Adductor pollicis muscle
What is Adductor pollicis muscle?
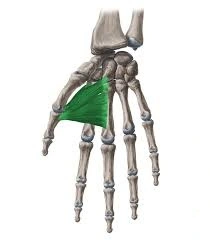
The adductor pollicis muscle is a hand muscle located in the palm of the hand, specifically at the base of the thumb. It has two parts: the oblique head and the transverse head. The oblique head originates from the capitate bone and the bases of the second and third metacarpal bones, while the transverse head originates from the distal third of the ulna and the interosseous membrane.
Both heads of the adductor pollicis muscle insert onto the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. The muscle is responsible for adducting the thumb towards the palm, as well as aiding in opposition of the thumb (bringing the thumb towards the other fingers). It also plays a role in gripping and grasping objects, particularly those that require a strong grip.
The adductor pollicis muscle is innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve, which arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus.
The hand’s intrinsic adductor pollicis is a triangular muscle. Along with the abductor pollicis, flexor pollicis brevis, and opponens pollicis, it is a member of the thenar muscles group. The thenar eminence is an elevation formed by the thenar muscles on the radial (lateral) side of the hand.
The adductor pollicis has two heads: tangential and transverse. From the capitate and third metacarpal bones to the base of the first proximal phalanx, this muscle stretches. The adduction of the thumb in the carpometacarpal joint is this muscle’s primary function.
Origin of Adductor pollicis muscle
The transverse head comes from the shaft of the third metacarpal, while the oblique head comes from the bases of the second and third metacarpals.
Insertion
The thumb’s medial side of the base of the proximal phalanx
Relations
The largest and deepest of the thenar muscles is the adductor pollicis muscle. The flexor tendons of the index finger, first lumbrical, and flexor pollicis brevis muscles cross the adductor pollicis on its ventral aspect. The muscle is connected to or sometimes joined to the first dorsal interosseous muscle on its dorsal side. Additionally, the deep branch of the ulnar nerve, the deep palmar arch, and the radial artery all pass through the passageway that is made up of the two heads of the adductor pollicis.
Innervation
The deep ulnar nerve branch that innervates the adductor pollicis muscle (root value C8, T1)
Blood supply
The anastomosis of the radial artery and the deep palmar branch of the ulnar artery forms the deep palmar arterial arch, which vascularizes the adductor pollicis.
Function of Adductor pollicis muscle
The hand’s most powerful intrinsic muscle is the adductor pollicis. The adduction of the thumb, or movement of the thumb from an abducted position toward the index finger, is its primary function. When performing tasks that necessitate pinching and grasping, this action is necessary. Furthermore, the adductor pollicis helps the later phases of the resistance of the thumb.
This development is a blend of activities, in particular, adduction, average turn, flexion, and adduction of the thumb so it can contact every fingertip of a similar hand. As a result, the examiner can measure the strength of the adductor pollicis by attempting to pull them apart while pressing the thumb against the index finger.
Clinical significance
The sign of Froment is used to look for a weak adductor pollicis muscle.
In neuromuscular monitoring, the adductor pollicis contraction strength is measured after the ulnar nerve is stimulated.
Adductor pollicis muscle stretching
At the metacarpophalangeal joint, the thumb’s abduction and extension stretch the adductor pollicis, which belongs to the central compartment group.
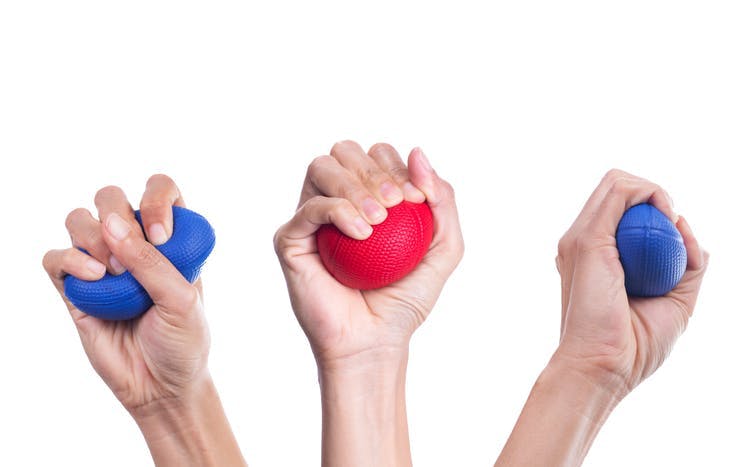
Adductor pollicis muscle strengthening exercise
Using a tennis ball or rubber stress ball, you can perform a straightforward exercise designed to strengthen this muscle. Hold the ball in place with all four of your fingers and your thumb for ten seconds before releasing. Perform 20 redundancies of this exercise 3 times each day.

FAQ
Where is the adductor pollicis located?
The Adductor Pollicis compartment is marked at the bottom right. Deep in the thenar compartment, beneath the long flexor tendons and the lumbrical muscles at the center of the palm, is a fleshy, flat, triangular, and fan-shaped muscle. It sits on top of the interosseous muscles and metacarpal bones.
What specific test is used to identify adductor pollicis?
The adductor pollicis muscle’s function can be evaluated using the Froment’s sign. If the adductor pollicis muscle is weak, the thumb IP joint will flex when pinching a piece of paper between the index and thumb against resistance.
What causes pain in the adductor pollicis?
Osteoarthritis, hand soft tissue trauma, or overuse can all cause pain in the adductor pollicis. The gamekeeper’s thumb, in which the ulnar collateral ligament above the adductor pollicis is overly strained, is one condition that can affect the adductor pollicis and thumb adduction.
How can pain in the adductor pollicis be alleviated?
Put your hand on a table with the palm confronting and clutch the thumb with your other hand. Pull the thumb back from the midline slowly. Remember to stretch both digits as you release after holding for thirty seconds.
How long does it take for adductor pain to go away?
Recovery can be significantly slowed and take anywhere from 12 to 16 weeks if the tear is high on the adductor tendon. Depending on the severity of the tear, the mid-belly muscle will typically heal in four to twelve weeks. You may need crutches to walk in some rare circumstances.


One Comment