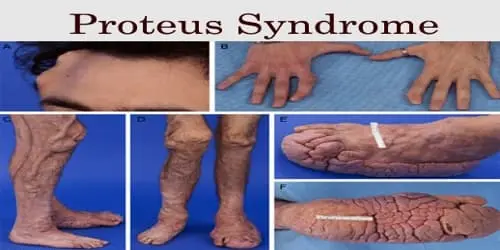
Proteus syndrome
What is Proteus syndrome? Proteus syndrome is a rare genetic disease that causes extreme growth of your skin, bones, organs, and/or tissues. The condition causes parts of your body to expand out of proportion with the rest of it. The overgrowth is generally asymmetrical, suggesting it involves the right and left sides of your body…