesia.
some other complications include to:
- Permanent joint stiffness
- Frozen shoulder
- Reduced rotator cuff strength
- Loss of motion ( ROM )
How to Prevent rotator cuff muscle pain?
- Always accomplish the warming up before the exercise.
- You are learning how to lift weights appropriately means using the legs and maintaining a straight back.
- Doing the stretching and strengthening shoulder exercises for the pain.
- Avoid smoking.
- Always try to have good posture.
- Keep to a healthy body weight.
FAQ
How do reduce rotator cuff muscle pain?
Stop doing what caused the pain & try to avoid painful activities. Limit heavy lifting or overhead movement until the shoulder pain subsides. Icing the shoulder may be beneficial it feels better. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) also may be beneficial.
How do know if have damaged my rotator cuff?
Problems and pain caused by lifting your arm. Popping or clicking sounds and sensations when moving your arm. Shoulder pain that worsens at night or when relaxing the arm.
Can a rotator cuff muscle pain recover on its own?
In most rotator cuff pain, the muscle partially or fully tears away from the bone. Rotator cuff pain won’t recover on its own. You’ll require rotator cuff repair to repair the shoulder joint. A shoulder surgeon is a perfect physician to see for rotator cuff damage.
Will rotator cuff pain go away?
Return to movements — Most people with rotator cuff tendinitis see improvement in pain & function after 6-12 weeks of restoration. If shoulder pain does not improve after many weeks of physiotherapy exercises, most clinicians will suggest further evaluation.
Can ignore a rotator cuff injury?
Although rotator cuff damage can be severe, many people don’t seek treatment as soon as they should. When they wait to seek therapy, they often risk worsening the injury and losing more function.
How do reduce rotator cuff pain at night?
Heat or Ice Therapy for Rotator Cuff Pain relieves
Try using a heating pad on the shoulder for 10 to 15 minutes at a time as you start your bedtime routine. Alternate 15 minutes of heat and 20 minutes off while winding down in the evening.

5 Comments