Basal Ganglia Stroke
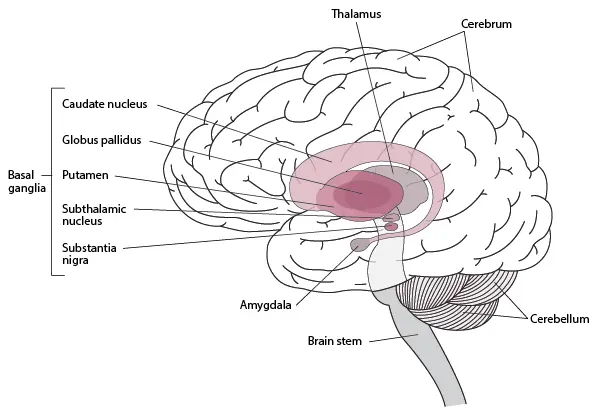
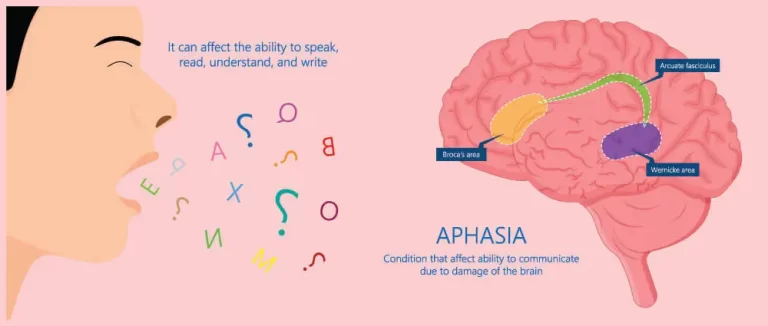
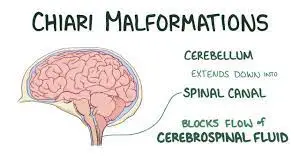
Introduction An uncommon form of stroke known as a basal ganglia stroke can have distinct long-term implications. The lack of spontaneous speech and emotional blunting are only a few of these side effects. Although these severe consequences may follow a stroke in the basal ganglia, recovery is possible with focused therapy. The possible long-term repercussions…