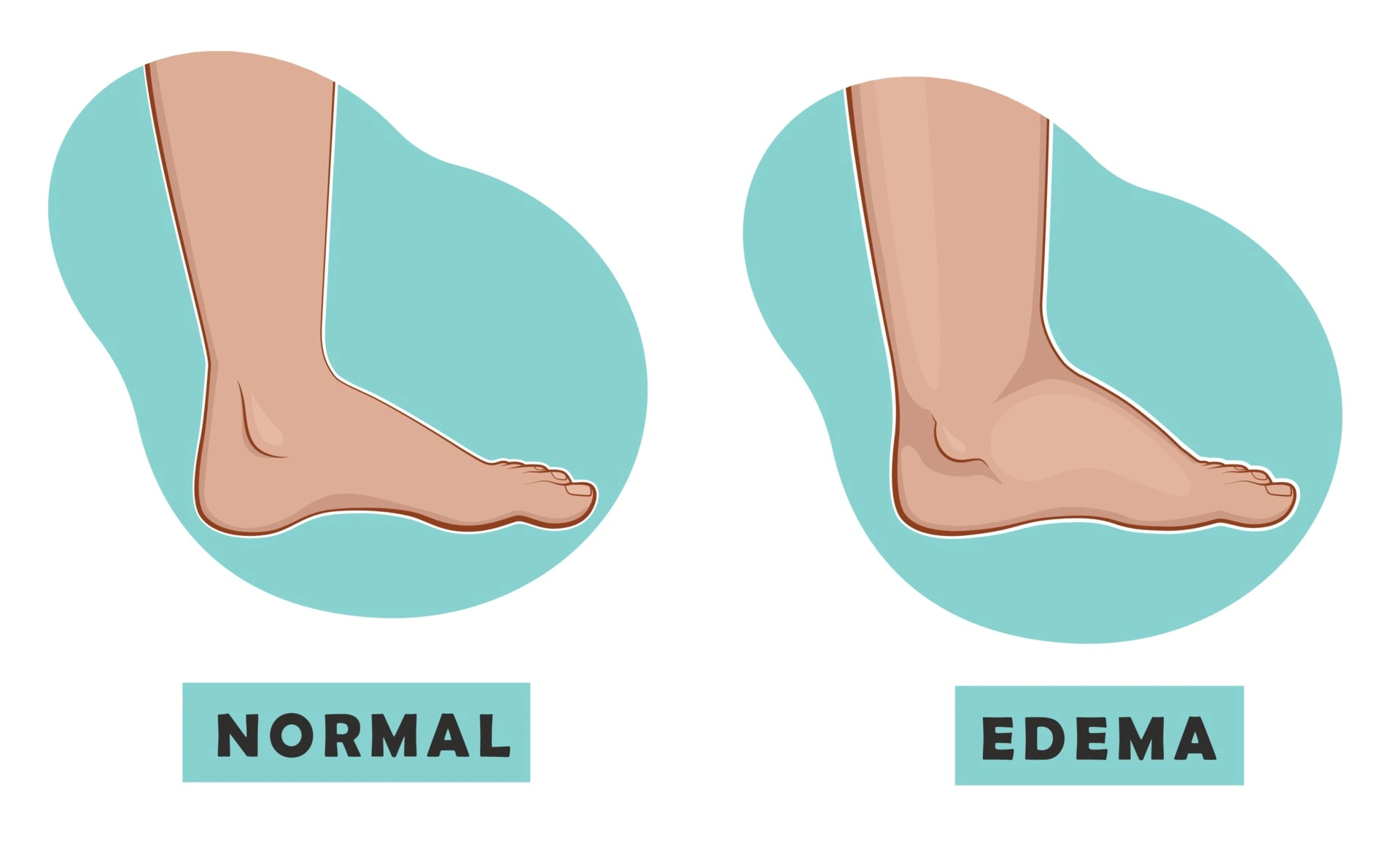
Edema
What is Edema?
Edoema, often spelled edema, is the accumulation of fluid in bodily tissue. It is also referred to as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy, and swelling. Legs or arms are most frequently afflicted. The sensation of tight skin, heavy areas, and stiff joints are a few signs. The fundamental cause will determine any additional symptoms.
Deep vein thrombosis, heart failure, renal problems with the liver, low protein levels, angioedema, certain medicines, and lymphedema are some of the possible causes. Additionally, it can happen to people who are immobilized due to a stroke, spinal cord damage, advanced age, or temporary immobility from extended sitting or standing, menstruation, or pregnancy. It is more dangerous if the sickness progresses fast or if pain or shortness of breath are present.
The underlying reason determines the course of treatment. A diuretic and less salt may be consumed if sodium retention is the underlying cause. For leg edema, elevating the legs and using support stockings may be helpful. More senior citizens are often impacted. The name is derived from the Greek word “da edema,” which means “swelling.”
Signs and symptoms
Specific area
An edema will develop in particular organs as a result of inflammation, such as tendonitis or pancreatitis. Edema may occur in some organs due to tissue-specific processes. Several examples of edema in certain organs:
Peripheral edema
Peripheral edema, also known as “dependent” edema of the legs, is an extracellular fluid buildup in the lower extremities brought on by the forces of gravity and happens when fluid collects in the lower body parts, such as the hands, feet, or legs. Due to hypervolemia or prolonged standing or sitting, this frequently happens in immobile patients, such as paraplegics or quadriplegics, pregnant women, or otherwise healthy persons.
It can happen as a result of decreased venous return of blood to the heart brought on by pulmonary hypertension or congestive heart failure. Because of Congestion in the lymphatic or venous veins draining the lower leg, it can also happen in individuals with elevated hydrostatic venous pressure or decreased oncotic venous pressure. Pedal edema can be brought on by some medications (amlodipine, for illustration).
The buildup of extracellular fluid in the brain is known as cerebral edema. Under toxic or abnormal metabolic conditions, such as systemic lupus or low oxygen levels at high altitudes, it might occur. It results in somnolence or unconsciousness, which leads to brain herniation and death.
Pulmonary edema
Due to a blockage in the pulmonary veins, pulmonary edema develops when the pressure in the blood vessels in the lung increases. This is often brought on by the heart’s left ventricle failing. It can also happen as a result of harmful chemical inhalation or altitude sickness. Breathlessness is a symptom of pulmonary edema. Fluid buildup in the pleural cavity can lead to pleural effusions.
In addition, glaucoma, acute conjunctivitis, keratitis, and after surgery can all cause edema in the cornea of the eye. People who are affected could see colored haloes surrounding bright lights.
An edema that surrounds the eyes is referred to as periorbital edema or swollen eyes. The swelling of the periorbital tissues is most pronounced just after awakening, possibly as a result of the fluid’s gravitational redistribution in the horizontal posture.
Mosquito bites, spider bites, bee stings (wheal and flare), and skin contact with specific plants, such as poison ivy or western poison oak, are common causes of cutaneous edema, which is also known as contact dermatitis.
Myxedema
Myxedema is a different kind of cutaneous edema brought on by an enlarged connective tissue deposit. Edema in myxedema (and a number of other uncommon disorders) is brought on by the tissue’s enhanced propensity to retain water in its extracellular space. In myxedema, this is brought on by an increase in hydrophilic carbohydrate-rich molecules deposited in the tissue matrix, presumably primarily hyaluronic.
It is unclear why senior people, who frequently sit on chairs at home or on airplanes, are more prone to developing edema in dependent areas. Estrogens affect body weight in part through altering the water content of tissues. Because of alterations in the tissue’s hydrophilicity or a failure of the ‘wicking’ function of terminal lymphatic capillaries, there may be a number of poorly understood circumstances in which the transfer of water from tissue matrix to lymphatics is hampered.
Myoedema
Myoedema is a localized swelling of muscle tissue brought on by percussion, such as flicking a relaxed muscle with the thumb and fingers. About 1-2 seconds after the tactile input, it creates a mound that is discernible, firm, and non-tender, which subsides back to normal within 5–10 seconds. It is an indication of a myopathy caused by hypothyroidism, such as Hoffmann syndrome.
Lymphedema
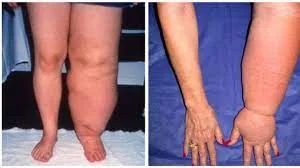
Failure of the lymphatic system results in inappropriate interstitial fluid clearance in lymphedema. This might be caused by blockage, such as pressure from cancer or enlarged lymph nodes, radiotherapy-induced lymph channel damage, or infection (such as elephantiasis) infiltration of the lymphatics. It is most plainly caused by muscular weakness brought on by immobility in conditions like multiple sclerosis or paraplegia. It has been proposed that the edema that some individuals experience after taking cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors that operate similarly to aspirin, such as ibuprofen or indomethacin, may be caused by the suppression of lymph heart activity.
Generalized edema
In heart failure, hydrostatic pressure increases. Nephrotic syndrome and liver failure both result in a drop in osmotic pressure.
Edema in various organs as well as peripherally might be brought on by edema-causing factors that are generalised throughout the entire body. For instance, pulmonary edema, pleural effusions, ascites, and peripheral edema can all result from severe heart failure. Anasarca is the medical term for such severe systemic edema. A parvovirus B19 infection can occasionally result in generalized edemas.
Even though a low plasma oncotic pressure is frequently listed as the cause of the edema associated with nephrotic syndrome, the majority of doctors point out that the edema may manifest itself before any detectable proteinuria or a drop in plasma protein levels. The biochemical and structural changes in the basement membrane of the capillaries in the kidney glomeruli that cause the majority of types of nephrotic syndrome also affect, albeit to a lesser extent, the vasculature in the majority of other bodily tissues. If the other capillaries are also more permeable, the consequent increase in permeability that results in protein in the urine might therefore explain the edema.
Edemas frequently develop in certain women during the later stages of pregnancy, in addition to the symptoms already stated. This is more frequent in those with a history of pulmonary issues or poor circulation, and it is worse in women who already have arthritis. Most frequently, women with pre-existing arthritic conditions must seek medical attention for discomfort brought on by excessive swelling. Pregnancy-related edema is typically located in the lower leg, typically from the calf down.
A kid with hydrops fetalis will have fluid buildup in at least two different bodily compartments.
Causes of edema
Edema is prevalent because several causes contribute to the disorder. The precise rate of recurrence is unclear since mild instances of edema resolve on their own.
Heart
The capacity of the heart to pump blood should contribute to maintaining healthy blood vessel pressure. However, the pressure shifts can result in extremely serious water retention if the heart starts to fail (a disease known as congestive heart failure). Water also builds up in the lungs, where it creates a persistent cough, although it is most noticeable in the legs, feet, and ankles with this illness. Diuretics are typically used to treat this illness because, without them, water retention might impair breathing and put additional strain on the heart.
Kidneys
Kidney failure, when the kidneys are no longer able to filter fluid out of the circulation and transform it into urine, is another reason for significant water retention. Inflammation is frequently the first sign of kidney illness, as is the case with conditions like lupus or nephrotic syndrome. Swollen legs and ankles are a common sign of this sort of water retention.
Liver
The liver’s cirrhosis, or scarring, is a prevalent factor in the development of abdomen and leg edema.
Others
- Another typical reason for water retention in the legs is inactivity. The leg veins may more effectively fight gravity and return blood to the heart with exercise. Too much fluid may be forced out of the leg capillaries and into the tissue spaces if blood flows too slowly and begins to pool in the leg veins. Small blood stains may appear beneath the skin as a result of capillaries rupturing. Varicose veins are a swelling, painful, and distorting disorder that can affect the veins themselves. In addition to helping the blood continue to flow through the veins, muscle activity helps the lymphatic system perform its “overflow” work.
- Water retention may result from protracted bed rest, long trips, disabilities that prevent movement, etc. Exercises as simple as wiggling your toes and turning your ankles will assist to lessen it.
Certain medications are prone to causing water retention. These include estrogens, which also includes HRT medications or oral contraceptives like the pill, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications and beta-blockers.
Pregnancy
Water retention may result from protracted bed rest, long trips, disabilities that prevent movement, etc. Exercises as simple as wiggling your toes and turning your ankles will assist to lessen it.
Water retention is a common side effect of several drugs. These include estrogens, which also include HRT medications or oral contraceptives like the pill. As well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications and beta-blockers.
The body retains more salt and water than typically during pregnancy due to hormones that promote fluid retention. The face, hands, feet, and lower limbs may enlarge.
Edema can also be brought on by eclampsia, which is high blood pressure that develops during pregnancy. Premenstrual water retention, which causes bloating and painful breasts, is very typical.
Conditions affecting the brain
The following are a few causes of brain swelling:
- Head injuries: A blow to the head might cause fluid to build up inside the brain.
- Significant strokes may cause brain swelling.
- Brain tumors: As it grows new blood vessels, a brain tumor will cause an accumulation of water surrounding it.
Allergies
People who have allergies or sensitivities to certain foods and bug stings may develop facial or skin edema as a result. Anaphylaxis may show symptoms of severe swelling.
A person’s airway may get blocked by throat swelling, rendering them unable to breathe. A medical emergency has occurred.
Issues involving the extremities
- The following are some causes of edema in the extremities:
- The flow of blood can be stopped by any blockage, including a blood clot in a vein. Edema develops as a result of fluid leakage into the surrounding tissue when venous pressure rises.
- Varicose veins: These often develop as a result of broken valves. Veins begin to swell as the pressure inside them rises.
- Additionally, the pressure raises the chance of fluids spilling into adjacent tissue.
- Any lump, whether it be a cyst, growth, or tumor, can result in edema if it rubs up against a lymph duct or vein. Fluids may seep into the surrounding tissue when pressure increases.
- The lymphatic system assists in removing extra fluid from tissues in cases of lymphedema. Edema can happen if this system is damaged in any way, such as by a tumor, an infection, or a surgical treatment.
Miscellaneous conditions
- Other potential edema causes include:
- Long-term inactivity: People who are inactive for a long time may get skin edema. This may be brought on by both fluid accumulations in places subject to gravity and the pituitary’s secretion of the antidiuretic hormone.
- High altitude: This might raise the risk of edema when paired with physical activity. High-altitude pulmonary edema or high-altitude cerebral edema can result from acute mountain sickness.
- Sunburn and burns: The skin retains fluid in response to burns. This results in localized edema.
- Swelling is a common symptom of infection or inflammation in any tissue. The skin is typically where this is most visible. This is usually most noticeable in the skin.
- Menstruation and menstruation: Hormone levels fluctuate during the menstrual cycle. Progesterone levels are lower in the days leading up to menstruation, which might result in fluid retention.
- Birth control pills: Fluid retention can be brought on by any estrogen-containing medicine. It is not uncommon for people to gain weight when they first start using birth control pills.
- Menopause: Hormone changes around the menopause may result in fluid retention. Edema can also be brought on by hormone replacement treatment.
- Thyroid disease: Hormonal imbalances associated with thyroid problems can lead to edema.
Mechanism
- Edema formation can be influenced by six different factors:
A rise in hydrostatic pressure; a fall in blood vessel colloidal or oncotic pressure; a rise in tissue colloidal or oncotic pressure. A rise in blood vessel wall permeability (as in inflammation); a blockage of lymphatic fluid clearance. Also alterations in the water-retention capabilities of the tissues themselves. Salt and water retention by the kidneys is typically indicated by an increase in hydrostatic pressure.
The forces of the Starling equation control the production of interstitial fluid. Water tends to filter into the tissue as a result of hydrostatic pressure within blood vessels. As a result, blood plasma and tissue have different protein contents.
As a result, the greater protein concentration in plasma tends to suck water back into the blood vessels from the tissue via colloidal or oncotic pressure. According to Starling’s equation, for a given force imbalance, the rate of fluid leakage is governed by the difference between the two forces as well as by the permeability of the vessel wall to water.
Capillaries or post-capillary venules, which contain a semi-permeable membrane wall that enables water to enter more readily than protein, are where the majority of water leakage occurs. (The protein is said to be reflected; a reflection constant up to 1 indicates the effectiveness of reflection.) The permeability to water increases initially as the spaces between the vessel wall’s cells widen, but as the spaces get bigger, the permeability to protein also rises along with a decline in the reflection coefficient.
Due to hydrostatic pressure
Changes in the variables in Starling’s equation can cause edemas to develop by elevating the hydrostatic pressure inside the blood vessel. Lowering the oncotic pressure inside the blood vessel, or increasing the permeability of the vessel wall.
The latter produces two results. It improves water flow and lessens the colloidal or oncotic pressure differential by facilitating easier protein exit from the vessel.
The lymphatic system, a different system of blood vessels, functions as an “overflow” and may return a significant amount of extra fluid to the bloodstream. However, even the lymphatic system has its limits. If there is just too much fluid or if the lymphatic system is clogged. The fluid will linger in the tissues and cause swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, belly, or any other portion of the body.
Diagnosis
- Grading of edema
- Grade Definition
- Absent Absent
- Mild: Both feet/ankles
++ Moderate: Both feet,
plus lower legs,
hands or lower arms
+++ Severe: Generalised
bilateral pitting edema,
including both feet,
legs, arms, and face
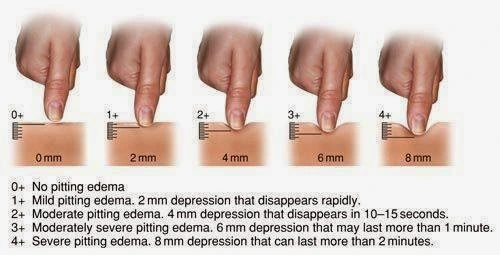
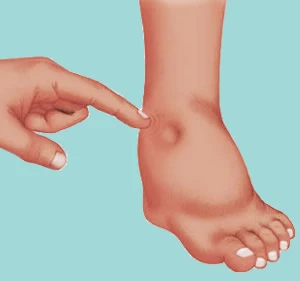
Pitting and non-pitting edema
- There are two main varieties of edema: pitting edema and non-pitting edema. Pitting edema occurs when pressure is applied to a tiny region and then released, leaving an indentation behind. The most typical variety of peripheral pitting edema, as seen in the figure, is brought on by water retention. It can be brought on by local illnesses such as varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, insect bites, and dermatitis as well as systemic diseases, and pregnancy in certain women, either directly or as a result of heart failure.
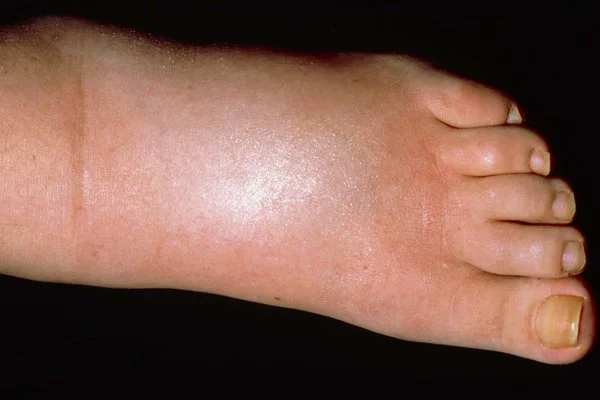
- When there is no longer an indentation, non-pitting edema is seen. It is linked to diseases including lymphedema, lipedema, and myxedema.
Kwashiorkor, an acute type of childhood protein-energy malnutrition characterized by edema, irritability, anorexia, ulcerating dermatoses, and an enlarged liver with fatty infiltrates, is described as edema brought on by malnutrition.
Treatment of edema
- A man’s face was bloated.
- Facial edema caused by vein blockage while sleeping.
- The same individual without any facial edema
- The swelling goes down after spending the entire day upright.
- Treatment usually includes addressing the underlying issue. Diuretics are frequently used in the treatment of renal or cardiac disorders.
In order to enhance drainage, the afflicted body parts may need to be positioned during treatment. For instance, lying down in bed or sitting with the feet elevated on cushions might help relieve swelling in the feet or ankles. It is possible to pressurize tissue in a limb using intermittent pneumatic compression, which causes fluids like blood and lymph to drain from the compressed region.
Complications of edema
Edema left untreated can result in:
- Stretched, itchy skin infection in the region of swelling scarring between the layers of tissue poor blood circulation loss of flexibility in the arteries, veins, and joints unpleasant swelling with worsening discomfort stiffness, and trouble walking
- Cutaneous ulcerations
- To keep an underlying illness from getting worse, it must get medical attention.
Prevention
Edema-related swelling and pain can be lessened by using compression stockings.
Edema can be lessened or avoided with the use of a few self-care methods.
- These consist of:
Lowering salt intake, if necessary losing weight, engaging in regular exercise, elevating the legs to improve circulation, using online-purchased support stockings, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, getting up and moving around frequently while traveling, and staying away from hot baths, showers, and saunas.
Wearing warm clothing while it’s chilly
By applying forceful strokes in the direction of the heart, a massage or physical therapist may aid in the removal of the fluid. Some kinds of edema may benefit from the usage of oxygen. For instance, if a person with cardiogenic pulmonary edema has trouble getting enough oxygen, they may require more oxygen.
An older study from 2004 suggests that oxygen administered through the nose may help the impaired eyesight caused by diabetic macular edema. The risk of pulmonary edema may, however, be increased by hyperbaric oxygen therapy, according to a certain Trusted Source study.
Could edema be avoided?
Stay as physically active as you can, limit your intake of salt, and adhere to your doctor’s recommendations for any problems that can lead to edema if you want to avoid developing it.
When is edema an emergency?
While the symptoms of edema will typically improve after rest and home treatment, they can be a sign of serious medical complications like heart or kidney failure.
In more specific situations, you should seek medical attention right away if you have trouble breathing since this might indicate pulmonary edema. Additionally, if you suddenly get edema while pregnant, notify your doctor right away because it might be an indication of difficulties.
Summary
The severity of edema varies depending on the etiology of each individual diagnosed with the disorder. As your due date approaches, it’s common to experience swelling if you’re pregnant. You may have a moderate case of edema, it usually goes away on its own. If you have a more severe condition, medication and therapy are available.
If you are not pregnant and you detect sudden swelling in a certain area of your body, schedule an examination with your doctor. The best prognosis may result from early detection and treatment of any underlying health issue that edema may be an indication of.
FAQs
Is edema a serious condition?
If your edema suddenly becomes more severe, uncomfortable, or new, or if it’s accompanied by chest discomfort or breathing difficulties, get medical attention right away. The latter might be a symptom of pulmonary edema, a dangerous medical illness where fluid fills the lung cavities.
How can I reduce edema naturally?
Healthful home remedies
Apply pressure: Wearing compression stockings, sleeves, or gloves may assist if edema affects the arm or leg.
Move: Moving fluid back towards the heart by movement and use of the muscles in the enlarged area of the body, particularly the legs, may be helpful
Raise the leg
Massage, protect, and so forth
Limit your salt consumption
Is Walking good for edema?
With the help of elastic stockings and walking, it is possible to lessen edema and discomfort in the legs over the course of the day.
Can edema be cured?
Treating the underlying problem is the only method to treat edema. A medication known as a diuretic may be prescribed by your doctor. A water tablet is another name for this. These medicines help the body eliminate extra salt and fluid through urine.
How do you measure edema?
The following methods are most frequently used to measure edema: Volume measurements (using a water volumeter)
(Using a tape measure) Girth measures.
Evaluation of the pitting edema based on the length and depth of the depression.
Is edema in the legs permanent?
Even while some forms of edema may be irreversible, there are still things you can do to lessen the swelling, ease the discomfort, and delay some of the long-term harm that edema may do. The effects of skipping edema therapy vary depending on the its underlying etiology.
Can edema be cured?
Treating the underlying problem is the only method to treat edema. A medication known as a diuretic may be prescribed by your doctor. A water tablet is another name for this. These medicines help the body eliminate extra salt and fluid through urine.
Does drinking more water reduce edema?
Edema is the medical word meaning swelling, and it may only affect one foot. There are practical strategies that may be put into practice to reduce edema. Swollen feet can be controlled by consuming less salt, constantly elevating the feet, and drinking lots of water.


14 Comments