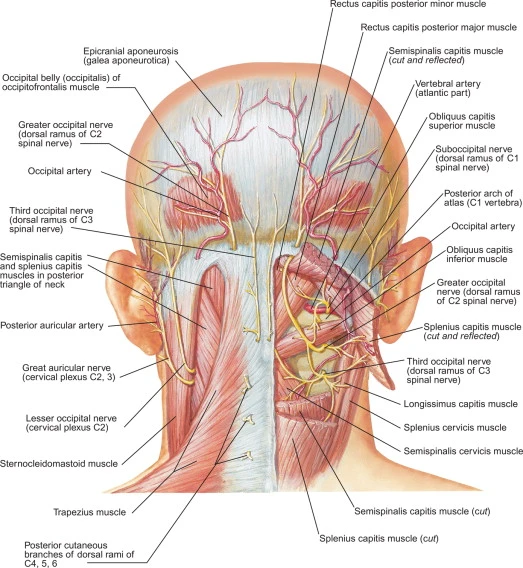
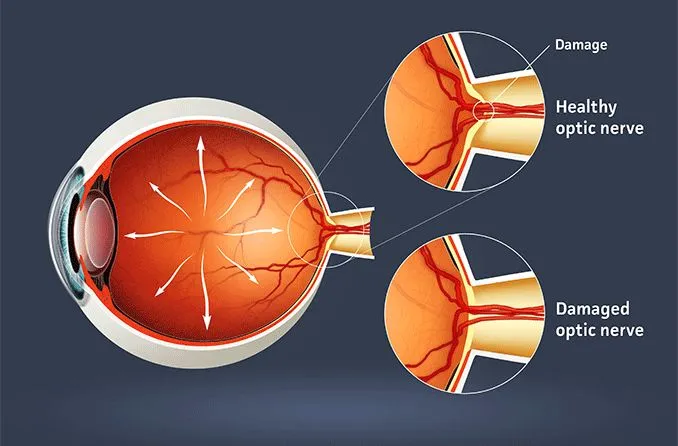
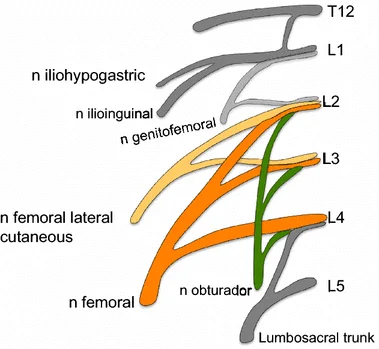
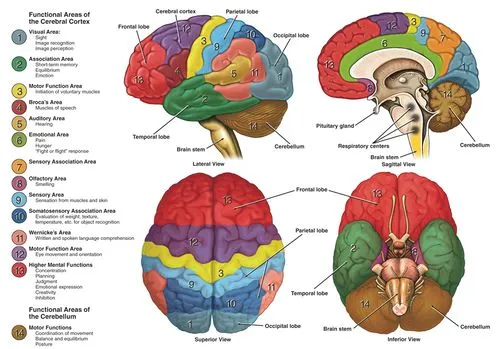
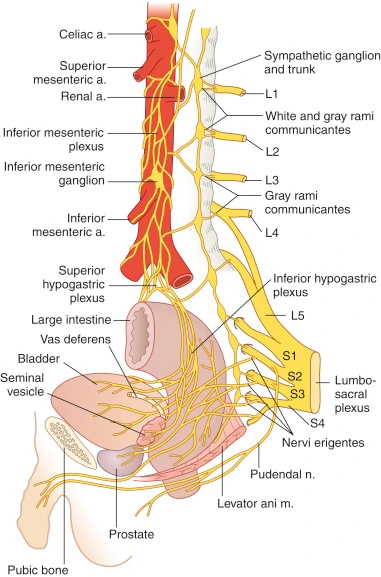
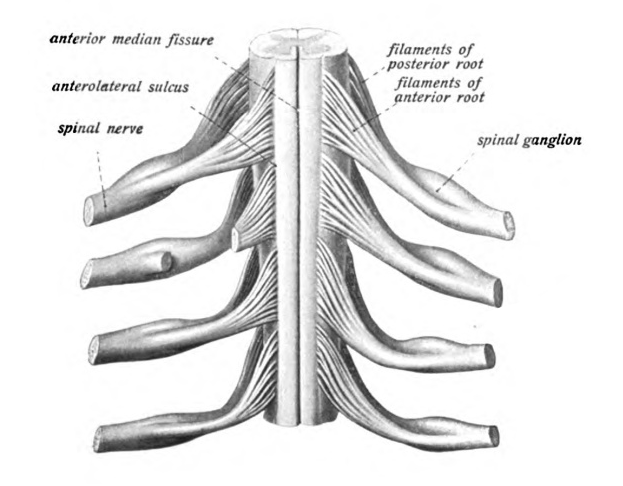
Brachial Plexus
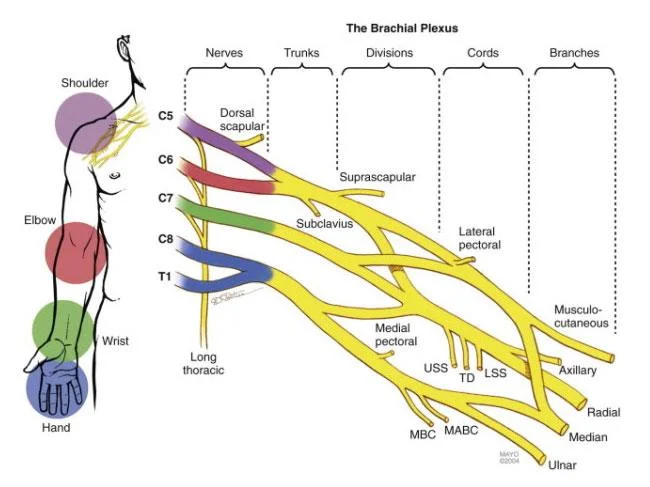
What is the Brachial Plexus? The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that originates from the spinal cord in the neck region and supplies the upper limb, including the shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand. It comes from nerve roots in the spinal cord’s cervical and upper trunk regions (C5-T1). Anatomy of Brachial Plexus: The…