Fenoprofen
Description
Fenoprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that belongs to the propionic acid class of NSAIDs. It is used for the treatment of pain, inflammation, and fever. Fenoprofen works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are responsible for causing pain and inflammation in the body.
For rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and mild to moderate pain, fenoprofen calcium is used. It has also been used to alleviate pain following surgery. Nalfon is how Fenoprofen is sold in the United States. Fenoprofen is a mitigating pain relieving used to treat gentle to direct agony notwithstanding the signs and side effects of rheumatoid joint inflammation and osteoarthritis.
- Metabolism: Primary urinary metabolites are fenoprofen glucuronide and 4′-hydroxy fenoprofen glucuronide
- Routes of administration: By mouth
- AHFS/Drugs.com: Monograph
- Elimination half-life: 3 hours
- Type – Small Molecule
- Groups – Approved
- Generic name: fenoprofen [ fen-oh-PROE-fen ]
- Brand names: Nalfon, Profeno
- Dosage forms: capsule to swallow (200 mg; 600 mg) and an oral tablet
- Drug class: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs conducted a medical review on October 24, 2022. Cerner Multum is the author.
Synonyms
- Fenoprofen
- Fénoprofène
- Fenoprofen
- Fenoprofenum
Associated Conditions
- Mild pain
- Osteoarthritis (OA)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Moderate Pain
Background – a highly bound antipyretic and anti-inflammatory agent in plasma. It is pharmacologically like ibuprofen yet goal less gastrointestinal deaths.
What is fenoprofen?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like fenoprofen are used to treat osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and mild to moderate pain. Fenoprofen can also be used for things that aren’t listed in this guide. For alleviation of the signs and side effects of rheumatoid joint inflammation and osteoarthritis. Additionally for the treatment of moderate to mild pain.
Why is this medication prescribed?
Fenoprofen is used to treat osteoarthritis (arthritis caused by a breakdown of the lining of the joints) and rheumatoid arthritis (arthritis caused by swelling of the lining of the joints) pain, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness. Fenoprofen can also be used to treat other mild to moderate pains. Fenoprofen is in a class of meds called NSAIDs. It works by preventing the body from constructing a substance that provokes inflammation, pain, and fever.
How should this medicine be used?
Fenoprofen comes as a case and a tablet to take by mouth. When used for arthritis or pain, it is typically taken with a full glass of water three to four times per day. Fenoprofen can be taken with a feast or milk to decrease stomach upset. Fenoprofen may also be prescribed by your doctor in conjunction with an antacid to alleviate stomach discomfort. Take fenoprofen at roughly the same times each day if you take it regularly. Follow the bearings on your medicine name cautiously, and ask your PCP or drug specialist to make sense of any part you don’t have any idea about. Take fenoprofen precisely as coordinated. Do not take it more repeatedly or less frequently than your physician has instructed. If you are taking fenoprofen to let the side effects free from joint pain, your side effects might start to work within a couple of days. You may not fully reap the benefits of fenoprofen for two to three weeks or longer.
Other uses for this medicine
Fenoprofen is used to treat headaches, dental pain, menstrual cramps, muscle aches, and other types of pain. Additionally, arthritis pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints can be alleviated with fenoprofen. A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) is fenoprofen. It works by preventing your body from making certain natural substances that make you feel swollen. This effect permits lower swelling, pain, or fever. Ask your doctor about non-drug treatments and/or other pain medications if you are treating a chronic condition like arthritis.
Ankylosing spondylitis (spinal arthritis) and gouty arthritis (attacks of severe joint pain and swelling caused by a buildup of certain substances in the joints) are also treated with fenoprofen. Diminishing fever is additionally in some cases utilized. Discuss the potential side effects of taking this medication to treat your condition with your doctor. Incidentally, this drug is endorsed for different purposes; Talk to your doctor or pharmacist for more details.
How to use Fenoprofen calcium
Before you start taking fenoprofen and every time you get a refill, read the Medication Guide that your pharmacist gives you. Ask your pharmacist or medic if you have any questions. This medication should be taken orally as prescribed by your doctor, usually three to four times daily or as needed. Unless your PCP directs otherwise, take this medication with a full glass of water (8 ounces, or 240 milliliters). After taking this medication, do not lie down for at least ten minutes. Take this drug with food, milk, or an antacid if you undergo stomach upset while taking it. Your condition and response to treatment determine the measurements. Take this medication as little as possible at the lowest effective dose to reduce your risk of stomach bleeding and other side effects. Do not exceed the recommended dosage or duration of treatment with this medication. Continue to accept this drug as endorsed for continuous circumstances like joint inflammation. Talk to your medic or pharmacist about the benefits and risks.
For some conditions, like arthritis, regular use of this medication may take up to three weeks before you see full results. In the occurrence that you are taking this medication “depending on the situation” (not on a standard timetable), recollect that aggravation drugs work best assuming that they are utilized as the primary indications of torment happen. In the occurrence that you hold on until the aggravation has declined, the medication may not function too. Inform your doctor if your condition does not improve or persists.
Pharmacology – decreases fever, pain, and inflammation probably by reducing prostaglandin synthesis and cyclooxygenase (COX-2 inhibitor) activity.
Chirality and biological activity
Fenoprofen is a chiral drug with chiral twins and a single stereogenic center. While the (R)-isomer is less active, the S)-enantiomer exhibits the desired pharmacological action. The stereoselective bioconversion of (R)- to (S)-fenoprofen has been observed. Chiral inversion is the name given to this stereoselective conversion.
Contraindications of fenoprofen
a history of severely compromised renal function; patients who are known to be allergic to any part of the product; patients who have taken aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and experienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic reactions; treatment of perioperative agony in the setting of coronary course sidestep join (CABG) medical procedure.
Adverse effects of fenoprofen – In October 2020, the U.S. Food and Medication Organization (FDA) required the medication mark to be refreshed for all nonsteroidal mitigating prescriptions to depict the gamble of kidney issues in unborn children that outcome in low amniotic liquid. They suggest staying away from NSAIDs in pregnant ladies at 20 weeks or later in pregnancy.
Drug interactions of fenoprofen
- Aminoglycosides (gentamicin, for instance): Aminoglycoside levels in the bloodstream may rise.
- Inhibitors of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE): ACE inhibitors may have less of an effect on blood pressure reduction.
- Anticoagulants: Coadministration might delay prothrombin time.
- Aspirin: Fenoprofen Cl might be expanded; Co-management is not a good idea.
- Diuretics: Loop diuretics and thiazides may have an unfavorable effect on fenoprofen-treated patients.
- Sulfonamides, hydantoins, and sulfonylureas: It is conceivable that fenoprofen will move these drugs away from where they bind.
- Lithium: Lithium toxicity may be more likely because lithium Cl levels may rise and fall in the blood and kidneys.
- Methotrexate: may raise levels of methotrexate.
- Phenobarbital: May diminish fenoprofen t 1⁄2. Dose changes of fenoprofen might be required assuming that phenobarbital is added or removed.
- SSRIs (like citalopram and fluoxetine): There may be an increased chance of gastrointestinal side effects.
Food Interactions
- Detour alcohol.
- Take it with food. Food diminishes irritation.
Drug interchanges could change how your solutions work or addition your bet for serious eventual outcomes. This report doesn’t contain all conceivable medication associations. Make a list of all the things you use, including homemade items and medicine/nonprescription medications, and give it to your primary care doctor and drug specialist. Try not to start, stop, or change the dosage of any medication without first consulting your primary care physician. A few items that might connect with this medication are aliskiren, Expert inhibitors (like captopril, and lisinopril), angiotensin II receptor blockers, (for example, losartan, and valsartan), cidofovir, corticosteroids (like dexamethasone, prednisone), lithium, methotrexate, “water pills” (diuretics like furosemide).
When taken with other drugs that can also induce bleeding, this medication may make bleeding more likely. Antiplatelet medications like clopidogrel and “blood thinners” like dabigatran, enoxaparin, and warfarin are two examples. Check all solution and nonprescription medication marks cautiously since numerous prescriptions contain pain killers/fever minimizers (anti-inflammatory medicine, NSAIDs like ibuprofen, ketorolac, and naproxen). If you take these and fenoprofen together, you might experience more side effects. However, unless your doctor tells you otherwise, you should continue taking aspirin if your doctor has prescribed a low dose (typically 81-162 milligrams per day) to prevent heart attack or stroke. For additional nuances, consult your physician or drug specialist.
This drug might disrupt specific lab tests, (for example, thyroid chemical tests), potentially causing misleading experimental outcomes. Guarantee lab staff and all of your essential consideration doctors acknowledge you use this prescription.
Laboratory test interactions
The Amerlex-M kit detected a false elevation in free and total serum T3.
Mechanism of action of fenoprofen
Although the precise mechanism of action of fenoprofen is unknown, prostaglandin synthase inhibition is thought to be involved. Prostaglandin synthetase includes been shown to be restricted when confined to ox-like original vesicles by fenoprofen.
TARGET Activities Organic entity
- Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 – inhibitor – People
- Peroxisome proliferator-actuated receptor alpha-activator – People
- Peroxisome proliferator-actuated receptor gamma – Not Accessible – People
- Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 – inhibitor – People
Pharmacodynamics of fenoprofen
An analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic propionic acid derivative, fenoprofen By decreasing the enzyme required for biosynthesis, fenoprofen prevents prostaglandin synthesis. In patients with rheumatoid joint inflammation, the mitigating activity of fenoprofen has been proven by the help of torment, expansion in hold strength, and decreases in joint expansion, term of morning firmness, and sickness movement (as evaluated by both the specialist and the patient). Fenoprofen’s anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties have been demonstrated in osteoarthritis patients by reducing the tenderness in response to pressure, nighttime pain, stiffness, swelling, and overall disease activity (as assessed by the patient and the researcher).
Pain relief while moving and at rest, as well as an increased range of motion in the involved joints, is additional evidence of these effects. Clinical studies have demonstrated that fenoprofen is comparable to aspirin in controlling the aforementioned measures of disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. nonetheless, gentle gastrointestinal reactions (like queasiness and dyspepsia) and tinnitus happened less frequently in patients treated with fenoprofen than in patients treated with ibuprofen. It isn’t known whether fenoprofen causes less peptic ulceration than anti-inflammatory medicine. Fenoprofen’s analgesic effects have resulted in a decrease in pain intensity, an increase in pain relief, an improvement in total analgesia scores, and a sustained analgesic effect in pain patients.
Absorption
Peak plasma levels of 50 g/mL are reached within two hours of oral administration of 600 mg doses, which are rapidly absorbed while fasting.
The volume of distribution – Not Available
Protein binding – 99% to albumin.
Metabolism
The major urinary metabolites of fenoprofen, fenoprofen glucuronide, and 4′-hydroxy fenoprofen glucuronide, account for approximately 90% of a single oral dose’s elimination within 24 hours.
Click on a product to see its reaction partners.
- Fenoprofen
- 4′-hydroxyfenoprofen glucuronide
- Fenoprofen glucuronide
Route of elimination – Not Available
Half-life – The plasma half-life is approximately 3 hours.
Clearance – Not Available
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs – Not Available
Toxicity of fenoprofen
Within a few hours, overdose symptoms typically affect the gastrointestinal and central nervous systems. They possess dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dizziness, headache, ataxia, tinnitus, tremor, drowsiness, and also confusion. Also included are dizziness and headache. Also included are dizziness and headache. Rarely, an overdose can result in hyperpyrexia, tachycardia, hypotension, and acute renal failure. Respiratory wretchedness and metabolic acidosis have likewise been accounted for following an excess of specific NSAIDs.
What special precautions should I follow?
Before taking fenoprofen,
- let your primary care physician and drug specialist know if you are susceptible to fenoprofen, anti-inflammatory medicine, or different NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), some other meds, or any of the idle fixings in fenoprofen cases or tablets. Request an index of the inactive ingredients from your apothecary.
- tell your primary care physician and drug specialist what medicine and nonprescription meds, nutrients, nourishing enhancements, and homegrown items you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following, in addition to the medications listed in the Important Warning section: benazepril (in Lotrel), captopril (in Vaseretic), enalapril (in Vaseretic), fosinopril (in Zestoretic), lisinopril (in Zestoretic), moexipril (in Univasc), perindopril (in Prestalia), quinapril (in Accutril), ramipril (in Altace), and trandolapril ( angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs, for instance, azilsartan (Edarbi, in Edarbyclor),candesartan (Atacand, available via Atacand HCT), as well as eprosartan (Teveten), irbesartan (Avapro, available via Avalide), losartan (Cozaar, available via Hyzaar), olmesartan (available via Benicar HCT, available via Tribenzor), telmisartan (available via Micardis, available via Micardis HCT), and valsart; beta blockers like atenolol (Tenormin, also known as Tenoretic), labetalol (Trandate), metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL, or Dutoprol), nadolol (Corgard, also known as Corzide), and propranolol (Hemangeol, Inderal, and Innopran); diuretics, or “water pills” lithium, or a Lithobid; diabetes medications taken orally; methotrexate (Trexall, Otrexup, and Rasuvo); phenobarbital; phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek); as well as sulfa antibiotics like sulfisoxazole and sulfamethoxazole (in Septra and Bactrim). Your doctor may need to adjust the dosage of your medication or closely monitor you for side effects.
- If you have asthma or any of the conditions listed in the Important Warning section, as well as if you frequently suffer from a stuffy or runny nose or nasal polyps (swelling of the lining of the nose), tell your medic. heart disease; hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs swelling; a deficiency in hearing; anemia, in which not enough oxygen is delivered to all parts of the body by blood cells; or illness of the kidneys or liver. Problems are more likely to arise if you are aged, dehydrated, have heart defeat and/or kidney disease, take certain medications, or are dehydrated (see also the Drug Interactions section). To prevent dehydration, follow your doctor’s instructions to drink a lot of fluids, and tell your doctor right away if you have pink or bloody urine or if the amount of urine changes in an unusual way.
- If you are breastfeeding or scheduling to become expectant, tell your physician. If taken around 20 weeks or later during pregnancy, fenoprofen may harm the fetus and cause complications during delivery. Unless your doctor tells you to, you should not take fenoprofen until you are at least 20 weeks pregnant. In the circumstance that you become pregnant while taking fenoprofen, call your PCP.
- If you are 75 years of age or older, discuss the benefits and risks of taking fenoprofen with your doctor. Do not take this medication for a longer duration of time or at a higher dose than your doctor or the label says.
- Previous to utilizing this drug, ladies of childbearing age ought to chat with their doctor(s) about the advantages and dangers. If you are expectant or prepared to become expectant, tell your doctor. This medication could harm an unborn child and disrupt normal labor and delivery. It should not be used during pregnancy between 20 weeks and delivery. Use the descending effective dose for as short a time as possible if your doctor decides that you need to take this medication between 20 and 30 weeks of pregnancy. This medication should not be employed after 30 weeks of incubation.
- Tell your doctor or dentist that you are taking fenoprofen if you are having surgery, including dental surgery.
- you should know that this pill may make you exhausted. Until you are aware of how this medication affects you, do not operate machinery or drive a vehicle.
- Keep in mind that this drug’s drowsiness can be exacerbated by alcohol. Dodge alcohol consumption while taking this medication.
This is not a total rundown of conceivable secondary effects. On the off chance that you catch various impacts not recorded above, contact your medic or drug specialist. If you live in the United States, ask your physician about any side effects. You might convey aftereffects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. If you live in Canada, ask your doctor about any side effects. You could report optional impacts to Prosperity Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
What special dietary instructions should I follow?
Preserve your normal diet unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
What should I do if I overlook a dose?
When you remember, take the dose you missed. On the different hand, if it is reaching close to the time for the next dose, skip the missed one and stick to your usual schedule. To make up for a skipped dose, do not take two doses.
What side effects can this medication cause?
There may be side effects from fenoprofen. Recollect that this drug has been endorsed because your primary care physician has decided that the advantage to you is more noteworthy than the gamble of secondary effects. A lot of individuals who take this drug do not experience any serious side effects.
Your blood pressure may rise with this medication. If you detect an increase in your blood pressure, consult your doctor. If any of these symptoms persist or become unbearable, confer your physician:
- headache
- nervousness
- drowsiness
- sweating
- constipation
- ringing in the ears
A few side effects can be serious. If you experience any of the ensuing symptoms or those noted in the IMPORTANT WARNING section, call your doctor immediately. Take no more fenoprofen until you address your medic.
- blurred vision
- shaking of an uncontrollable part of the body
- unexplained weight gain
- shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- swelling in the abdomen, ankles, feet, and also in legs
- fever
- blisters
- rash
- itching
- hives
- swelling of the eyes, face, lips, tongue, throat, hands, and also arms, feet, ankles, or lower legs
- hoarseness
- difficulty breathing or swallowing
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- excessive tiredness
- unusual bleeding or bruising
- lack of energy
- upset stomach
- loss of appetite
- stomach pain in the upper right corner
- flu-like symptoms
- pale skin
- fast or pounding heartbeat
- cloudy, discolored, or bloody urine
- back pain
- difficult or painful urination
Other adverse effects may occur with fenoprofen. If you experience any unusual side effects while taking this medication, consult your physician. There is no doubt that this is not a comprehensive list of all possible secondary effects. On the off chance that you notice additional impacts not recorded above, reach your medic or drug specialist. If you live in the United States, ask your medic about any side effects. You might bring aftereffects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. if you live in Canada, inquire about any side effects with your physician. You can contact Wellbeing Canada at 1-866-234-2345 to report secondary effects. On the off chance that you experience a serious secondary effect, you or your primary care physician might send a report to the Food and Medication Organization’s (FDA) MedWatch Unfavorable Occasion Revealing system on the web or by telephone (1-800-332-1088).
If you experience any of the following side effects, you should seek guaranteed medical attention: This condition can cause chest pain that spreads to your jaw or shoulder, sudden shortness or deadness on one side of the body, slurred speech, leg swelling, or windedness. Fenoprofen may cause severe adverse effects. If you’re using fenoprofen improperly, stop immediately and contact your doctor.
- changes in your vision;
- any skin rash, no matter how mild;
- exhaustion (even with minimal effort);
- a fast weight gain or expansion;
- stools that are bloody or tarry, coughing up blood, or vomiting that looks like coffee grounds are signs of stomach bleeding.
- Nausea, stomach pain, itching, fatigue, flu-like symptoms, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay-colored stools, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) are liver-related issues.
- kidney problems: almost no urination, swelling in the feet or lower legs, and feeling tired; or anemia, which is characterized by cold hands and feet, unusual tiredness, lightheadedness, and pale skin.
Common side effects of fenoprofen may contain:
- sickness, spewing, stomach torment, heartburn;
- the runs, stoppage;
- cerebral pain, discombobulation, sluggishness, sleepiness;
- being anxious;
- tingling, perspiring; or a ringing in the ears
There might be extra incidental effects, and this is certainly not a thorough rundown. Contact your primary care physician for clinical advice regarding the consequences. To report incidental effects, call the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What should I know about the storage and dumping of this pill?
Keep this medicine in the holder it came in, firmly shut, and far away from youngsters. It should be maintained at room temperature, away from moisture and heat (not in the bathroom). It is critical to keep all medicine carefully hidden and reach kids as numerous holders, (for example, week-by-week pill minders and those for eye drops, creams, patches, and inhalers) are not kid-safe and little youngsters can also open them without any difficulty. Constantly lock safety caps and immediately store the medication in a protected location that is up, away, and out of their sight and reach to prevent poisoning in young children.
To control pets, children, and others from swallowing unneeded medications, special disposal methods should be employed. In any case, you should not wash this medicine away for good. Rather, a medicine take-back schedule is the best way to get rid of your medication. Find out about your neighborhood’s take-back programs by speaking with your pharmacist or the department of Garbage and recycling in your area. If you do not have entrance to a take-back program, you can find additional understanding on the Safe Disposal of Medicines website of the FDA.
- Drugs A to Z
- Fenoprofen
Warnings
Taking fenoprofen can make you more likely to have a stroke or die from cardiovascular failure. Fenoprofen should not be taken before or after coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. Additionally, stomach or intestinal bleeding, which can be fatal, may occur with fenoprofen. Fenoprofen can make you more likely to die from respiratory failure or stroke, even if you don’t have any gambling-related risk factors. This medication should not be taken immediately before or after coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery.
Additionally, stomach or intestinal bleeding, which can be fatal, may be induced by fenoprofen. These circumstances can strike unexpectedly when you take fenoprofen, particularly in more established individuals. If you are allergic to fenoprofen or have ever experienced a severe allergic reaction or asthma attack after taking an NSAID or aspirin, you should not take it.
Ensure that you inform your PCP if you have ever experienced:
- heart disease, diabetes, high cholesterol, and/or high blood pressure;
- a stroke, heart attack, or blood clot;
- bleeds or ulcers in the stomach;
- asthma;
- liquid maintenance;
- kidney or liver disease; or on the other hand
assuming you take ibuprofen to control respiratory failure or stroke. Fenoprofen ought not to be taken if you are pregnant except if your primary care physician tells you to. If you take an NSAID in the last 20 weeks of your pregnancy, you may have problems with your pregnancy and the unborn child may have serious heart or kidney problems. Nursing mothers should not take Fenoprofen. Fenoprofen is not recommended for use by anyone under the age of 18.
How should I take Fenoprofen?
Read all medication instructions and adhere to all instructions on your prescription label. Choose the dose that is most effective for treating your condition.
- Fenoprofen can be taken with food or milk.
- Assuming that you utilize this prescription long haul, you might require standard clinical trials.
- It may take up to three weeks for your symptoms to get better. Continue to utilize the drug as coordinated and let your surgeon know if your side effects get worse.
- Certain medical tests may be influenced by this medication. Inform any physician who inquires about you that you are taking fenoprofen.
- Keep at room temperature, away from heat and moisture. When you are not using it, close the bottle tightly.
What happens if I miss a dose?
If it is getting close to the time for your next dose, disregard the missed dose and take the prescription as soon as possible.
What happens if I overdose?
Poison Help can be reached at 1-800-222-1222 or through an emergency medical watch. Too far side effects include sluggishness, heaving, stomach torment, or bleeding.
What should I avoid while taking Fenoprofen?
Before taking multiple prescriptions for pain, fever, growth, or cold/influenza side effects, consult a doctor or drug specialist. They could have parts that are like fenoprofen, similar to ibuprofen, ketoprofen, or naproxen. Do not take aspirin unless your physician informs you to. Make an effort not to drink alcohol. It might increase the likelihood of stomach bleeding. Check with your doctor before taking an antacid, and only use the brand your doctor recommends. If you take certain antacids, your body may have a harder time absorbing fenoprofen.
You ought to look for surefire clinical consideration if you experience side effects of an unfavorably susceptible response like hives, runny or stodgy nose, wheezing, trouble breathing, enlarging in front of you or throat, or a serious skin response like fever, sore throat, consuming eyes, skin torment, or a red or purple skin rash with rankling and stripping.
Fenoprofen dosing information
Usual Adult Dose for Osteoarthritis:
- 400 mg to 600 mg orally 3 or 4 periods every day
- Greatest portion: 3200 mg/day
Remarks:
- Portion changes ought to be made following the inception of treatment or during the intensification of the illness.
- Rheumatoid arthritis patients typically require higher doses than osteoarthritis patients; Utilize the lowest effective dose that provides an acceptable control for either condition.
Use: for the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis symptoms
Usual Adult Dose for Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Orally, 400 to 600 mg three to four times per day. Maximum daily dose: 3200 mg/day
Remarks:
- Portion changes ought to be made following the inception of treatment or during the intensification of the illness.
- Rheumatoid arthritis patients typically require higher doses than osteoarthritis patients; Utilize the lowest effective dose that provides an acceptable control for either condition.
Use: for the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis symptoms
Usual Adult Dose for Pain:
- 200 mg taken orally every four to six hours, as needed
Use: For the substitute of mild to moderate pain
In case of an emergency/overdose
In case of an excess, contact the toxic substance control helpline at 1-800-222-1222. Additionally, data can be accessed online. Call 911 as soon as possible if the victim has collapsed, experienced a seizure, has difficulty breathing, or is unable to be moved.
Symptoms of overdose may include:
- heartburn
- nausea
- vomiting
- stomach pain
- dizziness
- unsteadiness or difficulty balancing
- headache
- ringing in the ears
- shaking of a piece of the body that you have no control over
- drowsiness
- confusion
A person should immediately dial 911 if they have taken an excessive amount of medication and are experiencing serious side effects such as unconsciousness or difficulty breathing. On the off chance that not, promptly contact a toxin control focus. Poison control center call no. 1-800-222-1222. A commonplace toxin control focus can be reached by occupants of Canada. Results of abundance could consolidate serious stomach torture, slow/shallow breathing, preposterous sluggishness, and loss of awareness.
Notes
Never give anyone else this medication. While you are taking this medication, you may be subjected to laboratory and additional clinical trials, such as total blood count, kidney and liver capacity, and circulatory strain. Keep a record of all medical and lab appointments. For more nuanced information, consult your PCP. Flexibility and joint function can be improved with lifestyle changes like, if necessary, weight loss and strengthening and conditioning exercises. Ask your PCP for specific instructions.
Missed Dose
Accept the missed dose as soon as you remember if you are taking this medication on a regular schedule rather than “depending on the situation.” Skim the portion that you missed if it is getting close to the time of the next one. When you normally would, take your next dose… To make up for lost time, try not to double the amount.
Storage
Avoid light and dampness in a firmly fixed holder at room temperature. Keep it out of the washroom. Get drugs far from youngsters and pets. Try not to flush drugs into a channel or wash them away forever unless you are trained to. At the point when this item has lapsed or is not generally needed, as expected discard it. Talk to your local waste management company or your pharmacist.
Fenoprofen Pregnancy Warnings
NSAIDs should be avoided beginning at 20 weeks of pregnancy and continuing after that. Risk Summary: Not assigned Premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus may result from the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in pregnant women after 30 weeks of gestation; Using NSAIDs after 20 weeks of pregnancy can result in fetal renal dysfunction, which can cause oligohydramnios and, in some instances, neonatal renal impairment.
Comments:
A benefit-risk analysis should be used before 20 weeks of pregnancy to decide whether or not to use NSAIDs; NSAIDs should be avoided whenever possible during pregnancy, according to some authorities. If NSAID use is fundamental somewhere in the range of 20-and 30 weeks growth, limit use to the least powerful portion for the briefest term conceivable; ultrasound checking of amniotic liquid ought to be thought of assuming NSAID use stretches out past 48 hours; If oligohydramnios develops, stop taking an NSAID and treat as usual.
The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is not advised for pregnant women because they may reduce fertility. Following the use of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors in early pregnancy, animal studies have demonstrated evidence of an increased risk of miscarriage, pre-and post-implantation loss, gastroschisis, embryo-fetal lethality, and cardiac malformation. Premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus, pulmonary hypertension, fetal renal impairment, oligohydramnios, and inhibition of platelet aggregation are all potential side effects of taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) during the third trimester of pregnancy. There is no controlled information on human pregnancy.
Drug Safety Communication from the US FDA (10-2020): The FDA is requiring another admonition be added to NSAID naming portraying the gamble of fetal kidney issues that might bring about low amniotic liquid. The FDA advises pregnant women not to use NSAIDs after 20 weeks of gestation. The FDA has received 35 reports of low levels of amniotic fluid or kidney problems in pregnant women who took NSAIDs. Five babies kicked the bucket; Two of them had kidney failure with evidence of low amniotic fluid, while three had kidney failure without evidence of low amniotic fluid. The low amniotic liquid began as soon as 20 weeks of pregnancy. 11 pregnant women reported low levels of amniotic fluid, and when the NSAID was stopped, the fluid volume returned to normal. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) has been linked to low levels of amniotic fluid for a variety of durations—from 48 hours to several weeks—in the medical literature. Confusions of drawn-out oligohydramnios may incorporate appendage contractures and deferred lung development. After the drug was approved, invasive procedures like exchange transfusion or dialysis were required in some cases of impaired neonatal renal function. Other times, the condition went away within three to six days of stopping the NSAID, and it came back when the same NSAID was used again.
The administration should not be done during labor and delivery; With the mother and child having a higher tendency to bleed, labor may begin later and last longer. Female fertility may be affected by NSAIDs; withdrawal of NSAID treatment ought to be viewed as in ladies with troubles considering or who are going through examination of fruitlessness. US FDA has not assigned a pregnancy category: The pregnancy labeling rule for prescription drugs has been modified by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to include a summary of the risk, a discussion of the data supporting that summary, and pertinent information to assist healthcare providers in making prescribing decisions and advising pregnant women about drug use.
What other information should I know?
You should not give or not let any other person take your medicine. If you have any questions about reordering your medication, ask your pharmacist. All of your supplements, vitamins, and other dietary supplements, as well as all of your prescription and nonprescription (over-the-counter) medications, must be documented in writing. You ought to carry this rundown with you each time you visit a specialist or on the other hand if you are confessed to an emergency clinic. Additionally, it is essential information to keep on hand in case of an emergency.
IMPORTANT WARNING:
Other than aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like fenoprofen, people may be more likely to have a heart attack or stroke than people who don’t take them. These occurrences may result in death and may occur without warning. People who take NSAIDs for a long time may be at a higher risk for this. Try not to take an NSAID like fenoprofen on the off chance that you have as of late had a cardiovascular failure except if coordinated to do as such by your PCP. Let your primary care physician know if you or anybody in your family has or has at any point had a coronary illness, a cardiovascular failure, or a stroke in the possibility that you smoke, and assuming that you have or have at any point had elevated cholesterol, hypertension, or diabetes. If you experience any of the following signs, you should immediately seek emergency medical attention: chest torment, windedness, shortcoming in one section or side of the body, or slurred discourse.
In the circumstance that you will go through a coronary course sidestep unit (CABG; a kind of heart surgery), you shouldn’t take fenoprofen before or after the procedure. NSAIDs like fenoprofen can lead to stomach or intestine ulcers, bleeding, or holes. These issues can emerge whenever during treatment, happen without showing any side effects, and may bring about death.The gamble might be higher for individuals who take NSAIDs for quite a while, are more seasoned, have chronic weakness, or drink a lot of liquor while taking fenoprofen. If you take any of the following medications, tell your medic. anticoagulants (‘blood thinners’) like warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven); aspirin; different NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn); oral steroids like prednisone (Rayos), methylprednisolone (Medrol), and dexamethasone citalopram (Celexa), Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) include fluoxetine (Prozac, Sarafem, Selfemra, in Symbyax), fluvoxamine (Luvox), paroxetine (Brisdelle, Paxil, Pexeva), and sertraline (Zoloft). or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) like duloxetine (Cymbalta), desvenlafaxine (Khedezla, Pristiq), and venlafaxine (Effexor XR). Additionally, let your primary care physician know if you’ve at any point had a ulcer, stomach or digestive tract dying, or some other draining problem. Stop taking fenoprofen and call your doctor if you have any of the following symptoms: stomach pain, heartburn, bloody or tarry stools, blood in the stool, or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
Keep all of your lab and doctor’s appointments. Your symptoms will be closely monitored by your doctor, who may also order tests to determine how your body responds to fenoprofen. Be sure to let your doctor know how you’re feeling so that he or she can prescribe the right amount of medication to treat your condition with the fewest possible serious side effects. When you start taking fenoprofen and every time you get a refill on your prescription, your doctor or pharmacist will give you the manufacturer’s patient information sheet (Medication Guide). Peruse the data cautiously and inquire as to whether you have any inquiries. You can likewise visit the Food and Medication Organization (FDA) or the maker’s site to get the Medicine Guide.
What other drugs will affect fenoprofen?
If you are taking an antidepressant, talk to your doctor before taking fenoprofen. When you take an NSAID with some antidepressants, you might get bruises or bleed easily.
Be sure to tell your doctor about all of your other medications, especially:
- cyclosporine;
- lithium;
- methotrexate;
- blood more slender (warfarin, Coumadin, Jantoven);
- heart or blood pressure medication, such as a “water pill” or diuretic;
- diabetes medicine is taken orally;
- seizure medication (particularly phenobarbital or phenytoin);
- medication for steroids (like prednisone); or a drug with sulfa.
This list isn’t all there is. Fenoprofen may interact with vitamins, herbal products, prescription and over-the-counter medications, and other medications. All possible drug interactions aren’t on this list.
FAQ
Is fenoprofen an opioid?
Quieting pain killers like fenoprofen are moreover called non-steroidal relieving drugs (NSAIDs), or every so often ‘threatening to inflammatories’. Fenoprofen is used to treat rheumatic conditions like arthritis and sprains and strains. It eases suffering and reduces aggravation.
Is there an antibiotic in Fenoprofen?
A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) called fenoprofen is used to treat both acute and ongoing arthritis.
What brand of fenoprofen is most commonly used?
Nalfon’s description and brand names
200 Nalfon.
Fenoprofen’s contraindications are recorded beneath. ?
CONTRAINDICATIONS. Patients who have demonstrated excessive sensitivity to fenoprofen calcium should not take fenoprofen calcium tablets. Patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or unfavorably susceptible type reactions after taking anti-inflammatory medication or other NSAIDs should not take fenoprofen calcium tablets.
what is composition of fenoprofen ?
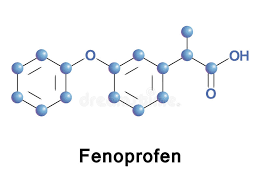
Fenoprofen Calcium is a salt of aryl acetic acid with the following chemical structure and molecular formula: C30H26CaO6•2H2O. The powder is translucent white. It breaks up into a 15 mg/mL liquor arrangement at 25°C (95%).
Can fenoprofen be taken with aspirin?
Do not take aspirin unless your medic tells you to. Avoid consuming alcohol. It could make stomach draining more probable. Check with your doctor before taking an antacid, and only use the brand your doctor recommends.
What advantages does fenoprofen provide?
Fenoprofen is used to treat pain, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness in osteoarthritis (arthritis caused by a breakdown of the lining of the joints) and rheumatoid arthritis (arthritis caused by swelling of the lining of the joints). Additionally, fenoprofen is used to alleviate pain from other conditions.
Can Fenoprofen be taken with alcohol?
Customers’ Suggestions: When taking this medication, don’t drink any alcohol. If you drink alcohol while taking this medication, your risk of stomach bleeding increases.
Is fenoprofen a prostaglandin?
1.10 – Fenoprofen was planned as a polymer-formed prodrug for this particular circumstance.
What is Fenoprofen’s half-life?
The half-life of plasma is approximately three hours. Fenoprofen’s major urinary metabolites, fenoprofen glucuronide, and 4′-hydroxy fenoprofen glucuronide are responsible for approximately 90% of the elimination of a single oral dose within 24 hours.