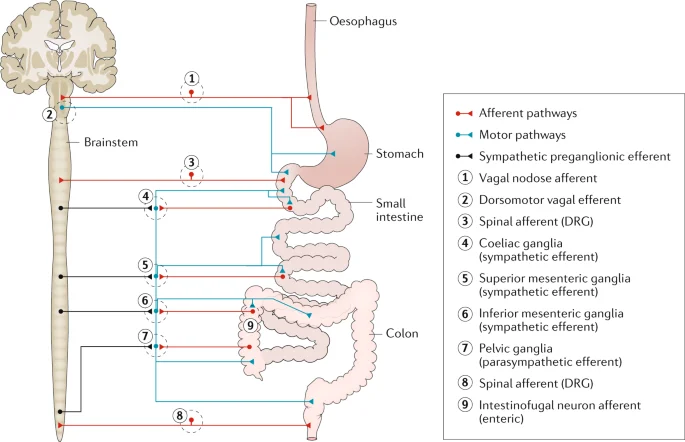
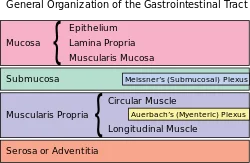
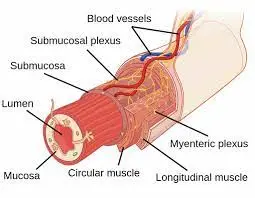
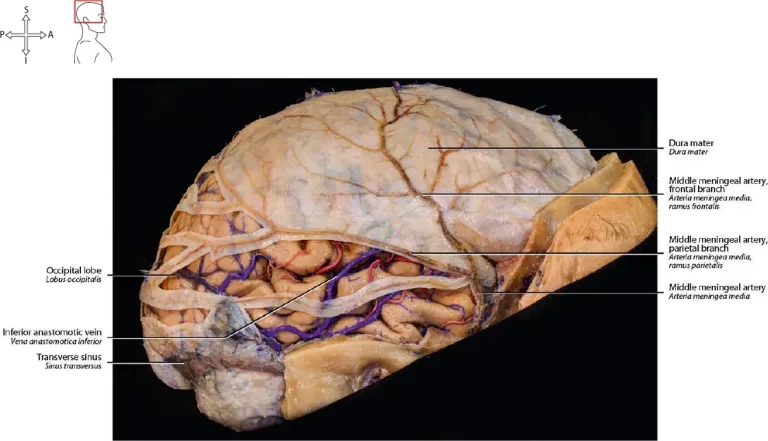
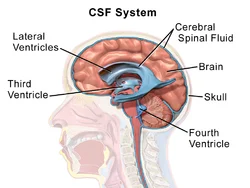
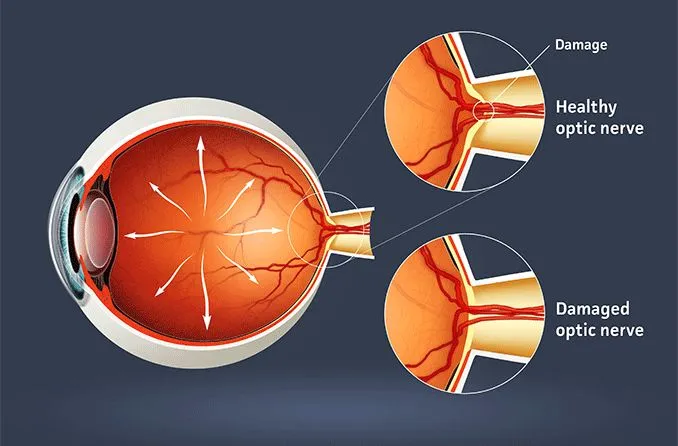
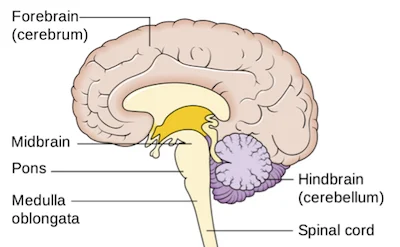
Enteric Nervous System (ENS)
Introduction The nervous system of the stomach. Types of Enteric Neurons Gastrointestinal neurons Preceptive afferent neurons Circular muscle motorneurons excitatory Circular muscle motorneurones inhibitory Motorneurons of longitudinal muscle Rising interneurons Motorneurons of longitudinal muscles Descending interneurons Neurons of the secretomotor and vasomotor Intestinofugal neurons Additional gastrointestinal regions Enteric neural networks Enteric nervous system modular organization…