Tensor Fascia Latae (TFL) Muscle Pain
When people feel pain in the top and outside of the hip joint and anterolateral part of the thigh, it is indicated to be Tensor Fascia Latae muscle pain, which mostly occurs in the runner. This pain arises due to tightness in the muscle.
What is the Tensor Fascia Latae muscle pain?
- This Tensor Fascia Latae is a small muscle on the top and outside of the hip joint.
- This Tensor Fascia Latae pain arises due to tightness and soreness in the muscle, which mostly occurs in runners.
- This Tensor Fascia Latae pain happens due to many causes like Hip Osteoarthritis, and Knock knee (valgus) posture.
- Tensor fasciae latae pain trigger points are in the hip joint region and an anterolateral portion of the thigh that extends as far as the knee joint.
- This pain is felt such as deep hip pain which is further aggravated by walking or laying down on the affected side.
- This pain is reduced due to the RICE principle and stretching and strengthening exercises.
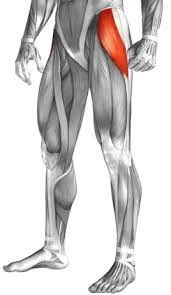
Anatomy of the Tensor Fascia Latae muscle
This Tensor fasciae latae muscle is a fusiform muscle that is situated in the lateral aspect of the thigh.
The Tensor Fascia Latae muscle is a small muscle that is located on the outside of the hip joint.
This muscle belongs to the muscles of the gluteal area, which means along with the gluteus medius, gluteus maximus, and gluteus minimus muscles.
The tensor fasciae latae muscle is found to be superficial in the anterolateral part of the thigh, which is spanning from the anterior part of the iliac crest to the superior portion of the tibia bone, which is inserts through the iliotibial tract.
The main function of this Tensor Fascia Latae muscle is to produce the extension and lateral rotation and external rotation of the leg on the knee joint. Additionally, it is also contributing to the movements of the thigh, which is acting as a relatively weak abductor and medial rotator-internal rotator on the hip joint.
Cause of the Tensor Fascia Latae muscle
- The main cause of TFL pain is overuse of the muscle.
- This pain also happens when the compensation for the weaker surrounding muscles of the leg.
- When the TFL muscles are compensated with the other muscle and working too much harder than to own muscle work it is indicated to overuse of this muscle and gives to result in muscle pain.
- This muscle compensation occurs because surrounding muscles are dysfunctional due to weakness in muscle or inhibition.
- The patient feels a problem in sitting position for long times with the hip joint flexed position up to 90 degrees or more.
- When in the patient occur of IT band tightness then it causes Tensor fasciae latae tightness, which produces pain.
- When they occur pelvic and iliac dysfunction which is caused by tightness in the Tensor Fascia Latae muscle.
The Tensor Fascia Latae muscle is also become overloaded with repeated use in the following situations:
- Walking and running movements
- Cycling, swimming, etc.
- The patient does the meditating with crossed legs.
- If wearing high heels too often.
- When the patient sitting, driving, and kicking for a long period.
- If the patient sleeps in the fetal position.
- If the patient standing with a swayed back.
Signs and Symptoms of the Tensor Fascia Latae Muscle Pain
- The patient feels pain which is referred to the outside of the thigh, and outer hip joint, and when lying on the affected side hip joint.
- This pain is increased when the patient is doing the weight-bearing movement on one side.
- The problem is walking quickly.
- The patient feels a problem laying down on the affected side.
- The patient feels a problem sitting for long periods with the hip joint flexed up to 90 degrees or more.
- The patient also feels muscle spasms due to overuse of the muscle.
- The patient feels weakness in the leg on the impacted side.
Which are common difficulties associated with Tensor Fascia Latae muscle pain?
Hip Osteoarthritis :
When the person is suffering from Tensor Fascia Latae which is sometimes generated in the hip osteoarthritis on the affected side.
This happens due to the new biomechanics in the Tensor Fascia Latae muscle which places excess stress and strain on the structures of the hip joint.
This muscle stress and strain ultimately lead to the early onset of degeneration and inflammation of the hip joint structures, which is given to result in an osteoarthritis condition.
Tension and tightness:
This muscle pain is usually associated with the worried and tight compensating muscles.
These muscles’ tension and tightness are due to the high alert which is issued by the brain.
When the muscle is on high alert and ready to spring into action at all times it increased muscular tone and feels as when the muscle is unable to fully lengthen.
When the muscle remains in this position for a long time it is unable to relax and heal from the tightened muscle and it will become chronically tight and shortened of muscle.
If the patient’s posture is poor, many positions and activities contribute to TFL tightness.
Knock knee (valgus) posture:
Due to the TFL muscle pain and tightness which is sometimes to the internal rotator of the hip joint, it is twisting the thigh inward from the hip joint, it can become shortened and tight resulting in a position called the knock knees position where the one or both of the knees are become too internally rotated.
Anterior pelvic tilt:
Another posture created is the result of a Tensor Fascia Latae muscle tightness which leads to muscle pain in an anterior pelvic tilt.
This abnormal posture is possible by the Tensor Fascia Latae muscle pain because the TFL muscle is doing the action of the hip flexion movement.
In the standing position, the legs are anchored due to the TFL muscle tightness pulling the front of the pelvis where the arises down and give to result in the anterior pelvic tilt.
Lateral pelvic tilt:
On the other side, when the happen tightness of the TFL muscle unilateral means in one side, which is pull this side of the pelvis down, which is given to results in the pelvis dropping to one side.
Treatment of the Tensor Fascia Latae ( TFL ) muscle pain
Trigger Point Release:
The trigger point therapy involves the application of firm pressure which is a hyper irritable spot or taut band, which is known as a trigger point. This pressure is work to release the tension in the muscle, by reducing the blood flow of this place and decreasing the pressure felt.
When the pressure is removed, blood flows back to the place and flushes any toxins released by the muscle.
These points are often released the referred pain to other parts of the body in a few seconds.
Dry Needling:
Dry needling is a procedure that is used to reduce muscle restriction by releasing the trigger points with acupuncture needles.
A soft tissue occupational therapist uses individually packed sterilized acupuncture needles to directly the needle on the trigger point and produce a local response within the muscle, which quickly disperses and allows the muscle to relax.
Myofascial Release:
Myofascial release is a manipulative treatment which is attempts to release the tension in the fascia due to trauma, posture, and inflammation.
These connective tissues called the fascia surround the muscles, bones, nerves, and organs of the body.
Points of the restriction in the fascia which is placed a great deal of pressure on the nerves and muscles causing chronic pain.
An occupational therapist is given long stretching strokes meant to balance tissue and muscle mechanics which is to improve joint range of motion ( ROM ) to relieve pain.
Heat:
Using heat on the painful Tensor Fascia Latae muscle through the use of a heat pack which is help to alleviate the pain. Heat is an affordable, effective form of pain relief which is works by the increases blood flow to the site, relaxing the muscles, and increasing ROM ( range of motion ) and flexibility.
By increasing the circulation and blood flow throughout the area so that healing effects are delivered to the muscles and aiding in repairing and relieving the symptoms of tensor fascia lata muscle pain.
Physiotherapy treatment for the tensor fascia latae muscle ( TFL )
The physiotherapy treatment includes stretching and strengthening exercises for reduced tensor fascia lata muscle pain.
Strengthening exercise for TFL muscle pain :
- Clamshell exercise with bands
- Sidesteps with bands
- Quadruped hip extension
- Quadruped hip extension with bent knee
- Single glute bridge
Clamshell exercise with bands:
The patient’s position is lying down on the side with both legs together and knees flexed at 45 degrees.
Rest the head on the lower arm and keeping the feet together, lift the upper leg as high as the patient can.
After then the patient is briefly paused at the top and then slowly back into starting position.
Perform this exercise 3 sets per day and 10 repetitions on both sides.

Sidesteps with bands:
The patient’s position is to stand with the feet hip-width apart in an athletic stance with the knees slightly bent and leaning forward.
After then step to the side so that the feet are slightly wider than the shoulder-width apart, and step the other foot towards the first foot.
Repeat this exercise on the opposite side, and do this exercise 3 sets per day and 10 repetitions on both sides.

Quadruped hip extension:
The patient’s position is getting onto the ground with the hands stacked under the shoulders and knees under the hip joint.
Keep the back straight and engage the core muscle, and then press one leg up and back behind till the leg is fully extended.
Then slowly back to starting position, and repeat this exercise on the other side.
Perform this exercise 3 sets per day and 10 repetitions on both sides.
Quadruped hip extension with a bent knee:
The patient’s position is getting onto the ground with the hands stacked under the shoulders and knees under the hip joint.
Keep the back straight and engage the core muscle, and press one leg back behind keeping the knee joint flexed at 90 degrees.
Then slowly back to starting position, and repeat this exercise on the opposite side.
Perform this exercise in the 3 sets per day and 10 repetitions on both sides.
Single glute bridge
The patient’s position is lying down on the back with the knees bent and feet planted on the ground and arms on our sides for extra support.
Then lift one leg off the ground and extended it in front of the patient, and must keep the upper back on the floor, and contract the glutes muscle.
Push through the heel of the foot on the ground, and raise the hips off the floor till the knee, hips, and shoulders are created in a straight line.
Must be Keep the core muscle engaged the whole time pause briefly at the top for 1 to 2 seconds then back to starting position.
Repeat this exercise on the other side, perform the 3 sets per day and 10 repetitions on both sides.

Stretching for the tensor fascia latae muscle:
The best form of relief from the tensor fascia muscle pain includes resting from the aggravating movements.
The gentle stretching exercise is important in assisting to relieve pain and help to speed up the healing.
Gentle stretching decreases the pain associated with the tensor fascia muscle pain by encouraging the circulation and blood flow to tissues which is decreasing muscle stiffness and spasm. On the secondary side, correcting the muscle imbalances and building strength in the hip joint area is important in helping to reduce the demands and stress on the tensor fascia latae muscle & subsequently reducing the tensor fascia latae muscle pain.
- TFL stork standing stretch
- Outer hip stretch
- foam roller to stretch
- Static standing TFL stretch
- Quadruped active TFL stretch
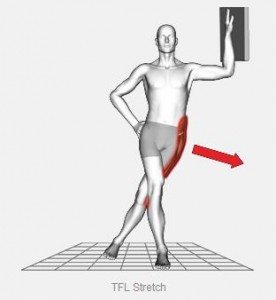
TFL stork standing stretch:
The patient’s position is in standing position beside the wall and places their hand on the wall to support the body.
Then raise the leg which is closest to the wall and bend the knee joint and place it on the other leg’s right side above the knee joint to be in a stork standing position.
Put the other hand’s tensor fascia latae muscle over the going to stretch, and then in the standing position on one leg, slowly flex them toward the wall.
Maintain the leg still and flex the torso.
The patient feels the tension power over the tensor fascia latae muscle.
Maintain this position for 30 seconds, and repeat this stretching 3 times every day.
Outer hip stretch:
The patient’s position is lying down on the ground on the back, crossing the left foot over the right knee joint.
Must hold the left knee bent.
After then using the right hand, pull and push the left knee across the body.
It is highly important to keep the left shoulder on the ground.
Maintain this stretching exercise for 10 to 20 seconds.
Foam roller to stretch:
The patient’s position is to lie down on the foam roller on the right or left side in a way that the foam roller is placed on the upper lateral part of the thigh at the level of the side pocket one inch below the anterior iliac crest.
After then place the opposite leg in front of the right leg, and support the body with the elbow on the ground. Then start to move slowly up and down on the foam roller from the anterior iliac crest level to 1/3 upper part of the thigh for 5 to 10 seconds.
Maintain this stretching exercise for 10 to 20 seconds.

Static standing TFL stretch:
The patient’s position is in the standing position for the stretching.
In the standing position, the patient is staggered stance with the foot which is behind the pointing outwards, and rotating the hip joint at 45 degrees.
After then contract the glutes muscle driving the patient’s weight forward till the patient feel a stretch.
Reach up the across and back with the arm on the affected side.
Maintain this position for 15- 30 seconds, and repeat 3 times in 1 time the 3 times every day.
Quadruped active TFL stretch:
The patient’s position is getting down on the floor with hands stacked under the shoulders and knees under the hip joint.
Then extend one leg behind the contracting of the glutes muscle.
The hip joint is Externally rotated and the toes are out at 45 degrees.
Must be Keep the spine in a neutral position and adduct the hip joint.
Maintain this exercise for up to 15 to 30 seconds, and repeat this exercise 3 times in 1 time 3 times per day.
FAQ
How do you treat sore tensor fasciae latae?
Stretching is ideal for pain relief; start by placing your good hip in the opposing movement of the TFL to stretch. For successful results, the client should be laying the strain on a massage ball (or even a tennis ball), and moving the ball along the TFL until the strained region is evident.
What does tensor fasciae latae muscle pain feel like?
Tensor fasciae latae pain presents as outer hip pain situated at the TFL muscle belly. Pain when lying on the impacted side, walking up and down stairs, running, walking, & hiking. Treatable non-surgically within weeks to months with complete healing probable.
How long does it take for a TFL strain to recover?
Once get to the root cause of the TFL overload and begin turning on the right muscles, then the TFL can breathe again and the pain dissipates fast. It will take 4 to 6 weeks to complete the 4 R’s so that the pain does not recur.
What is tensor fascia lata syndrome?
Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome, or IT Band Syndrome, is a typical problem that can cause pain in the outside of the thigh or knee. This happens when the tensor fascia latae (TFL) muscle at the hip evolves overactive.
What muscle is under the fascia lata?
In its superior aspect, tensor fasciae latae is located between the sartorius and gluteus medius muscle, where it overlays the gluteus minimus muscle. While descending the thigh, the muscle is located between the two layers of fascia lata. Due to its superficial position, this muscle is efficiently palpated.
Can massage help TFL?
The use of a spikey massage ball to target the TFL is a significant way to self-manage tightness and give you some relief. You can do this self-massage lying face down or standing if your muscle is too sensitive.
What happens if don’t tap in Tensor fasciae latae?
If you don’t touch in and out, we can’t tell where you’ve traveled from or to, so your journey will insufficient. Maximum fares don’t count toward capping.