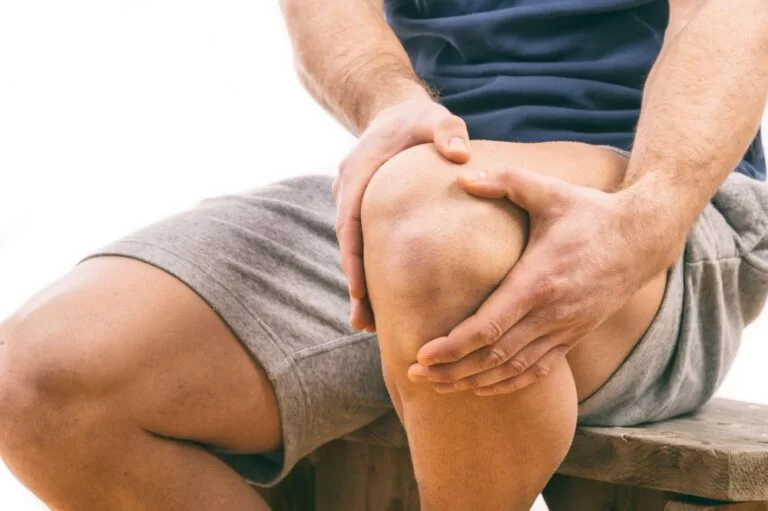
Pain when Knee is Bent
Knees bend many times throughout the day. Movement is essential for daily activities, such as climbing the stairs and sitting in a chair. You also bend the knees during exercises like squats and lunges. The wear and tear of everyday life could take a toll on a knee. there are many ligaments, tendons, muscles, and bones in an area.
If there is a problem with one of these structures, you may have knee pain when bending the leg. A few leads to knee pain are minor and could be treated with home remedies. Others need medical attention. Here, we will discuss the potential leads of knee pain while bending, along with signs you should see the doctor. Knee pain could have causes that are not due to underlying disease. Examples include heavy physical activity, lack of use, injuries such as sprains or/and strains, sitting in a constrained area, or sitting on knees for a prolonged period.
Knee pain when bending is a common problem. Forces up to seven times body weight can go through a knee as it bends, so it comes as no surprise that it is such a widespread problem. Bending knee pain may begin suddenly after an injury or gradually come on over time depending on the cause. There are several different causes of knee pain when bending, but they typically all result from a problem with one (or more) of the structures in or/and around the knee, affecting how it moves. This changes how the forces travel through the various parts of the knee and can result in too much pressure going through certain parts, which leads to knee pain bending. Here we will look at the different types of bending knee pain, the most common causes of knee pain when bending, treatment options, and what is going on in the knee as it bends.
How Does The Knee Bend?
A knee is a hinge joint, which means its main movement is bending and straightening (aka flexion and extension). As the knee moves, several things are occurring:
- The Muscles: They work in pairs with one relaxing and another contracting (tightening) to allow the movement e.g. to bend the knee the hamstrings contract and the quads relax
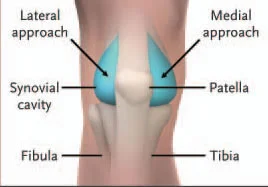
- The Bones: A femur (thigh) and A tibia (shin) have to roll, spin and glide to move smoothly. The patella (kneecap) shifts, tilts and rotates as it glides up and down via a groove on the thigh bone – the position and movement of the patella are controlled by the surrounding muscle.
- The Cartilage: The special shock-absorbing cartilage that lines the knee known as the meniscus moves and changes shape slightly to stop it from getting trapped.
- The Ligaments: These assist control movement and keep stability by preventing excessive movement of the bones. Those are two pairs of ligaments, the cruciate ligament in the middle of the joint, and the collateral ligament on either side.
These structures all require working together properly to allow for smooth, pain-free knee bending and straightening. Problems in any of these areas could lead to knee pain when bending. For eg, if there is muscle weakness or ligament instability, the bones might move slightly out of position leading to them catching or grinding on other structures in the knee.
Why does the knee hurt when bending it?
There are many causes of knee pain while bending. Possible conditions include:
- patellofemoral syndrome, which leads to a dull ache in front of your knee
- patellar tendonitis, which causes burning and pain in or at the base of the kneecap
- iliotibial (IT) band syndrome, which can lead to burning pain outside of the knee that spreads to your hip or thigh
- hamstring tendonitis, which leads to pain behind the knee and thigh
- quadriceps tendonitis, which causes pain above or in front of the knee
- knee bursitis, which may lead to swelling, warmth, and pain over or below the knee
- osteoarthritis, which leads to diffuse knee pain, swelling, and stiffness in the morning
- injury or trauma to a knee joint or ligaments, which may cause sharp pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee
- Baker’s cyst, which might lead to tightness and swelling behind your knee
The location of the knee pain can help you pinpoint the cause. Take note if you have:
Pain behind the knee when bending
If it hurts behind the knee while bending, it’s likely due to:
- hamstring tendonitis
- Baker’s cyst
- knee injury
Very sharp pain in the knee when bending
Conditions that might cause sharp pain while bending include:
- torn ligament or meniscus
- knee or patellar fracture
- osteoarthritis
- patellar tendonitis
Pain above the kneecap when bending
If you have pain above the knee when bending, you may have:
- quadriceps tendonitis
- osteoarthritis
- knee bursitis
Pain in the front of the kneecap when bending
Potential causes of pain in front of or over the kneecap include:
- patellofemoral pain syndrome
- patellar tendonitis
- quadriceps tendonitis
- knee bursitis
- patellar fracture
Knee pain when bending or squatting
Wear and tear of your knee over time can cause pain when bending the knee due to damage to the bones, ligaments, muscles, and/or tendons in and around the knee joint. For roughly every 500g of body weight, about 3kg of pressure is applied to the knees when they are bearing weight eg when bending, running, squatting, or walking.
Why Does Bending Cause Knee Pain?
Knee pain when bending could be split into two types:
Weight-Bearing: when there is weight going through the knee bend it such as when squatting down, going up and down stairs, and as sit down in a chair.
Non-Weight-Bearing: when there is no weight going through the knee when bending it e.g. when sitting in the chair and moving the knee or/and standing but with the leg lifted off the floor as bending it. Knee pain when bending tends to be worse when there is weight going through the knee as you bend it due to the compression and pressure on the various structures in the knee.
This should come as no surprise when we realize how large the forces going through various parts of the knee. For eg, when bending the knee to climb stairs, a force of approximately 3 times body weight goes through the knee. When squatting down the force is even greater at seven times body weight and when jumping, a huge force of ten times body weight goes through part of a knee.
Causes Of Knee Pain When Bending:- Knee pain when bending might be the result of any number of causes, including arthritis, overuse, or sports injuries. All of these could result in knee pain when bending or/and activating the knee joint. Some knee discomfort may have an obvious cause. For example, if you fell on the knee during an athletic exercise, it is safe to assume that is why the knee hurts. Other causes of knee pain, such as arthritis or a degenerative condition, will need a clinical evaluation and expert diagnosis.
The most common lead to knee pain include:
Traumatic Injuries
Traumatic injuries lead to knee pain that you will likely notice right away. Directly following an injury, or perhaps up to 24 hours later, the knee will start to swell as pain and inflammation set in. Traumatic injuries generally happen during sports, falls, work-related accidents, or car accidents. Direct impact and twisting are common mechanisms of an injury.
Traumatic injury is noticeable right away and worsens dramatically the next day as pain and inflammation set in. traumatic injuries commonly happen playing sports, during slips, falls, and other work-related accidents. The trauma is caused by the injury exceeding the tolerance of a knee structure leading to breaks, tears, or ruptures. Knee ligaments, bones, and menisci are the most typically damaged structures in the knee joint. Injuries to bone and connective tissue result in long-term pain and will impede normal knee function a few times after the initial injury. Less serious traumatic injuries might result in only painful, superficial contusions (bruises) which heal relatively quickly. If you believe you have incurred serious knee trauma you should visit the doctor as soon as possible. If bone or connective tissue within the joint is damaged a surgical assessment could be required.
Overuse Injuries
Overuse injuries develop gradually over time as the knee goes through consistent use and overexertion. These types of injuries will result in pain that comes and goes with varying intensity. generally, performing the activity that is responsible for the overuse will cause the pain to flare up again. Overuse injuries normally cause knee pain that comes and goes and varies in intensity. a few times our favorite activities subject our knees to stressful movement patterns repetitively. Think to jump, squatting, kneeling, running, and lunging type movements. Moving in this way over and over again could irritate knee structures such as bursae, tendons, and articular cartilage.
Arthritis
Arthritis in the knee is a degenerative or inflammatory condition that would worsen with time unless properly treated. Arthritic joints might be most painful and stiff instantly after waking up or being sedentary and vary in intensity when walking or performing daily activities. Body weight, weather conditions, and other factors might also play a role.
Arthritis of the knee could be either osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These types of arthritis have various root causes, but both feel burning, twisting, aching, or/and pins-and-needles pains. Arthritis might also lead to the knee locking up when you bend it or hurting when you try to bear weight on that leg.
Osteoarthritis—the more common type of knee arthritis—happens when the joint structures break down. generally known as wear-and-tear arthritis, it is generally due to past injuries or overuse that comes with aging. In osteoarthritis, the soft tissues and cartilage that cushion the joints erode, making movement painful. Without the soft tissues to protect the bones in the knees, the knees may lock in place or be more prone to injury.
RA(rheumatoid arthritis): Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes the immune system to attack the joint tissues. Over time, the inflammation leads to the soft tissues breaking down. With RA(rheumatoid arthritis), the knees may feel stiff, and it might be difficult for you to rotate the legs or bend the knees. And after you sit down, it might be difficult to extend the legs so you can stand up again.
So let’s look at the most common lead to knee pain when bending and how to treat them:
Runner’s Knee
- Runner’s Knee is the most common reason for knee pain when bending but don’t be fooled by a name. It is just as possible to affect office workers as runners! Runner’s Knee is also, more accurately, known as anterior knee pain or/and patellofemoral pain syndrome. Runner’s knee, also known as patellofemoral syndrome, is pain near your knee cap that occurs due to damage to the soft tissues in your knee.
- What Is It: Runners Knee is a problem with how the knee cap moves place extra stress and friction on the cartilage as when the knee bends and straightens
- Causes: Weakness of the muscle and/or tightness or altered biomechanics such as foot arches and a hip angle.
- Runner’s knee can be caused by:
- Overexertion during exercise
- A hamstring injury that puts more strain on the knees
- Being born with an abnormally shaped kneecap
- A kneecap that doesn’t glide properly
- Track and field and contact sports athletes are particularly prone to runner’s knees.
- Symptoms: Knee pain when bending a knee is the most common symptom and tends to be at a front of the knee, just below and to the sides of the kneecap. It may occur during bending activities such as squatting or coming downstairs, or when you first move the knee after sitting down for prolonged periods e.g. driving or watching TV. Another common feature is a grinding or/and grating sound as you bend and straighten the knee.
- Symptoms of runner’s knee include:
- A dull ache when sitting down.
- Pain when bending or straightening the knee.
- The knee pain when standing up after sitting for too long.
- Onset: Symptoms develop gradually.
- You might experience knee weakness or notice a rubbing or/and clicking sensation. You might also hear a popping or cracking noise as you bend the knee. Any of these symptoms can lead to discomfort and make exercise difficult. Runner’s knee is usually temporary and can improve with rest, physical therapy, and knee support, the healthcare provider can help you come up with a particular care plan that works for the specific condition.
Knee Bursitis
- Bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that sits between bone and soft tissues to reduce friction.
- What Is It: Bursitis is inflammation of one or more of the bursa located surrounding the knee.
- Causes: Prolonged/repetitive pressure, excessive friction, a fall or blow to a knee.
- Symptoms: Knee pain when bending the knee – the location will depend on which bursa is affected.
- Onset: in most cases, a gradual onset of knee pain can develop suddenly after an injury.
Housemaid’s Knee
- This is a common cause of swelling and knee pain when bending in individuals who spent a lot of time kneeling
- What Is It: Housemaids Knee is inflammation on a prepatellar bursa found just below a kneecap at the front of the knee
- Causes: Prolonged/repetitive kneeling e.g. housework or/and tradesmen work, a blow to the knee e.g. falling onto a knee
- Symptoms: front knee pain when bending and straightening the knee, swelling at a front of a knee
- Onset: Generally gradual unless there was a direct force through the knee
Bakers Cyst
- A Baker’s cyst is a fluid-filled sac in a back of a knee joint. The excess knee-joint fluid pushes through the back of the joint capsule, leading to a cyst that protrudes into the back area of the knee (popliteal fossa). It is a few times called a popliteal cyst and causes a visible bulge. Baker’s cysts cause pain and swelling in a back of a knee joint that gets worse with activity. The pain is often described as joint tightening and stiffness upon bending or/and straightening.
- What is it: The Bakers Cyst is swelling of the semimembranosus bursa at a back of a knee.
- Causes: Excess fluid in a knee joint seeps back into the bursa and collects resulting in swelling. Commonly caused by arthritis but can develop with any condition that leads to swelling in the knee joint e.g. a cartilage tear or gout.
- Symptoms: Stiffness and knee pain when bending the knee and straightening the knee, worse with activity and better with rest. People can often feel a small bulge at the back of the knee that feels like a water balloon. Symptoms of a Baker’s cyst are similar to DVT(deep vein thrombosis), a dangerous type of blood clot, and should be evaluated by the healthcare provider.
- Onset: Bending knee pain symptoms develop gradually.
Knee Sprain
- The knee has four ligaments that assist control the stability of the knee. The cruciate ligaments sit inside a joint and the collateral ligaments are found on either side of the knee.
- What is it: A knee sprain is when one of the knee ligaments gets overstretched and/or tears. Those are three various grades of knee sprain depending on how much of the ligament is damaged.
- Causes: Excessive force through the knee or/and sudden twisting of the knee.
- Symptoms: Pain with activity and difficulty bending the knee and straightening the knee. Instability of the knee and swelling. The more severe an injury, the more severe the symptom.
- Onset: Immediate or/and within a couple of days of an injury.
Meniscus Tear
- The meniscus is a special, extra thick layer of cartilage that lines the knee joint to provide cushioning and protection to a knee. It also assists to transmit the forces via a knee correctly. Meniscus tears are a common lead to knee pain when bending.
- What is it: A meniscus tear is when there is tearing or fraying in the meniscus resulting in inflammation, and reduced cushioning of the joint. a few times the torn fragment gets stuck in the joint limiting movement
- Causes: Wear and tear or sudden twisting of a knee when a foot is fixed
- Symptoms: Knee pain when bending especially going up a stair or squatting down. Knee movement may be limited and in a few cases, the knee gets stuck when the loose fragment gets locked in the joint. The knee would most likely be swollen.
- Onset: May develop gradually from wear and tear or/and suddenly after an injury such as twisting the knee when the foot is fixed.
Knee Arthritis
- Arthritis means “inflammation of a joint” and affects millions of persons worldwide. There are over 200 various types of arthritis, but the one that most commonly causes knee pain when bending is osteoarthritis.
- What is it: Osteoarthritis is where there is thinning and wear and/or tear of the cartilage lining a knee joint, and the formation of bony lumps in a joint. These result in excessive friction through the bones of a knee.
- Causes: There is a multitude of causes of arthritis including previous damage to a knee, genetics, being overweight, and altered biomechanics changing the way the forces travel through the knee.
- Symptoms: Knee pain, mainly first thing in the morning or after prolonged sitting when they try and bend the knee. There is often so much knee pain when bending or straightening the knee fully that the joint begins to stiffen. The pain tends to ease with gentle movement but gets worse if you do too much, mainly on a bent knee such as stairs or bending down.
- Onset: Symptoms develop slowly over time and often come and go. Osteoarthritis most commonly affects individuals over the age of 65.
Other Causes of Knee Pain When Bending
Other less common leads to knee pain when bending include:
- Patellar Tendonitis: Inflammation and micro-tears in the patellar tendon just below the kneecap, commonly after prolonged jumping or kicking movements resulting in bending the knee pain. The most defining feature of patellar tendonitis is that it is painful if pressed on a tendon.
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS): Irritation and inflammation of a thick fibrous band on the outer side of the thigh and the knee. It commonly develops from overuse and most repeatedly affects runners. Sending bending knee pain from Iliotibial Band Syndrome tends to be on the outer side of the knee and there may be a popping/grinding sensation as you bend the knee. iliotibial Band Syndrome Pain on the outside or lateral side of the knee commonly indicates a problem with the iliotibial band (the connective tissue that runs from the side of a hip down to a shin bone) or the lateral meniscus (a piece of cartilage that sits between the femur and tibia). Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) is common in long-distance runners, as well as cyclists and rock climbers. The repetitive bending of the knee could lead to this condition. Meniscus tears, on another hand, are caused by sudden twisting movements of a knee, which is common in basketball, soccer, tennis players, and football.
- Osgood Schlatters: A common cause of bending knee pain in teenagers is commonly associated with sudden growth spurts where the bones grow quicker than the soft tissues leading to excessive tension via the patellar tendon which damages the underlying bone.
When to see a doctor
Mild knee pain while bending isn’t commonly a cause for concern. Although, you should see a doctor if you have the following:
- severe knee pain
- chronic knee pain
- inability to bend or straighten your knee
- limping
- swelling or redness in your knee
- knee weakness
- popping or crunching noises associated with pain
- fever
You should also seek medical help if you recently had a knee injury accompanied by a popping noise, swelling, or/and an inability to bear weight on a leg.
What does a knee injury feel like?
Depending on the underlying cause, the knee injury can cause sharp, shooting pain, a dull ache, or a burning pain. You may notice swelling and the knee may feel tender to the touch. You may also have difficulty bending, straightening, or bearing weight on the knee and may find that the knee gets stuck (locks). A knee injury can also make you feel as if the knee is about to give way when you try to walk on it.
Diagnosing Knee Pain
A doctor will use the following tests to diagnose the cause of the knee pain:
- physical exam, which allows a doctor to check for joint swelling, instability, and signs of swelling.
- imaging tests, like an X-ray or MRI(Magnetic resonance imaging) scan, to analyze the bone and tissues in the knee.
- blood tests, which let the doctor check for signs of systemic inflammatory disorder, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), or infection
Diagnosing knee pain often needs a combination of a physical exam, imaging studies, and blood work. the healthcare provider may use the following to evaluate the knee pain.
Physical Exam
A physical exam can assist the healthcare provider to understand precisely where and why you are hurting. The healthcare provider may feel the knee to pinpoint swelling, irritation, or potential injuries. They may ask you to walk, stretch, sit down, or bend the knee to observe the range of motion.
Lab Tests
After you have a physical exam, the healthcare provider may request blood work. Lab tests can assist differentiate between osteoarthritis and RA or other autoimmune diseases. Blood work also rules out infections, cancer, Lyme disease, or other illnesses that can lead to knee pain.
Imaging
An X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help the healthcare provider visualize the condition of the bones and joints. Imaging studies are commonly used to identify bone fractures, arthritis, soft-tissue injuries, and other structural problems with the knee.
Treating Knee Pain When Bending
Conditions that result in knee pain when bending might be initially treated at home with rest/ice/compression/elevation and self-care. the treatment plan would depend on the cause and severity of the knee pain. Treatment options range from basic lifestyle modifications to surgery.
Changing exercise and activity
Avoid high-impact activities as these put greater strain on the knee joints. Instead, try low-impact activities such as cycling, swimming, walking, and water aerobics.
Lifestyle Changes
A Few interventions for knee pain include modifications to your lifestyle. Weight loss is typically recommended as a first-line treatment for knee pain. the doctor might recommend walking, swimming, and other low-impact exercises to assist you to burn calories without putting too much stress on the knees. A few people find the anti-inflammatory diet useful for relieving knee pain. In addition, turmeric, lemon water, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids may help decrease the inflammation in the knee joints. If the knees hurt when sitting down at rest, it could be a sign that you are sitting in an awkward position or simply sitting too long. To differentiate between the knee pain caused by structural problems versus the way you sit, try the following:
- Stretch the legs during the day. Sitting for six to eight hours during the workday may make the knees stiff and increase the risk of other health concerns like cardiovascular disease. Get up and walk around every hour or half hour to give the knees some gentle exercise.
- Avoid or limit certain sitting positions. Some sitting positions can cause more stress on the knees than others. For example, sitting on the floor cross-legged, kneeling, or sitting on the heels stresses the ligaments around the kneecap.
- Find a comfortable chair. When sitting, your knees should be comfortable—about the same level as the hips and at a 90-degree angle. If you are adjusting an office chair, ensure the seat is just below the kneecaps when standing next to it. This should help ensure the feet are flat on the floor while sitting.
- Check with the healthcare provider if the knees still hurt after making these adjustments. They can assist you to determine if a condition is causing knee pain.
The best treatment for knee pain when bending will depend on the underlying cause of the knee pain. In most cases it will involve:
PRICE- it stands for protection, rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
Strengthening Exercises
Stretches
Knee Braces
Injections
Knee Surgery
You will find loads more information on the various conditions we have looked at including the best ways to treat knee pain when bending by using the links above.
Here we have looked at the most common causes of knee pain when bending, but almost any problem with the knee could result in pain as you move it. If none of these is sounding quite right, visit the knee pain diagnosis section for more assistance to work out what is leading to the bending knee pain.
Medical treatment
The best treatment for knee pain while bending depends on the lead. A doctor might recommend:
OTC medication
To decrease or reduce pain and swelling, consider taking NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). These medications are available over the counter (OTC), so you don’t require a prescription. Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers such as Tylenol (acetaminophen), Advil (ibuprofen), and Alleve (naproxen) are commonly used to reduce knee pain. If OTC medications don’t relieve the pain, the healthcare provider may prescribe a stronger non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) or a steroid pain reliever, such as prednisone. A short course of opioid pain relievers might also be prescribed for severe, acute pain. though, opioids have a high risk of addiction and should only be used sparingly. Always follow directions for dosage and frequency unless instructed by the doctor.
Physical therapy
A physical therapist can show you specific exercises for the condition. These exercises are designed to enhance strength, mobility, and flexibility in the knee. Depending on the cause of the knee pain, the healthcare provider may recommend physical therapy. The physical therapist can provide exercises to strengthen the muscles that support the knee and other therapies, including electronic muscle stimulation and ultrasound.
Knee exercises
Knee exercises can assist manage knee pain. This includes strengthening exercises that target the muscles that support the knee. When the muscles are healthy and strong, there is less stress on the knee. It’s also important to do knee stretches. Stretching reduces tension in the surrounding muscles, which decreases pressure on the knee joint.
It is important to keep the knees active so the muscles that support the knee do not become weak. this can place greater strain on the knees. Knee-strengthening exercises that target these muscles can, therefore, assist decrease knee pain.
Be sure to move slowly. If an exercise leads to more pain, stop doing it immediately.
Massage
Massage can assist relieve knee pain. However, you should see a doctor first before trying to massage to find out if it is appropriate given the underlying cause of your knee pain.
During the massage, a therapist uses their hands to apply pressure on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments. This can assist relieve and manage knee pain. Consider sports massage if the knee pain is due to sports or/and overuse. Sports massages are used to treat athletic injuries.
You can also try:
- Swedish massage
- trigger point massage
- deep tissue massage
Acupuncture
Research shows acupuncture can assist to relieve chronic pain. Though, the research is mixed on whether it is effective for knee pain. One study found no benefit of acupuncture treatments on individuals over age 50 with knee osteoarthritis. While another study found it might also be effective in decreasing osteoarthritis knee pain.
Braces and Orthotics
Orthotics are shoe inserts that stabilize the ankle and the foot. They can alleviate pain by easing pressure on the knee. Depending on the condition, you might also be able to purchase an orthotic at the drugstore. Alternatively, the doctor may suggest a custom-made shoe insert.
The knee brace may be used to support the knee while working or exercising. Orthotic shoe inserts may also assist to reduce knee strain.
Immobilization
If the knee pain is due to the injury, the doctor might have you wear a brace or/and cast. This will protect the knee and prevent you from moving it, assisting to alleviate pain and allow healing.
Surgery
If the condition doesn’t get better with nonsurgical treatments, you may require surgery.
In general, surgery is only required or needed for severe cases. There are more types of surgery used for knee issues. Here are a few examples:
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction, and the surgery to repair a torn anterior cruciate ligament
- meniscectomy or/and meniscus repair, to treat a torn meniscus
- total knee replacement
- tibial tubercle transfer, the procedure to improve knee stability
Home remedies for pain when bending the knee
If the knee pain is mild, home remedies might offer relief. Here’s what you can do:
Change the activity
Pay attention to how the knees feel during various activities. If a certain movement makes the knees hurt, avoid it until you feel better. You can also restrict the movement or do low-impact activities instead.
Low-impact activities put less stress on your joints. Examples include:
- biking
- swimming
- water aerobics
- walking
RICE
The RICE method is a treatment for minor muscle injuries, including those that involve a knee.
“RICE” is an acronym that stands for:
- Rest and avoid placing weight on your knee. This will assist the surrounding muscles to heal.
- Ice to alleviate swelling and pain. Wrap ice in a plastic bag or clean cloth, and then apply to the affected area for 20 minutes at a time, multiple times a day.
- Compress by wrapping your knee with an elastic bandage, which will help decrease swelling. Make sure a bandage is snug but not tight.
- Elevate or raise the knee by placing it higher than the heart. Do this as much as possible to ease the swelling.
Heat or ice
If the knee pain is caused by arthritis or you have a stiff knee, applying heat can assist by improving the blood flow.
Holding a cold or hot compress to the knee may assist decrease pain and joint swelling. Ice is commonly recommended for new injuries and inflammation. Heat can assist relieve pain associated with joint stiffness and chronic pain. If you have arthritis or stiffness, applying heat may offer better relief. Heat increases circulation.
Recovery
Commonly, it takes about 6 weeks to recover from a knee injury.
If you require surgery, recovery time can range between 8 weeks to 12 months.
Total recovery time depends on several factors, including:
- the severity of the condition
- type of surgery or injury
- the overall health
- the strength and activity level before surgery
- the age
- the treatment plan
- As you recover, you will need physical therapy to restore strength and function in the knee. You will continue the physical therapy after the initial recovery period.
How to prevent knee pain when squatting and bending?
It is not always possible to prevent a knee injury and/or subsequent knee pain. However, you can decrease the risk by making sure you always stretch your legs before and after exercising and stop exercising if you feel any knee pain. You should also avoid suddenly raising the intensity of the exercise regime and instead gradually work your way up. Practicing regular strengthening exercises and stretching exercises that target the muscles that support the knees can also decrease the risk of a knee injury. If you are overweight, losing excess weight will decrease the strain on the knees, making a knee injury less likely. If the work involves kneeling a lot, use knee pads to decrease the chances of developing knee bursitis. eventually, make sure you wear well-fitting, supportive shoes.
Preventing knee pain: It’s possible to prevent or reduce the risk of knee pain. Consider the following tips:
- Avoid or limit movements that lead to knee pain. It’s the best way to stop overuse, which can lead to more severe pain or injuries.
- Do low-impact activities like biking or swimming. Low-impact activities are a great way to stay active while alleviating pressure on the knee.
- Lose weight if you’re overweight. Extra weight can add stress to the knee and increase the risk of knee pain.
- Warm up and cool down before exercise. This will protect the muscles and assist prevent injury.
- Add weight training to the workout regimen. Focus on strengthening the muscles that support the knee joint.
- Stretch regularly to loosen tight muscles and improved flexibility.
- Use knee pads while working on the knees. Knee pads will protect the kneecaps and decrease pressure.
Knee problems are more common in individuals who are overweight or obese. Keeping an active lifestyle and following a healthy diet can help manage weight and stop some knee pain. Exercises such as swimming and yoga can keep the knees flexible without much of the joint strain of high-intensity sports. Moderate strength-building exercises can also assist you to avoid knee injuries by strengthening the thighs and the legs. Strong leg muscles can decrease the stress on the knees.
Takeaway
If the knee hurts while bending the leg, take it easy. It might be a sign that the legs need to rest. Home remedies like stretching or/and ice packs can also alleviate pain. See a doctor if the pain is severe or/and persistent. A doctor can determine what’s causing the symptoms and help you find relief.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended or purposeful for your general informational purposes only and does not address particular circumstances. it is not a substitute for professional advice(or guidance) or help( or assistance) and should not be relied on to make decisions of any kind. A few or any actions you take upon the information presented in this article are strictly at your own risk and responsibility.
FAQs
How long should the knee pain last before seeing the doctor?
Typically, athletes should see the healthcare provider for pain lasting more than 48 hours and other adults should see an expert if there seems to be no change for three weeks. commonly, most healthcare providers recommend that you schedule an appointment as soon as you notice that the symptoms impact the way you live.
What does arthritis feel like when you bend the knee?
A knee joint affected by arthritis may also be painful and inflamed. Commonly, the pain develops gradually over time, although sudden onset is also possible. There is another symptom, as well: The joint may become stiff and swollen, making it difficult to bend and straighten the knee
What does it mean when you bend the knee and it feels tight?
Tightness in the knee can happen as a result of injury to the tendons, ligaments, or cartilage inside the knee. In a few cases, it may be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. Anyone who experiences tightness in one knee or both knees should see a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Can walk but can’t bend the knee?
The inability to bend or straighten the knee may be the result of a truly locked knee (in which torn knee cartilage becomes wedged in the joint) or a pseudo-locked knee (in which severe knee pain triggers a defensive reaction that impedes a knee movement).
What did I hurt if I can’t bend my knee?
Potential causes of knee pain when bending
Muscle strains — The muscles surrounding the knee can become tight and strained, actually making it painful to bend. Arthritis — The breakdown of knee cartilage and the drying out of lubricating joint fluid can cause joint inflammation and associated stiffness and pain.
Can you bend the knee with a torn ligament?
Grade 3: The grade 3 injury is a complete tear or rupture of a knee ligament. grade 3 injuries frequently involve more than one knee ligament. With this level of injury, you would experience severe bruising, swelling, and pain. You won’t be able to put weight on the leg or bend a knee.
Why does my knee hurt on the side when bending it?
Pain on the outer (or lateral) part of a knee can be caused by an injury. It might also be the result of inflammation in a band of tough fibrous tissue that runs down the outside of the thigh and attaches to the front of the tibia (shin bone). Pain in these areas may also be caused by arthritis.
How do I know if I have damaged the knee cartilage?
Symptoms of cartilage damage
joint pain – this may continue even when resting and worsen when you put weight on a joint.
swelling – this may not develop for a few hours or/and days.
stiffness.
a clicking or grinding sensation.
the joint locking, catching, or giving way.
How do you fix knee pain when bending?
Rest and avoid placing weight on the knee. This will assist the surrounding muscles to heal.
Ice to alleviate swelling and pain.
Compress by wrapping the knee with an elastic bandage, which will assist reduce swelling.
Elevate the knee by placing it higher than your heart.
How do I know if the knee pain is serious?
Call the doctor if you:
Can’t bear weight on the knee or feel as if the knee is unstable or gives out.
Have marked knee swelling.
Are not able to fully extend the knee or flex the knee.
See an obvious deformity in the leg or the knee.
Have a fever, in addition to redness, pain, and swelling in a knee.
Should I go to a doctor if it hurts to bend my knee?
Schedule a doctor’s visit
Make an appointment with the doctor if your knee pain was caused by a particularly forceful impact or if it’s accompanied by: Significant swelling. Redness. Tenderness and warmth around the joint.