21 Best Back Strengthening Exercises for Every Fitness Level
Introduction
A strong and resilient back is crucial for maintaining overall physical health and preventing injuries. Back strengthening exercises can help improve posture, enhance stability, and alleviate back pain. These exercises target the muscles that support the spine, including the erector spinae, which run along the length of the spine, as well as the deep stabilizing muscles that promote core strength and stability.
When performed correctly and regularly, back strengthening exercises can contribute to better flexibility, balance, and coordination. These exercises often involve a combination of movements that engage various muscle groups, such as the back extensors, abdominals, and glutes. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional or a certified trainer before starting any new exercise program, particularly if you have a history of back problems or any existing medical conditions.
By incorporating back strengthening exercises into your fitness routine, you can build a stronger, more resilient back that supports your overall well-being and helps you maintain an active lifestyle.
Anatomy of back muscles
The back muscles, also known as the posterior chain, are a complex group of muscles that play a crucial role in supporting the spine, maintaining posture, and facilitating movement. They can be divided into two main categories: superficial and deep muscles.
Superficial Back Muscles:
- Trapezius: The trapezius muscle is a huge muscle that goes across the upper back and neck. It helps to move and stabilize the shoulder blades, as well as extend and laterally flex the neck.
- Latissimus dorsi: Commonly referred to as the lats, these muscles are located on the sides of the back. They play an important role in shoulder extension, adduction, and internal rotation.
- Rhomboids: The rhomboid muscles are situated in between the shoulder blades. They help to retract and stabilize the scapulae, allowing for proper posture and shoulder movement.
- Erector spinae: This group of muscles runs along the length of the spine and consists of three parts: iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis. The erector spinae muscles are responsible for extending and laterally flexing the spine.
Deep Back Muscles:
- Multifidus: The multifidus muscles are small muscles that run along the spine. They provide stability and support to the vertebrae, helping to maintain proper alignment and control movement.
- Rotatores: The rotatores are a group of small muscles that assist in rotating and stabilizing the vertebrae.
- Interspinales and intertransversarii: These small muscles connect adjacent vertebrae and aid in spinal stability and movement control.
In addition to these specific muscles, there are also several other smaller muscles in the back that contribute to its overall function and strength.
To effectively train the back muscles, it is important to incorporate a variety of exercises that target different muscle groups. Some common exercises include pull-ups, rows (e.g., bent-over rows, seated cable rows), deadlifts, lat pulldowns, and back extensions. It is important to use proper form and technique when performing these exercises to prevent injury and maximize results.
Overall, the back muscles are essential for maintaining proper posture, supporting the spine, and facilitating movement. Regular strength training exercises that target the back can help improve posture, prevent injuries, and enhance overall functional fitness.
Back strengthening exercise
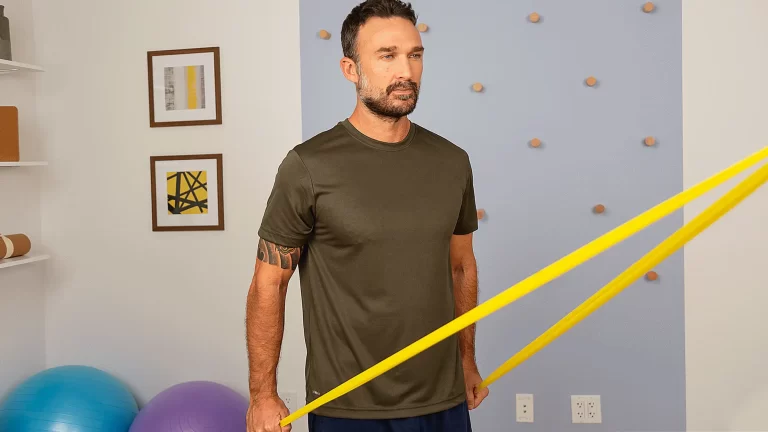
Half-Kneeling Archer Row
This warmup exercise is wonderful for your shoulders, but it also works on your posterior delts and rhomboids. Use this as a warm-up for back-day workouts to prepare for larger lifts.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Begin with a half-kneeling position your left knee should be on the floor, and grasp the ends of the resistance band in each hand.
- Lift your right arm up a little over your shoulder level in the same plane as your torso.
- Maintain your thumb pointing in the direction of the ceiling.
- Keep your grip on the band with your left hand, too, grasping at roughly even with your right elbow.
- Pull the resistance band straight back over your chest with your rhomboids (back) and rotator cuff muscles, as if shooting a bow and arrow.
- Maintain the elbow of your pulling arm near to the body during the whole exercise make sure your stable arm is completely straight.
- Do the 3 sets of 12 to 15 repetitions.
Band Bent-Over Row
If you are working on your back, you will get used to the cycle in its various forms, so begin with a light-resistance variation that can serve as a warmup or a crucial component of your program. The band will help you to work across the range of motion without using weights while providing some resistance.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Hold a low-resistance band and set it out on the floor.
- Stand in the middle of the band, keeping the two ends in either hand with a pronated (overhand) grip, hips hinging and knees slightly bent in an athletic stance.
- Make sure that your back is not making any arch.
- Compress your back to pull the band ends simultaneously to your chest, or as close as the band allows.
- Hold for a second at the top of the motion, then gradually go back to the starting position while working against the band’s resistance.
- Do 3 to 4 sets of 12 to 15 repetitions.
Bent-Over Reverse Fly
This basic but effective action is a must-do in any back workout plan. During this movement, keep a long neutral spine and a solid core.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Begin with a standing position and feet hip-distance distance and keep a dumbbell in each hand.
- Maintain your body weight in your heels as you tilt forward from your hips, enabling the weights to travel down your thighs and stop right at knee height.
- Squeeze your shoulder blades together at the top and open your arms out to the side.
- Gradually go back to the position from which you started.
Arnold Press
This motion adds rotation to the classic shoulder press, hitting all angles of the deltoids and recruiting a ton of stabilizing back muscles.
To perform this exercise follow these steps
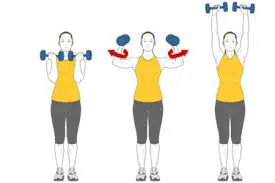
- Start with standing tall with your feet hip-distance away and keep a dumbbell in each hand.
- Maintain your arms bent and palms should be facing your shoulders, just like performing a bicep curl.
- As you lift your arms overhead, rotate them so that your palms are facing away from you.
- Make sure your biceps are fully extended and reaching your ears before rotating your arms as you descend back down.
- Do it again for a few repetitions.
Straight Arm Lateral Raise
Mastering the lateral raise needs muscle stabilization through the whole arm, shoulders, and back. begin with light weights to make sure of proper form.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Initiate with standing position and feet hip-distance distance and keeping a dumbbell in each hand.
- Maintain arms fairly straight with a slight bend in the elbows as you lift your arms out to the sides about an inch or two more than shoulder level.
- Make sure to maintain your core engaged, latismus activated, and shoulders downward and relaxed.
- Lower down to initiate position.
- Do it again for a few repetitions
90 Degree Lateral Raise
Develop sculpted and strong shoulders and back muscles with this easy but impactive lateral raise variation.
To perform this exercise follow these steps
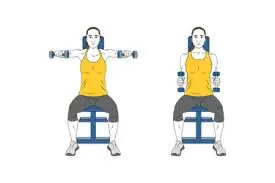
- Begin with sitting on a bench or chair and feet hip-distance distance and keeping a dumbbell in each hand.
- Bend your elbows to form a ninety-degree angle and palms should be facing towards the body.
- Maintain the ninety-degree angle, and lift your arms upward so your elbows come in line with your shoulders.
- Be sure to maintain your core engaged, latismus activated, and shoulders downward and relaxed.
- Lower down to initiate position.
- Do it again for a few repetitions
Y-Press
This shoulder press variation targets several angles of the upper back and shoulders, providing intense activation and toning. Because the angle can be difficult to adjust to, begin with lesser weights and gradually increase as you become more at ease with the action.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Begin with standing position and feet hip-distance distance and keeping a dumbbell in each hand.
- Maintain your core tight as you raise the dumbbells to your shoulders with your elbows rotated out to the side.
- Press the weight upward and outward diagonally so that your arms make up a “Y.”
- Bring back the dumbbells to your shoulders.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
Upright Rows
The upright row focuses many large muscles in the whole upper back and shoulders.
To perform this exercise follow these steps
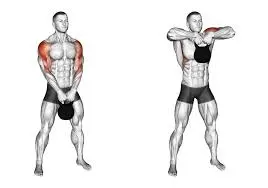
- Start with standing tall and your feet hip-distance distance and keep a kettlebell (or dumbbell) and palms should be facing your body.
- Maintain your core tight and chest tall as you take the weight up towards your chin, leading with the elbows and maintaining the weight near to your body.
- The arms should not go on a higher level than parallel with the shoulders.
- Hold at the top, then come back to the initiate position.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
Plank Up Downs
Another best bodyweight movement that builds strength in everything from the back to your core and glute muscles, plank up-downs are an advanced exercise and can be scaled to the knees if needed.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Behin within a high plank position, and maintain your core engaged.
- Decesend one arm at a time into a forearm plank and then, one arm at a time.
- Go back to a high plank position.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
Superman
Bodyweight back exercises can be just as impactful and need activation of the whole body.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Start with lying face down on the ground, maintaining your arms straight out in front of you.
- Compress your glutes and lower back to raise your legs, arms, and top of your chest off the ground.
- Maintain for a count, then gradually go to the initiate position.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
W Superman
It incorporates this Superman variation for even more back sculpting benefits.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Start with lying face down with your elbows directly out to your sides and your forearms on the ground in line with the sides of your body.
- Compress your glutes and elevate your chest and arms off the ground while compressing your elbows together behind you.
- From above, your arms will seem like the letter “W.”
- Maintain for several seconds, then gradually come to the initiate position.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
Lat Pullovers
Your latismus is a very essential muscle for building strength and also maintaining your back and shoulders stabilized.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Start with lying on your back, knees should be bent and feet should be flat on the ground.
- Grasp a dumbbell (or dumbbells) in both of your hands just over your chest.
- Maintaining a slight bend in the elbow and your back pressed into the ground, descend the weight overhead, stopping right before it touches the surface of the floor.
- Gradually raise back upward to initiate the position.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
Reciprocal Rows
Altering arms in this bent-over-row variant is an excellent method to mix up your home-back workout regimen.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Begin with standing with feet hip-distance away and keeping a dumbbell in each hand.
- Maintain your body weight in the heels of your feet while you hinge in the forward direction from the hips allowing the dumbbells to slide down your thighs and stop right at knee level.
- Keeping a long neutral spine and tight core, move your right elbow up behind you and compress at the top.
- As you lower the right arm back down to the initiate position, simultaneously raise the left arm up behind you and squeeze at the top.
- Keep on switching this movement, ensuring that both arms are functioning in harmony.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
Rotator Cuff Rotation
The rotator cuff is a collection of muscles and tendons that embraces the shoulder joint. This workout especially strengthens your shoulders and back, and might additionally assist you in improving your posture.
To perform this exercise follow these steps
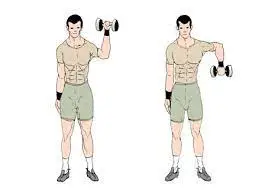
- Start with standing tall and feet hip-width distance and the core should be engaged.
- Keeping a dumbbell in each hand, begin with arms bent in a ninety-degree angle with palms facing in the direction of the ceiling.
- Maintain your arms bent and elbows locked in place as you turn your forearms out and in the direction of your back.
- Place your arms in a straight line with the sides of your body.
- After that turn back to initiate position in front of the body.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
W to T Pulses
These little pulses can help activate the shoulders and back muscles and are great to begin your workout or end on a high note.
To perform this exercise follow these steps
- Begin with standing tall with feet hip-width distance apart and the core should be engaged.
- Take a set of light dumbbells and keep them straight out to the sides and palms should be facing towards the ceiling so your body creates the shape of a “T.”
- Bend your elbows a little in so they make a “W” shape, and then with purpose extend back out.
- For 30-45 seconds, alternate between a “W” and a “T” position.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
Russian Kettlebell Swing
Kettlebell swings work almost every muscle in the body, however, they focus mostly on the back. A full kettlebell swing extends above your head, but a Russian kettlebell swing stops at eye level.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Start with standing and your feet should be hip-width distance apart and a slight bend in your knees.
- Engage your core muscles and be sure to maintain a flat back during the whole movement.
- Grasp the kettlebell with both hands in an overhand grip and begin with the kettlebell hanging in between your thighs with arms straight and engaged.
- tilt forward, then use your hips to swing the kettlebell up to eye level.
- Lower back down.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
Barbell Assisted Modified Pull-Up
The pull-up is the ultimate back and upper body exercise, needs a ton of strength and stabilization. However, this difficult movement can take more time for strength training and practice. do this modified version if you have access to a pull-up bar to help work your way up.
To perform this exercise follow these steps
- Check that your barbell is securely attached to the rig.
- Begin by sitting down directly underneath the barbell in an L-shaped position with your legs straight out.
- Lift your arms upwards and secure a firm grasp on the barbell (tune the barbell height so that it’s not too high that you have to reach for it, but not too low that you must bend your arms).
- Squeeze your shoulder blades together and tighten your core as you bend your arms and pull up until your chin meets or is just above the bar, then gradually descend back downward.
Swimmers
This is one of the functional back exercises that can be done in the comfort of your own home or at the gym.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Start with lying face down on the ground, stretching your arms straight out in front of you.
- Compress your glutes and lower back muscles to lift your right arm and left leg off the ground.
- Hold at the top, and gradually come back to the initiate position.
- Do it again, raising your left arm and right leg off the ground.
- Hold at the top and then come back to the initiate position.
Rack Pull
Rack pulls are not for the faint of heart. It is a deadlift modification that, like a standard deadlift, develops all of your erector spinae muscles, as well as your lower, mid, and upper back muscles.
Rack pulls require you to pull with a limited range of motion, with the bar beginning either above or just beneath your knees. Because you are pulling from an upper starting point, maintaining a neutral spine all throughout the lift is easy. You can also lift more weight with this deadlift variation, adjusting your body to larger weights and increasing your strength.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Place the barbell up on the squat rack either over or below your knees.
- Imagine your standard deadlift stance and grip.
- Hinge down and take an overhand shoulder-width hold on the barbell.
- compress your armpits together and engage your core.
- Maintain your chest up and shoulders back.
- Maintain the bar near your body, just as in a regular deadlift.
- Hinge back to the initiate position.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
As in a typical deadlift, maintain the bar right next to your body.
Barbell Good Morning
The barbell good morning is an excellent exercise for strengthening the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings. If shoulder mobility or back pain are issues, it is best to perform an alternative.
Lighter loads should be mastered before increasing intensity and range of motion. Once learned, it is an excellent exercise for strengthening and building posterior muscle.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Step beneath a weighted barbell in a power rack.
- Set up in the same way as when practicing for a back squat and take a couple of steps backward.
- Hinge at the hips with a slight bend in your knees, maintaining your chest up and shoulders downward.
- Bend your torso until it is virtually parallel to the surface of the ground.
- Reverse the lift by squeezing your glutes and hamstrings until you are back standing.
- This is one repetition.
- Do it again for several repetitions.
Use a safety squat bar if possible to increase the stability and safety of this exercise.
Bird-dog
Back extensor muscles, which connect to the back of the spine and enable a person to stand, bend, and lift items, are exercised with this exercise.
To perform this exercise follow these steps

- Begin on your hands and knees, and your shoulders should be over your hands, and your hips should be exactly over your knees, as you begin.
- Stretch your core muscles and extend your right arm in front of you.
- Maintain your balance while keeping the stance.
- Take a few deep breaths before gradually raising your left leg and stretching it straight behind you.
- After you’ve completed step five, hold that position for 15 seconds.
- Return to the beginning position and do it again on the opposite side.
- This procedure should be repeated five times.
Why is back strength important?
Back strength is important for several reasons:
Spinal support: The back muscles, particularly the erector spinae, provide support and stability to the spine. A strong back helps maintain proper alignment of the vertebrae, reducing the risk of spinal injuries and conditions like herniated discs.
Posture: Weak back muscles can lead to poor posture, which can cause muscle imbalances, joint stress, and chronic pain. Strong back muscles help maintain good posture by keeping the spine in its natural alignment.
Injury prevention: A strong back helps protect against common injuries, such as strains and sprains. It provides stability during movements like lifting heavy objects, reducing the risk of muscle strains or other soft tissue injuries.
Functional movements: The back muscles play a crucial role in everyday movements like bending, twisting, and lifting. Having a strong back improves your ability to perform these movements safely and efficiently.
Athletic performance: A strong back is required for maximum performance in many sports and physical activities. Whether it’s running, jumping, throwing, or swinging a golf club, a strong back enhances power, stability, and overall athletic ability.
Balance and coordination: The back muscles work in conjunction with other muscles to maintain balance and coordination during movement. A strong back helps improve overall body control and stability.
Overall, maintaining a strong back is essential for overall health, injury prevention, and optimal physical performance. Incorporating regular strength training exercises that target the back can help improve back strength and enhance overall functional fitness.
How often should you do back strength training?
The usual rule of thumb for strength training is that the larger the muscle, the longer it takes to recover from a session. For instance, your abdominal muscles are small, so you can work on your core every day. You cannot perform strength work on the quads two days in a row because they are so huge. They require a break.
Because the muscles in the upper back are smaller than, for example, the quads, you shouldn’t work them out twice consecutively. However, you may perform back exercises 3 to 4 times each week. That being said, start small. If you have never attempted back strength training before, begin by doing it once a week. Once your body has adjusted, you will be able to tell because those muscles will begin to feel less fatigued after working out, and you can progressively increase the frequency of back strength training you perform.
FAQ
What are some exercises that can help strengthen the back?
Some exercises that can help strengthen the back include deadlifts, rows, lat pulldowns, back extensions, and Superman exercises.
How often should I perform back-strengthening exercises?
It is recommended to perform back strengthening exercises at least 2-3 times per week. It is still vital that you pay attention to your body and not overload it. If you are experiencing any pain or discomfort, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional.
Should I exercise my back without using weights or any other equipment?
Yes, there are several bodyweight exercises that can help strengthen the back, such as planks, bird dogs, and bridges. These exercises can be performed at home without using any equipment.
Are there any specific precautions or modifications I should consider when performing back-strengthening exercises?
It is important to maintain proper form and technique during back-strengthening exercises to avoid injury. It is also recommended to start with lighter weights or resistance and gradually increase as your strength improves. If you have any pre-existing back conditions or injuries, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new exercise program.
How much time does it take for back-strengthening workouts to show results?
The time it takes to see results from back-strengthening exercises can vary depending on individual factors such as genetics, current fitness level, and consistency of movement. However, with regular practice and proper form, you can expect to see improvements in back strength and posture within a few weeks to a couple of months.
Do back strengthening exercises contribute to back pain?
Yes, strengthening the muscles in your back can help alleviate back pain by improving posture, reducing muscle imbalances, and providing better support for the spine. However, if you are experiencing chronic or severe back pain, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
References
- Nasm-Cpt, S. S. M. R. C. (2020, December 11). 20 Best Back Exercises for Women, According to Top Fitness Experts. Good Housekeeping. https://www.goodhousekeeping.com/health/fitness/g34896393/best-back-workouts-for-women/
- Nasm, B. W., & CSCS, E. S. (2021, November 2). Add the Superman Hold to Your Back Workouts. Men’s Health. https://www.menshealth.com/fitness/a20694965/superman/
- Tomko, J. (2022, March 15). How to Do the Cat-Cow Stretch for Better Movement. Men’s Health. https://www.menshealth.com/fitness/a39438579/cat-cow/
- McLean, S. (2023, October 4). The 10 Best Lower Back Exercises for Stability and Strength. BarBend. https://barbend.com/best-lower-back-exercises/
- Image: Nasm, B. W., & CSCS, E. S. (2019, April 4). This Badass Row Bulletproofs Your Shoulders. Men’s Health. https://www.menshealth.com/fitness/a27041591/half-kneeling-archer-row/
- Image: Y-Press. (2020, May 29). GymCube. https://www.gymcube.com/exercise-library/y-press
- Image: 90-degree dumbbell lateral raise – Exercises routines. (n.d.). https://www.workoutsprograms.com/exercises/90-degree-dumbbell-lateral-raise
- Image: Ryan, M. (2021, December 21). Lateral Arm Raise | Best Dumbbell Arm Exercises | POPSUGAR Fitness UK Photo 4. POPSUGAR Fitness UK. https://www.popsugar.co.uk/fitness/photo-gallery/37721062/image/37721057/Lateral-Arm-Raise
- Image: STANDING ARNOLD PRESS – Exercises, workouts and routines. (n.d.). https://www.workoutsprograms.com/exercises/standing-arnold-press
- Image: Bent Over Dumbell Reverse Fly. (n.d.). skimble.com. https://www.skimble.com/exercises/31473-bent-over-dumbell-reverse-fly-how-to-do-exercise
- Image: Log in or sign up to view. (n.d.). https://www.facebook.com/106769687599681/posts/bent-over-row-with-bandyoull-get-used-to-the-row-in-its-many-forms-if-youre-work/132206175056032/
- Image: Dominguez, D. (2023, July 24). The Russian Kettlebell Swing: Correcting 5 Common Errors – BoxLife Magazine. BoxLife Magazine. https://boxlifemagazine.com/6390-2/
- Image: Reynolds, C. (2014, December 15). Rotator Cuff Treatment. Pinterest. https://www.pinterest.ca/pin/259379259764800841/
- Image: Falk, M. (2022, June 18). Master These Dumbbell Row Variations to Improve Your Posture and Strengthen Your Back. Shape. https://www.shape.com/fitness/workouts/dumbbell-row-exercise-variations
- Image: Lat Pullover. (n.d.). skimble.com. https://www.skimble.com/exercises/74450-lat-pullover-how-to-do-exercise
- Image: Weiner, Z., Weiner, Z., & L. (2020, June 4). Trainers Say the ‘Superman Exercise’ Is the Best Way to Work Your Obliques and Back. Well+Good. https://www.wellandgood.com/superman-exercises/
- Image: Plank Up-Downs. (n.d.). skimble.com. https://www.skimble.com/exercises/27383-plank-up-downs-how-to-do-exercise
- Image: Luna, D. (2023, June 13). Kettlebell Upright Row: Benefits, Muscles Worked, and More. Inspire US. https://www.inspireusafoundation.org/kettlebell-upright-row/
- Image: How to Do the Barbell Good Morning. (2023, July 25). Experience Life. https://experiencelife.lifetime.life/article/break-it-down-the-barbell-good-morning/
- Image: Cpt, C. F. (2023, August 4). How to Do the Swimming Exercise Move. Get Healthy U | Chris Freytag. https://gethealthyu.com/exercise/swimmers/
- Image: Duffy, M. (2021, July 14). Modified Pull Ups : Ultimate Guide. Health Increasing. https://www.healthincreasing.com/modified-pull-ups/