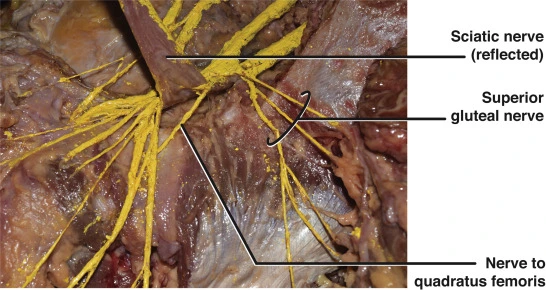
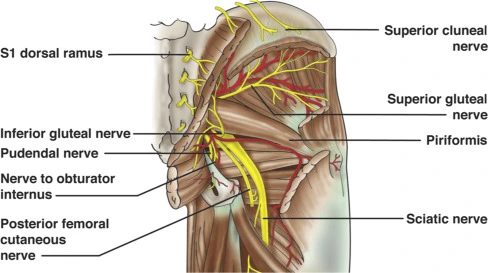
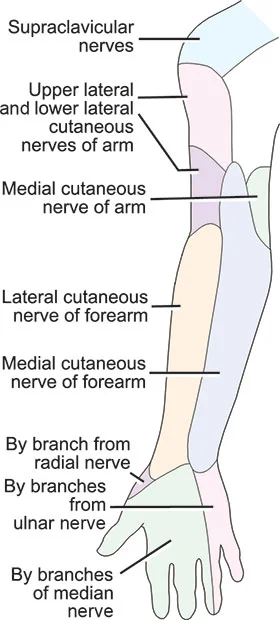
Nerve to Quadratus femoris and Inferior gemellus
Introduction The nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus is formed from the anterior or ventral divisions of the L4, L5, and S1 nerve roots of the sacral plexus. The nerve gives muscular branches to the quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles as well as giving an articular branch to the hip joint. Gross anatomy…