Coccydynia and Physiotherapy management
What is a Coccydynia?
Coccydynia is a medical term used to describe pain in the coccyx or tailbone, which is the small, triangular bone at the bottom of the spine. Coccydynia can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, injury, or repetitive strain to the coccyx, as well as infections or tumors in the area. Symptoms of coccydynia may include pain, tenderness, or discomfort in the tailbone area, especially when sitting or during activities that put pressure on the area. Treatment options for coccydynia may include pain medication, physical therapy, or in severe cases, surgery to remove the coccyx.
- Coccydynia is described as a disabling pain in and around the coccyx, The pain typically is triggered in a seat position and may intensify when the patient rises to a standing position.
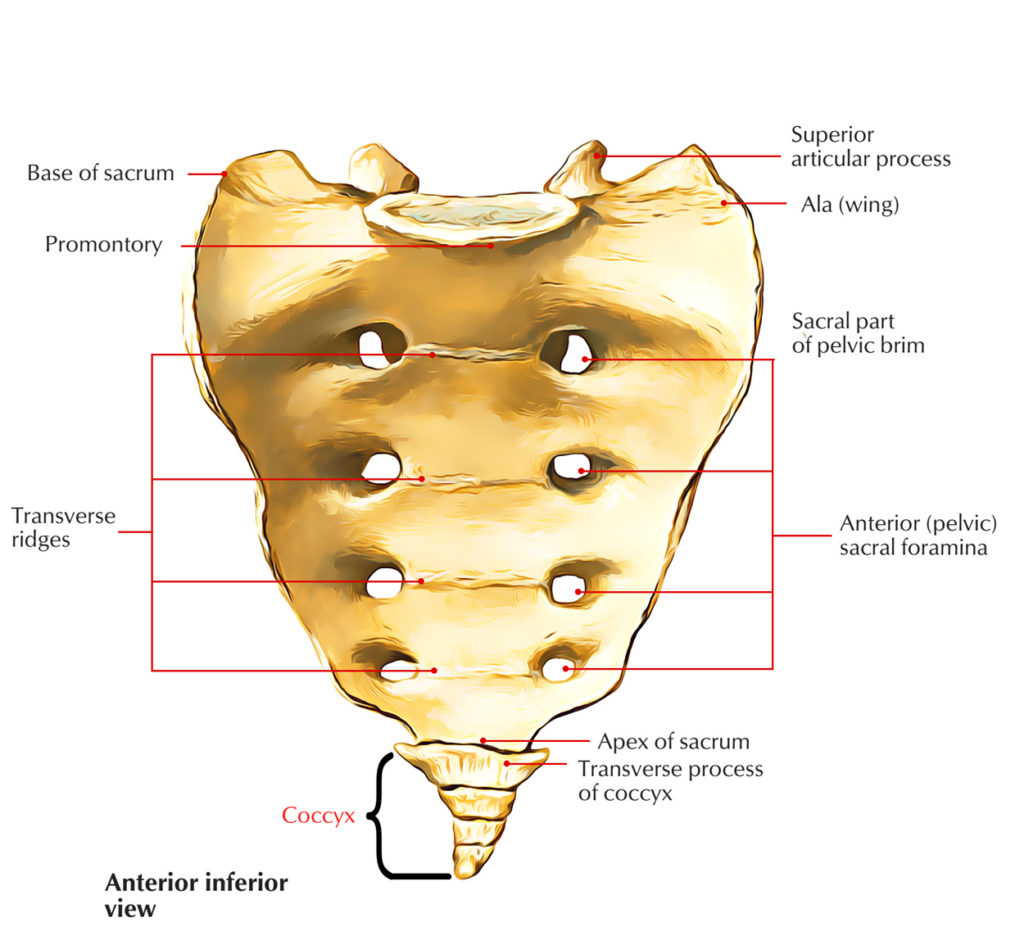
Anatomy related to Coccydynia
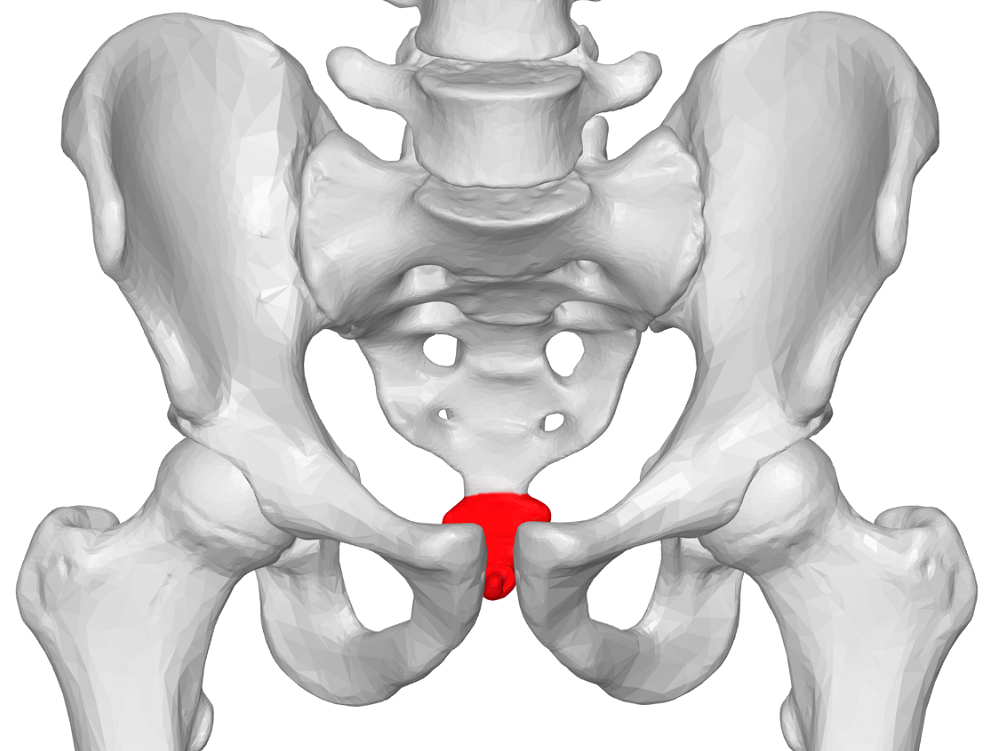
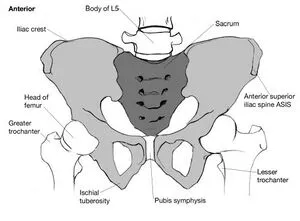
- The coccyx is the most distal aspect of the vertebral column, and consists of three to five rudimentary vertebral units that are typically fused.
- The ventral part of the coccyx is concave, and the dorsal aspect is convex and features coccygeal articular processes.
- The coccyx articulates with the sacral cornua of the inferior sacral apex at S5. The anterior aspect of the coccyx serves as the attachment site of ligaments and muscles important for many functions of the pelvic floor. The levator ani muscle includes the coccygeus, pubococcygeus, and iliococcygeus.
- The coccyx supports the position of the anus. Attached to the posterior side of the coccyx is gluteus maximus. Muscle weakness disturbed tonus or damage to muscles or ligaments can cause abnormal positions of the coccyx.
Causes of Coccydynia
- Direct trauma due to fall on the tail bone
- Fracture
- Dislocation and malalignment
- During delivery of baby pressure exerted on the coccyx
- Prolong sitting on a hard surface
- Professionals on desktop job
- Obesity
Symptoms of Coccydynia
- pain over the bottom part of the spine
- pain aggravated on sitting
- pain while passing stool
- swelling and bruise in case of trauma or injury
- ain in sitting position
- Pain with the transition from sitting to standing
- Pain with standing, walking, forward flexion
- Pain with defecation, coughing
- Increased pain during menstruation
- Inflammation
- Poor sitting posture
- Frequent shifts in sitting position, sitting down carefully
- Luxation, hypermobility, hypomobility of the coccyx
- Difficulty sitting, impacting the ability to perform work and daily activities
- Difficulty
- pain with defecation
Diagnosis of Coccydynia
- Based on patient’s history and physical examination
- examination of the entire spine
- tenderness over tailbone
- x-ray in case of trauma
- MRI to rule out other conditions
Physiotherapy management of Coccydynia
PAIN RELIEVING MODALITY
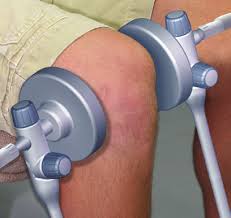
- SWD: short wave diathermy is a deep heating modality that uses heat to provide pain relief, it improves the blood supply to targeted muscle, removal of waste products
PELVIC STABILISATION EXERCISE
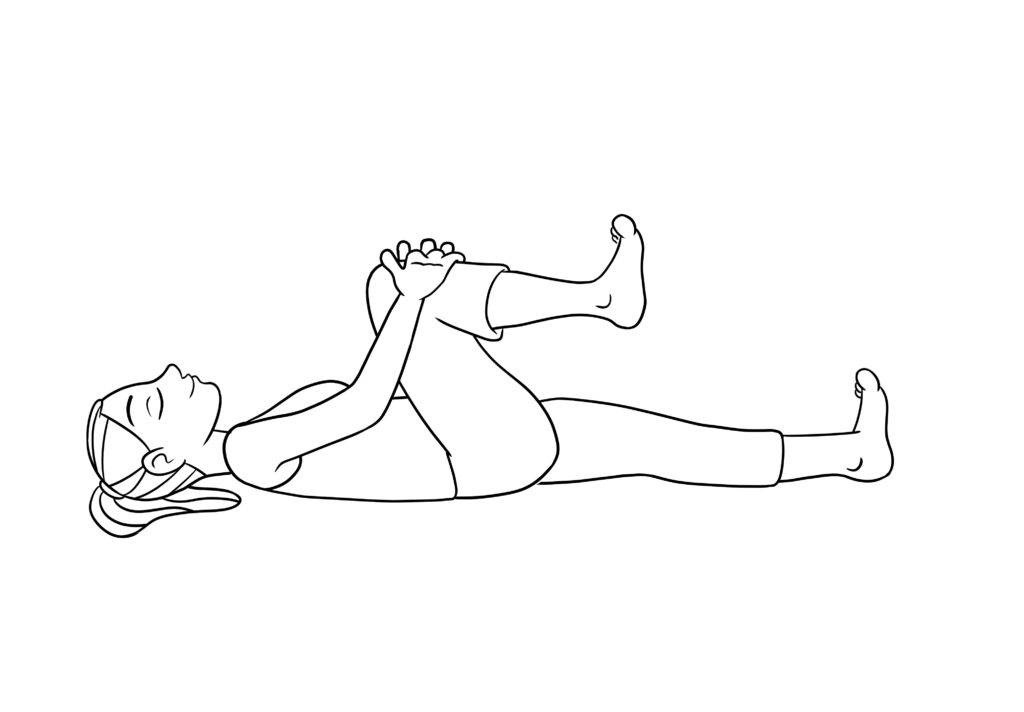
- Laying on your back, gently pull your knees to your chest, holding for a second, then extending your arms back out straight.
- With your feet on the ground, bend your knees, and gently move them from side to side in a windscreen wiper motion. This exercise for lower back pain works by gently rotating your lumbar spine.

- Laying on your stomach, gently press up and extend your lower back. Do not hold this, but repeat the movement 10 times, for 3 sets
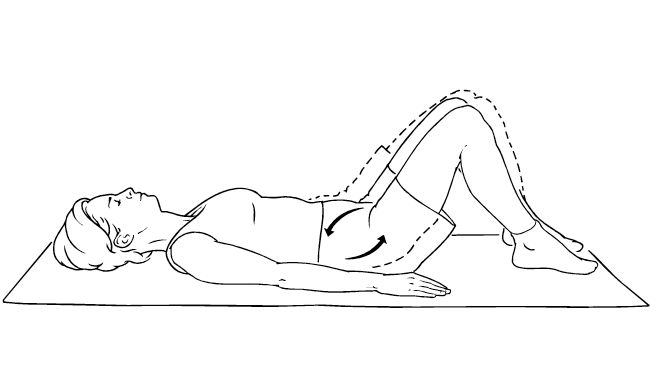
- Laying on your back, arch your lower back, then flatten it into the ground.

HAMSTRING STRETCH
- The hamstring stretch can help stabilize your lumbar spine. Lie on your back with your knees bent, keeping your spine in a neutral position.
- Raise your left leg into the air and straighten it by lifting your heel toward the ceiling. Hold your leg behind the upper thigh using both hands and gently pull the leg closer to your body. Hold the stretch for up to 30 seconds, then release and repeat on the opposite side.


6 Comments