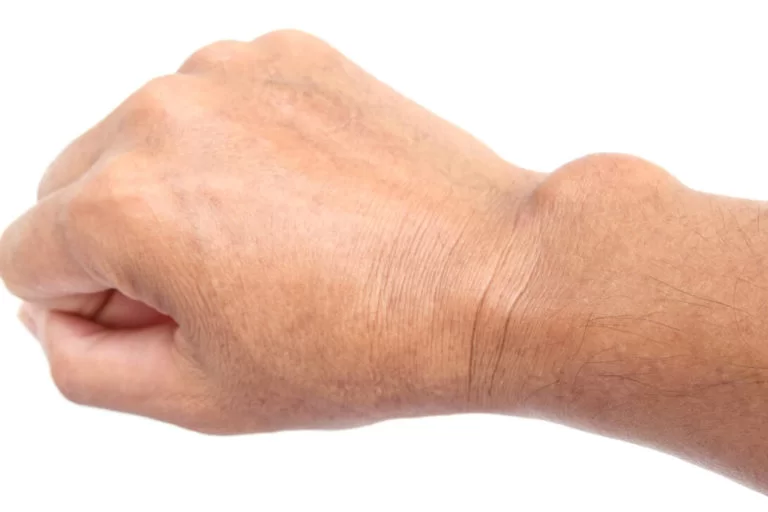
Dinner Fork Deformity
What is a Dinner Fork Deformity?

⇒ Dinner fork deformity is due to colle’s fracture in which the fracture of the distal radius in forearm with dorsal(posterior) and radial displacmentof the wristand hand.
⇒ Dinner fork also called “bayonet” deformity due to the shape of the forearm.
Causes of Dinner Fork Deformity
⇒ Wrist fracture Mainly Colle’s Fracture
⇒ Over stretched hand (common in child)
⇒ People who are suffering from osteoporosis
⇒ Traumatic accident
⇒ Sports man, skiers, skaters and bikers.
⇒ Calcium deficincy is not the direct cause but a contributing factor for the deformity.
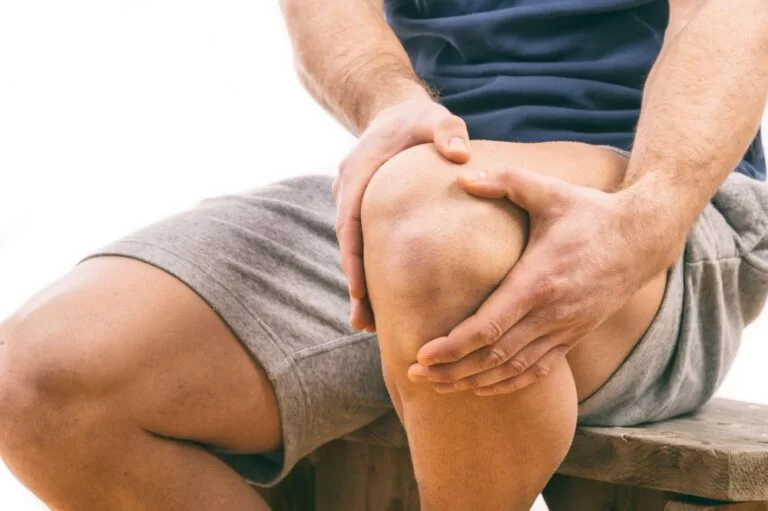
Symptoms of Dinner Fork Deformity
⇒ The patient finds difficulty in moving his wrist.
⇒ The pain increases when wrist is flexed.
⇒ There is swelling of the wrist area.
⇒ The area is tender to touch.
⇒ Bruising is common as a result of severe impact.
⇒ There is numbness in hand. Fingers may become pale.
⇒ Patient finds difficulty in gripping anything.
Diagnosis

⇒ Dorsal tilt
⇒ Radial shortening
⇒ Loss of ulnar inclination
⇒ Radial angulation of the wrist
⇒ Dorsal displacement of the distal fragment
Treatment of Dinner Fork Deformity
⇒ Medical treatment – upper limb Elevation, Compression, Medication.
⇒ Surgical treatment – Management depends upon severity of fracture.
An undisplaced fracture may be treated with a cast alone
A fracture with mild angulation and displacement may require closed reduction.
Significant angulation and deformity may require an open reduction and internal fixation or external fixation.
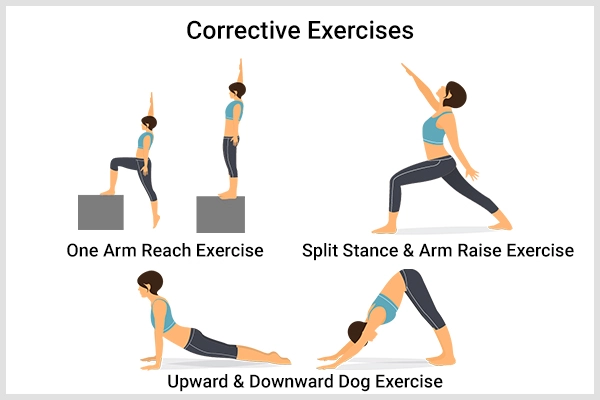
Physiotherapy Treatment in Dinner Fork Deformity


⇒ After fracture in cast –
Check the plaster cast any loss or too much tight
Sling shoud be check it will be with perect neck padding
Depend odema shoud be treat with elevation and massage from fingertip to palm.
Active Rang of motion exercise in non-affected side digit, thumb,elbow and shoulder joint to prevent stiffness.
In affected side only supination and pronation not allowed otherwise all other movement encourage.

⇒ In second week –
Recasting adviced if cast is too loose or craked.
Continue ROM exercise to the shoulder, elbow,digit and thumb.
If external fixation given then- check for any infection and active supination and pronation along with those mention above.



⇒ After second week –
› Wrist Mobilization – To reduced pain, oedema and discomfort – Hydrotherapy and Thermotherapy given.
Active wrist mobilization is initiated. Patient is made to sit on a chair and to keep his forearm in mid prone over a table. With the affected forearm fixed by the other hand patient is instructed too actively flex and extend the wrist with gravity eliminated.

› Passive wrist mobilization: This is begun after about 7- 10 days of the above treatment. He patient sits with the affected hand resting on the edge of the table. Fixing it with the normal hand the affected arm is lowered below the table (palmer flexion) and raised above the table (dorsiflexion) periodically.
Alternatively the Indian Salutation method of namaskar (for dorsiflexion) and reverse salutation (for palmer flexion) achieves the same results
Pronation and Supination.
Exercises through activity like turning the keys, doorknobs, scooping beans and putting them in the box.
To improve the grip and writing skill ulnar deviation exercises are encouraged.



2 Comments