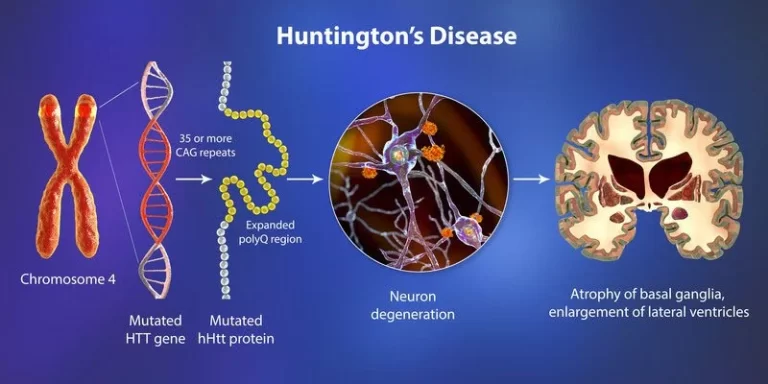
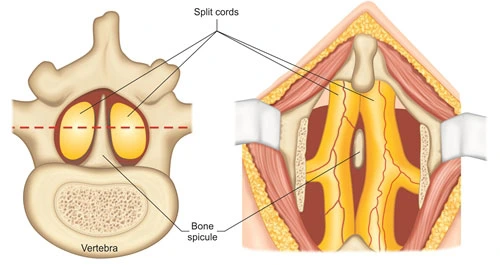
Huntington’s disease (HD)
Overview Huntington’s disease (HD) is a rare genetic disorder that causes the progressive breakdown of nerve cells in the brain. It is also known as Huntington’s chorea because one of the most characteristic symptoms of the disease is involuntary movements, or chorea. HD is caused by a mutation in the huntingtin (HTT) gene, which provides…