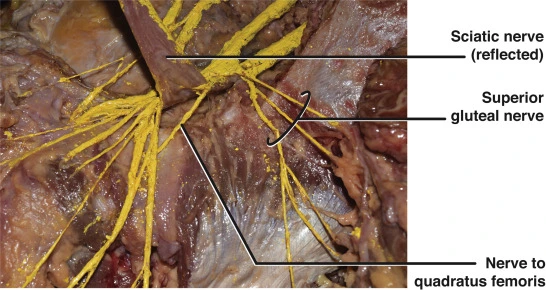
Nerve to Quadratus femoris and Inferior gemellus
Introduction
The nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus is formed from the anterior or ventral divisions of the L4, L5, and S1 nerve roots of the sacral plexus. The nerve gives muscular branches to the quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles as well as giving an articular branch to the hip joint.
Gross anatomy
Origin
The nerve to quadratus femoris gets arises from the anterior divisions of the sacral plexus. It is formed by the L4 to S1 nerve roots and leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle and deep to the sciatic nerve. The nerve to quadratus femoris, not like the other nerves in the gluteal regions, it lies anterior to the surface of the deep muscles of the gluteal surface.
Course
It descends along with the ischium and runs posterior to the hip joint, to which it forwards an articular sensory branch. In this position the nerve present deep to the tendon of the obturator internus muscle and Gemelli which thus split it from the overlaying sciatic nerve.
Branches
The nerve continues downwards to penetrate the deep (anterior) aspect of the quadratus femoris muscle. The nerve also innervates the inferior gemellus muscle.
Relations
The nerve to the quadratus femoris is divided from the sciatic nerve by the obturator internus and the Gemelli muscles.
Variant anatomy
It has been noted in cadaveric studies that the nerve to quadratus femoris and obturator internus frequently get arise from a common root and the link between these two nerves has been regularly observed. The inferior gemellus muscle has been recorded to normally receive an additional supply by branches of the nerve to the obturator internus.
FAQ
What nerve goes to the quadratus femoris?
The quadratus femoris muscle is composed of an adductor and external rotator of the hip. It is supplied by a small branch of the sacral plexus. particularly, it derives its innervation from the L4, L5, and S1 spinal nerves.
Which nerve Innervates the inferior gemellus?
nerve to quadratus femoris
The inferior gemellus receives innervation from the nerve to quadratus femoris which is a branch of the sacral plexus. It gets arises from L4/5 and S1 spinal nerves.
Where does the nerve to quadratus femoris come from?
The nerve to quadratus femoris is a branch of the sacral plexus which get arising from the ventral rami L4, L5, and S1. It gives supply to the quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles, which help to laterally rotate and abduct the hip.
What nerve supplies the quadratus muscles?
Quadratus lumborum is supplied by the subcostal nerve (T12) and anterior rami of spinal nerves L1-L4.
What happens if the inferior gluteal nerve is get damaged?
Inferior gluteal nerve injury results in weakness and atrophy of the gluteus maximus muscle with impaired leg extension. A deep aching pain may be described, especially in association with the tumors compressing the nerve.
What is the primary function of the quadratus femoris muscle?
The main action of the quadratus femoris muscle is it externally (lateral) rotate the thigh.
What causes pain in the quadratus femoris?
The quadratus femoris muscle is the hip external rotator and assists with adduction. any Injury to the quadratus femoris has been described as a cause of groin pain and pain in the gluteal region that can radiate distally from the posterior thigh, certainly by irritation of the sciatic nerve either from hematoma or edema
Where do you feel femoral nerve pain?
Pain that radiates from the back and hips into the legs (radicular pain) is a common sign of femoral nerve damage. other symptoms comprise Leg, ankle, or foot numbness, weakness, tingling, paralysis, and pain. Lower back pain, hip pain, and groin pain.
What weak muscles cause tight QL?
Excessive sitting and lack of exercise are by far the number one reason that the QL muscles get tight. For people who do not sit all day and still experience QL pain, weak glutes and abdominal muscles are often what need to be improved.
What is the function of Quadratus?
The quadratus lumborum muscle is act as the extensor of the lumbar spine, and a stabilizer of the lumbar region, capable of tilting laterally and capable of acting as an inspiratory accessory muscle.
What movements is the QL responsible for?
The quadratus lumborum muscles, or QLs for short, are found on each of two sides of the lumbar spine (lower back) and are important core muscles that help to stabilize the lower back. They fundamentally connect the lower spine to the pelvis and support with movements like side bending and raising the hip.
What nerves cause leg weakness?
injury or Compression of the cauda equina (which is a group of spinal nerves that descend from the spinal cord in the lower back) may cause severe pain, numbness, and weakness in both legs.



2 Comments