Biceps Tightness: Cause, Symptoms, Exercise
Introduction:
Biceps Muscle tightness refers to a tight decent feeling in the front of your arm and also you feel discomfort while bending or extending elbow joints. Biceps muscle tightness constantly arises after changing exercise routines, stereotyping of the muscles, or being physically inactive for long ages of time. Else, muscle tightness can be caused by a beginning condition, including myopathy, neuromuscular condition, and neurological diseases, or may see after prolonged paralyzed (stroke) or may after fracture casting (pop) around the joint which is the most common cause seen in the people nowadays.
typically strain biceps muscle tightness can be treated at home by applying heat and deep freeze, stretching, and puffing the muscle. Muscle tightness most generally arises when the overuse of skeletal muscles, which tends to be after a long period of minimum stir (e.g., after extended bed rest, immobilization of the joint in fracture case) or after engaging in new exercises. This conduct can beget temporary damage to the muscle cells, leading to stiffness. Muscle stiffness from overuse of the muscles occurs almost constantly among people who don’t exercise frequently.
Muscle stiffness refers to a sensation of muscle tightness which is frequently difficult to move after.
There are three types of muscle first is skeletal muscle, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle stiffness primarily affects skeletal muscle, which is a freely- controlled type of muscle that enables humans to move and perform daily activity.
In general, these conduct are attainable after a signal from the nervous system stimulates compression of the skeletal muscle, performing in movement. However, the muscles may remain contracted and affect stiffness, If any problems intrude with the communication between the nervous system and the muscle cells or muscle miserliness. Muscle tightness is the incapability of muscles or muscle groups to move through a full range of motion for a specified body part. The muscle may suffer a modification in towel quality and affect a semi-contracted state during which the muscle is unfit to relax or outstretch.
Common causes of biceps muscle miserliness or strained cubital in the middle of the bicep include muscle strain, bruises, and DOMS after exercise. other than that any Mild injuries generally to the elbow joint or cubital joint or mainly seen in the supracondylar fracture of the humerus bone or also seen in any open or close fracture of the elbow joint. biceps muscle miserliness is also seen in the case with a neurological condition like palsy and cerebral paralysis ( brain complaint) or rather than that seen in the patient with neuropathy or myopathy.
Anatomy Of The Biceps muscle
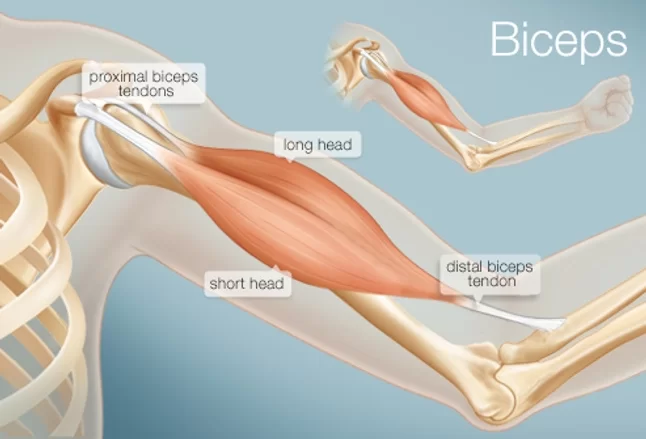
Origin
- The biceps brachii consists of two heads and they both originate from the scapula.
- Short Head: Apex of the coracoid process of the scapula.
- Long Head: Supra-glenoid tubercle of the scapula.
Insertion
- Radial tuberosity and fascia of forearm via bicipital aponeurosis.
- Innervation of bicep brachii is by the musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6, C7)
Blood supply
- Blood supplied by them muscular branches of brachial artery.
Function
- Primary functions of the biceps brachii is flexion of the elbow and supination of the forearm. In fact, it’s the high transport of forearm supination. Since it crosses the gleno-humeral joint, it also serves to help shoulder elevation.
- In colorful angle of the elbow, the biceps brachii conduct else to movements to the upper branch.
- Extended elbow Biceps is a pure elbow flexor until it reaches 90 degree flexion
- At 90 degrees flexion and forearm supinated Most effective to produce elbow flexion
- At 90 degrees flexion and forearm pronated Biceps becomes the primary forearm supinator
Causes of the biceps muscle tightness
- Biceps muscle tightness most commonly occurs after the overuse of the muscles, which tends to tighten after a long period of minimum stir (e.g., prolonged bed rest) or after engaging in new exercises. This conduct can beget temporary damage to the muscle cells, leading to stiffness. Muscle tightness from overuse of the muscles occurs most constantly among people who don’t exercise regularly.
- Electrolyte imbalances may also invoke biceps muscle pinching, especially after exercise. Electrolytes (e.g., sodium, potassium, etc.) are important minerals in the body that play a part in conducting nerve impulses and constricting muscles, among different functions. When a person exercises, electrolytes are lost with water (e.g., sweat), making it more delicate for the nervous system to grease muscle movement.
- Muscle stiffness can also develop due to an underpinning myopathy, or a disease of the muscles, which can affect from metabolic, inflammatory, endocrine, spreading, or medicine-related causes. Metabolic illnesses, like as mitochondrial disorder and Mcardle’s disease, disrupt the balance of nutrients and energy in the body.
- Inflammatory conditions, such as polymyalgia rheumatica, are characterized by increased inflammation in the body due to an overreaction by the body’s immune system. Endocrine disorders, like hypothyroidism and acromegaly, are caused by hormone imbalances in the body.
- disturbances in metabolic processes, the immune system, and hormone situations can all produce muscle stiffness. Infections, similar as the flu, and meningitis, are also frequently associated with muscle tightness. Eventually, muscle tightness can do as a side effect of certain specifics, similar as statins, which are specified to treat high cholesterol, or anesthetics, which are generally given during surgery.
- Since muscle movement depends on communication between the nervous system and the muscles, muscle stiffness can also arise from issues with the nerves and muscles ( i.e., neuromuscular diseases) or problems affecting only the nerves ( i.e., neurologic diseases).
- Biceps Muscle tightness may seen in patient with neuromuscular disease in which motor neurons can cause involuntary muscle spasms. Other diseases, similar as Parkinson’s disease, Myasthenia gravis, and Lambert Eaton pattern, are characterized by precipitously worsening muscle stiffness. Individuals with a history of brain stroke or paralysis may also witness muscle stiffness or muscle tightness.
Signs and symptoms of biceps muscle tightness :
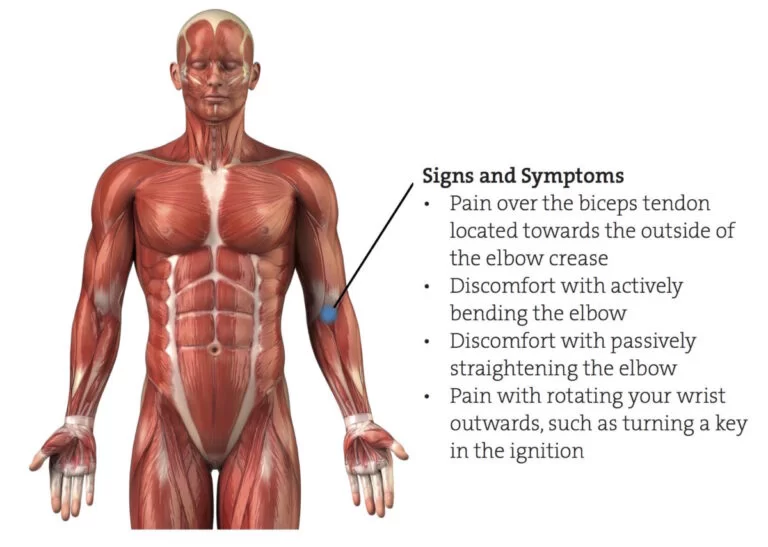
- Pain or tenderness in the front of the shoulder, which worsens with overhead lifting or exertion.
- Pain or achiness that moves down the upper arm bone.
- An occasional snapping sound or sensation in the shoulder.
- Discomfort while moving arm or bending elbow.
- Muscle pinching is generally characterized by soreness and difficulty moving arm or extending front of arm, sometimes accompanied by cramps, pain, or weakness.
- In cases of neuromuscular affection, muscle stiffness may also be accompanied by angle of the lower spinal column ( i.e., lumbar hyperlordosis) and nervous system problems
- Muscle spasm also present after fracture of any external injury around your arm so arm may not suitable to extend properly or may you feel pain while doing stretch.
- Most oftentimes, biceps muscle closeness felt a couple of days after engaging in new or more challenging exercise. may you feel tight muscle around your front of arm.
Stretching Guidelines: How to Stretch Biceps muscle?
- The Right Way to Stretch is slow and relaxed.
- When stretching, hold each stretch for 10 to 30 seconds.
- Avoid bouncing or Stretching to the point of pain. This can actually beget you to pull the muscle you’re trying to Stretch.
- Breathe deeply to consolidate the Stretch as you exhale.
- Stretch two or three further times with each Stretch.
- Try to Stretch a little farther with each Stretch. Remember to do it only to the point of mild pressure.
- For any Stretch that involves bending your knees, make certain that your knee does not go beyond your toe. Else, there is too important stress on the knee.
When to Stretch your Biceps muscle?
- To maintain your Inflexibility, Stretch at least three times a week.
- You can Stretch anytime you feel like it (e.g. at your office, staying for a machine) and at colorful times of the day when you can.
- Each Stretching Session should last for about 10 to 20 twinkles.
- To ameliorate your performance and help injury, Stretch before doing some drill routines or playing a spor
- For all kinds of exercises, whether calisthenics or weight training, do the Stretches Before and After Exercises.
- Avoid emphatic Stretching for one to two hours after eating.
- During hot or sticky days, do your Emphatic stretching early morning or evening, when it’s cooler or lower sticky.
- Do not Stretch a muscle that you’ve lately injured, unless your croaker gives you a go signal. Still, try to use supports like wrist and knee wraps.
How Long to Stretch Biceps muscles?
- If you’re involved in a stretching program you’re presumably wondering how long tostretch. Factors that impact the capability to stretch the connective apkins in a muscle are as follows
- muscle fatigue
- the presence of scar towel
- muscle temperature
- exertion previous to the stretch
- collagen/ elastic content (varies with age)
- hydration/ dehumidification
- medical conditions (diabetes, connective towel diseases, smoking)
- Still then our focus will be on gentle static stretches where the stretches are to be done for a period of 20 to 30 secs and reiterations needed are 5 to 7 in 2 to 3 sets.
Adjuncts to Stretching Interventions
- Interventions that promote general or original relaxation can round a stretching program.
- Therapists managing cases with impairments, including habitual pain, muscle guarding, or imbalances, and confined mobility may find it useful to integrate relaxation exercises into a case’s plan of care.
- Superficial or deep heat, massage, biofeedback, and common traction also are useful adjuncts to stretching procedures.
Relaxation Training
- Relaxation training, using styles of general relaxation ( total body relaxation), have been used to help cases learn to relieve or reduce pain, muscle pressure, anxiety or stress, and associated physical impairments including pressure headaches, high blood pressure, and respiratory torture.
Common Rudiments of Relaxation Training :
- Relaxation training involves a reduction in muscle pressure in the entire body or the region that’s painful or confined by conscious trouble and study.
- Training is done in a quiet terrain with low lighting and soothing music or an audile cue on which the case may concentrate. The case performs deep breathing exercises or visualizes a peaceful scene.
- When giving instructions the therapist uses a soft tone of voice.
Heating therapy before stretching
- Warming up previous to stretching is a common practice in recuperation and fitness programs.
- As intramuscular temperature increases the extensibility of contractile and non-contractile soft apkins likewise increases.
- Also as the temperature of muscle increases, the quantum of force needed and the time the stretch force must be applied diminishments.
Indication of the stretching :
- Rom is limited because soft tissue have lost their extensibility as the result of adhesion, contractures and scar tissue formation, causing function limitation or disabilities.
- There is muscle weakness and shortening of opposing tissue.
- may be used prior to and after vigrous exercise potentiality to minimize post exercise muscle soreness.
When not to stretch your biceps muscles
- A bony block limits joint motion
- There are recent fracture, and bony union is incomplete. There is an acute inflammatory or infectious process like swelling.
- There is sharp acute pain with joint movement or muscle elongation.
- A hematoma or other indication of tissue trauma is observed.
Stretching exercise for biceps muscle tightness.
Seated bicep stretch

- Sit with fraudulent knees and your bases flat on the bottom in front of your hips.
- Place your hands on the bottom behind you with your fritters facing down from your body.
- Unevenly distribute your weight between your bases, buttocks, and arms.
- Sluggishly scoot your buttocks forward, toward your bases, without moving your hands.
- Hold this position for over 10 seconds.
- Return to the starting position and relax for a many moments.
Wall biceps stretch
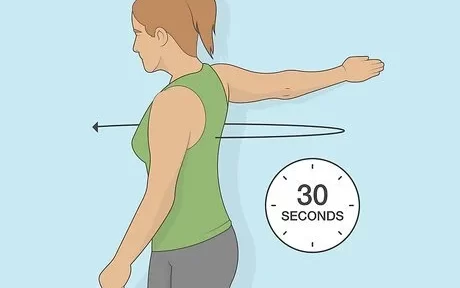
- To do this stretch
- Press your left win against a wall or sturdy object.
- Sluggishly turn your body down from the wall.
- Feel the stretch in your casket, shoulder, and arm.
- Hold this position for over 10 to 20 seconds.
- Reprise on the contrary side.
Standing bicep stretch :
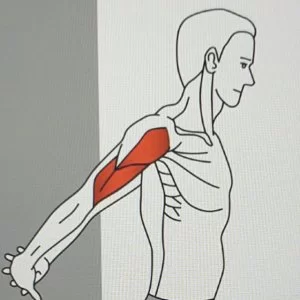
- Interlace your hands at the base of your spine.
- Unbend your arms and turn your palm to face down.
- Raise your arms up as high as you can.
- Hold this position for over 2 to 3 minutes.
- Reprise 1 to 2 times.
Doorway bicep stretch:
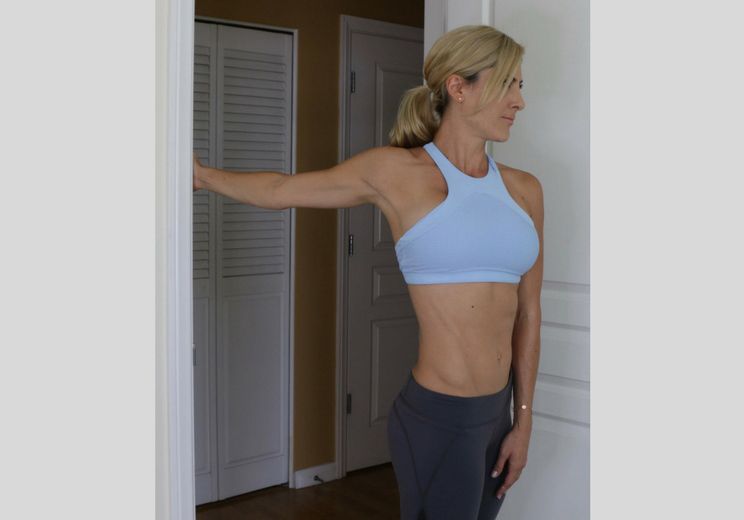

- This doorway stretch is a great way to open up your casket while also stretching your biceps.
- To do this stretch
- Stand in a doorway with your left hand grasping the doorway at midriff position.
- Step forward with your left bottom, bend your knee, and yield your weight forward.
- Feel the stretch in your arm and shoulder while maintaining a slight bend in your elbow.
- Hold this position for over 10 to 20 seconds.
- Reprise on the contrary side
Biceps Stretch
- Shoulder Extension with club
- Hold one end of club in hand of involved arm, other end with other hand.
- Keep elbow of involved arm straight and use other arm to push involved arm backward as shown.
- Hold and repeat.
- Hold end position for 10-20 second Reprise for 4 to 5 times
Biceps stretch sitting on a chair
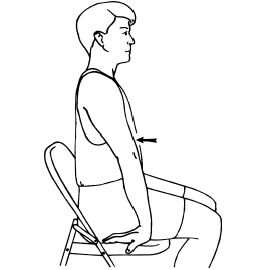
- Begin with sitting on a president with triumphs flat and fritters pointing backward.
- Sluggishly spare backwards until a stretch is felt in the front of your arm.
- Hold the stretch for 10 to 20 seconds.
- Reprise for 10 to 12 times.
Bilateral biceps stretch
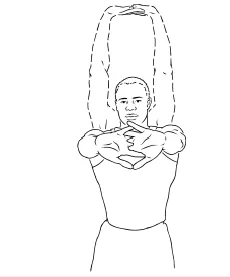
- Begin with standing position arms straight and fritters amalgamated.
- Raise your arms above.
- Hold the stretch for 10 to 20 seconds.
- Reprise 10 to 20 times.
Biceps stretch with tubing
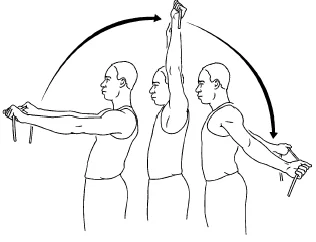
- Biceps stretch with use of tube.
- Begin with standing position arms forward, triumphs down. Hold a tubing in your hands as shown.
- Sweep up and above also before back with elbow straight.
- Hold the stretch for 10 to 20 seconds.
- Reprise for 8 to 12 times.
Biceps stretch in lying ( Useful in elbow recovery) :
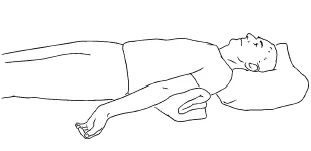
- Taradiddle down on your reverse. Keep a folded kerchief slightly above the elbow as shown with the arms slightly down from the body, win facing up.
- Let your hands fall down with the pull of graveness a stretch is felt in the front of your arm
- Hold the stretch for 10 to 20 seconds.
- Reprise for 10 to 12 times.
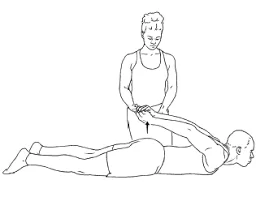
Supported biceps stretch lying :
- lie down on your stomach with both hands behind the reverse with fingers interlaced.
- Ask your mate to raise hands as shown until a stretch is felt in the front of your arm.
- Hold the stretch for 10 to 20 seconds.
- Reprise for 8 to 12 times.




One Comment