Anatomical Snuffbox
Introduction
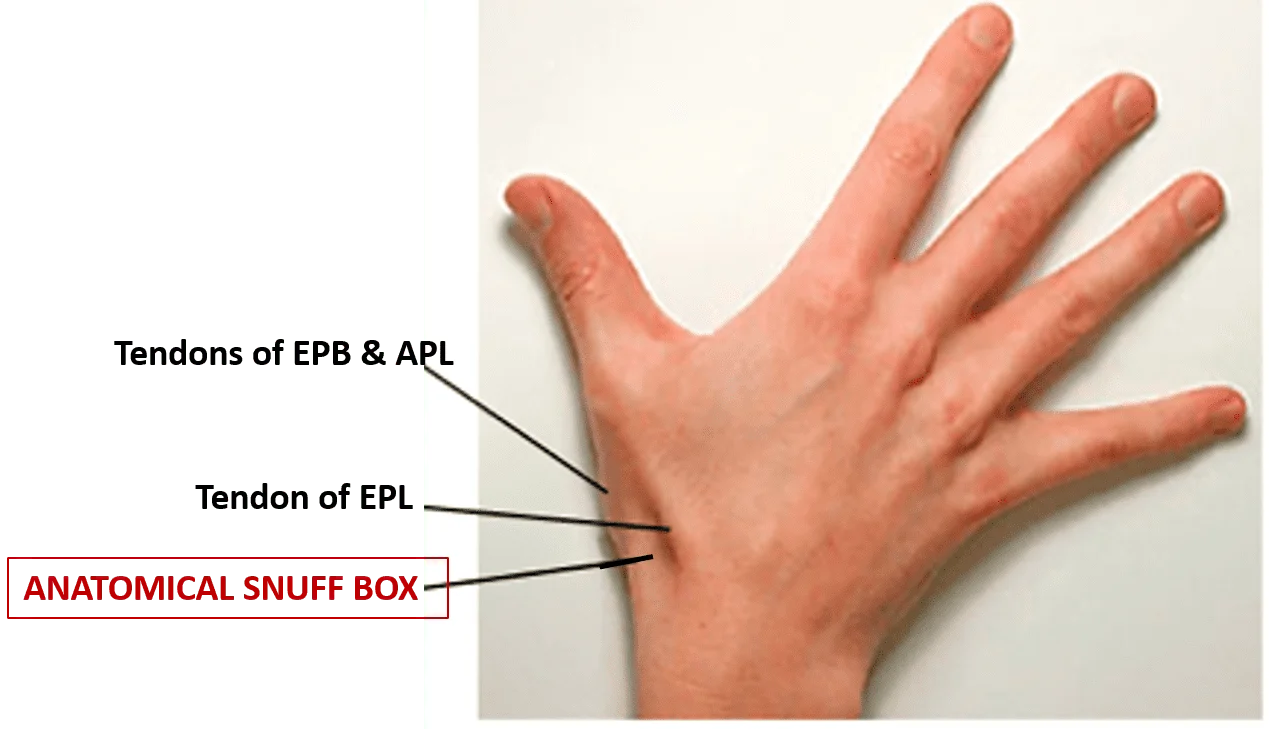
The Anatomical Snuffbox is a small, triangular depression located on the dorsal aspect of the hand, specifically at the base of the thumb. This anatomical feature is of considerable clinical significance due to its unique structure and accessibility.
The anatomical snuffbox, so named because of its historical connection to the once-common practice of inhaling snuff tobacco, is an important landmark for medical practitioners when evaluating and diagnosing a range of hand and wrist disorders.
It is a crucial point of reference in physical examinations because of its clear borders and contents, which help in the assessment of potential diseases or injuries in this area. The anatomical snuffbox, its borders, therapeutic importance, and the structures that travel through it will all be thoroughly discussed in this talk.
Borders of Anatomical Snuffbox
The anatomical snuffbox, also known as the radial fossa, is defined by distinct anatomical borders. These borders help healthcare professionals identify and locate this specific region of the hand with precision. The borders of the anatomical snuffbox are as follows:
Lateral Border (Radial Border):
The extensor pollicis brevis and the abductor pollicis longus, two intimate and parallel tendons, form the lateral boundary (radial side).
Medial Border (Ulnar Border):
The tendon of the extensor pollicis longus (EPL) muscle forms the medial border. This tendon helps to define the medial boundary of the snuffbox as it travels from the forearm and crosses the back of the wrist.
Proximal Border (Posterior Border):
The styloid process of the radius.
Floor:
Carpal bones: scaphoid and trapezium.
Roof:
Skin.
It’s crucial to remember that the borders are not formed by the muscles themselves, but rather by their tendons.
Structure of Anatomical Snuffbox
The radial artery, a division of the radial nerve, and the cephalic vein are the primary components of the anatomical snuffbox:
Radial artery:
The radial artery passes across the anatomical snuffbox’s bottom before turning medially and passing between the adductor pollicis muscle’s heads.
Some people can feel the radial pulse by putting two fingers on the anatomical snuffbox’s proximal end.
Superficial branch of the radial nerve:
The radial nerve’s superficial branch innervates the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the anatomical snuffbox. The corresponding region on the back of the hand as well as the dorsal surface of the lateral three and a half digits are innervated.
Cephalic vein:
The cephalic vein rises from the hand’s dorsal venous system, passes through the anatomical snuffbox, and then ascends to the anterolateral side of the forearm.
Function of Anatomical Snuffbox
The three thumb-acting muscles (APL, EPB, and EPL) arise (“crop out”) from a groove in the lateral region of the forearm that splits the extensors. These muscles are deep to the superficial extensors. They are referred to as outcropping muscles because of this feature. The triangular anatomical snuff box is constrained medially by the tendons of the EPL and laterally by the tendons of the APL and EPB.
When the thumb is fully extended, the snuff box is evident as a hollow on the lateral side of the wrist; this pulls the APL, EPB, and EPL tendons up and creates a concavity between them. Be aware that the Radial artery is on the snuff box’s floor. The base of the first metacarpal can be felt distally and the radial styloid process can be felt proximally in the snuff box. Between the radial styloid process and the first metacarpal, the snuff box’s floor can be felt to be scaphoid and trapezoidal.
Clinical Importance
The most frequent method of fracture for the hand’s scaphoid bone is falling on an outstretched hand (FOOSH).
Pain and tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox are the defining clinical features of a scaphoid fracture.
Due to its so-called “retrograde blood supply,” which enters at its distal end, the scaphoid is particularly susceptible to avascular necrosis after fracture. This means that the proximal portion of the scaphoid bone may become avascular if it sustains a fracture in the middle (or “waist”) of the bone.
Osteoarthritis of the wrist is more likely to occur in older patients who have a missed scaphoid fracture.
Idiopathic Radial artery aneurysm
Aneurysms in the radial artery are quite uncommon. They are typically connected to penetrating or iatrogenic trauma. They are less frequent than ulnar artery aneurysms, although the difference is not known. After blunt trauma, incidents have been described.
Summary
These well-defined borders create the triangular depression known as the anatomical snuffbox. This anatomical structure serves as a reference point for locating various structures, assessing wrist injuries, and conducting physical examinations of the hand and wrist region. Understanding the borders of the snuffbox is crucial for healthcare professionals when diagnosing and treating conditions affecting this area.
FAQs
What is an anatomical snuff box?
A triangular dip at the base of the thumb on the dorsum of the hand is referred to as the anatomical snuffbox. Upon ulnar wrist deviation and extension and abduction of the thumb, the anatomical snuffbox is clearly apparent.
The anatomical snuff box is made up of how many muscles?
Three muscles that work on the thumb form the medial and lateral borders of the snuffbox:
the longus pollicis kidnapper.
pollicis brevis extensor.
lengthy pollicis extender.
What is the anatomical snuff box and scaphoid fracture?
On the back of the wrist, it is situated near the bottom of the depression created by the thumb tendons. This region, which is frequently referred to as the “anatomic snuffbox,” is usually where you experience the most sensitivity or pain when a scaphoid fracture takes place. The wrist’s scaphoid can be seen in an image and on an X-ray.
What is a snuff box test?
While palpating the patient’s anatomic snuffbox with the other hand, the examiner places one hand on the patient’s wrist to stabilize it. carrying out the test. The scaphoid (navicular) bone, along with three tendons, makes up the anatomical snuffbox.
What is a snuff box fracture?
Scaphoid fracture symptoms are characterized by “snuffbox” pain. You can find the snuffbox, also referred to as the radial fossa, by giving the thumbs up. The snuffbox is the skin depression at the wrist that is located below the thumb.

3 Comments