Infrared Radiation Therapy Light: Physiotherapy Treatment
What is Infrared light therapy?
- Infrared radiation therapy also called light therapy are use in physiotherapy to manage acute or chronic pain (mainly joint and muscle pain) in patients.
- In this therapy various wavelengths of light are focused to the parts of the body that have injuries.
- A key characteristic of infrared light is that it has the ability to get below the skin layers and provide a much greater depth.
- This in turn can be more effective in providing pain relief.
- This method of Physiotherapy is natural and painless and can provide numerous health benefits, without causing damage to the skin.
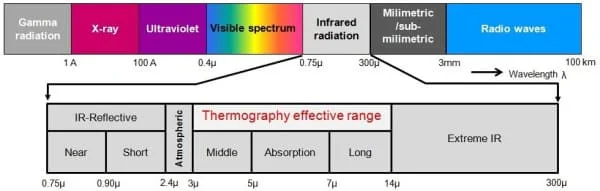
- Infrared (IR) or thermal radiation is a band of energy in the complete electromagnetic spectrum. IR are the radiations of longer wavelength than the red end of the visible spectrum and extend to the microwave region, i.e., from 760 nm to 1 mm.
- IR radiation is generated by Sun.
- Many ancient therapies have utilized sunlight for wound healing and pain relief.
- When Sun rays reach the ground, they get absorbed by gases or water molecules in the atmosphere.
- The human body is made of 70% water, so it can potentially accumulate a large amount of energy that could modulate biological processes by strong resonant absorption of IR radiation from sunlight mediated by water molecule .
Electromagnetic spectrum :
Purpose of Infrared Radiation Therapy
- The purpose of infrared light therapy application is to achieve
- Decrease in inflammation
- Pain control
- Wound care
- Tissue repair.
Classification of Infrared radiation
Depend on:
- International Commission on Illumination (CIE)
- International Organization for Standardization ( ISO ) 20473
International Commission on Illumination (CIE )
| Type | Wavelength | Photon energy (Hz) |
| IR A | 0.7– 1.4 µm (700-1400 nm) | 215– 430 |
| IR B | 1.4– 3.0 µm (1400-3000 nm) | 100– 215 |
| IR C | 3.0– 100 µm (3000 nm– 0.1 mm) | 3 – 100 |
International Organization for Standardization ( ISO ) 20473
| Type | Wavelength |
| Near IR | 0.78-3 |
| Mild IR | 3-50 |
| Far IR | 50-1000 |
Production of Infrared radiation:
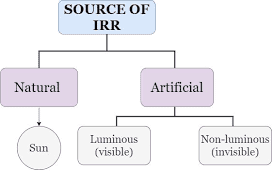
Types of Infrared Generators :
- Luminous generators
- Non-luminous generators
Luminous generators:
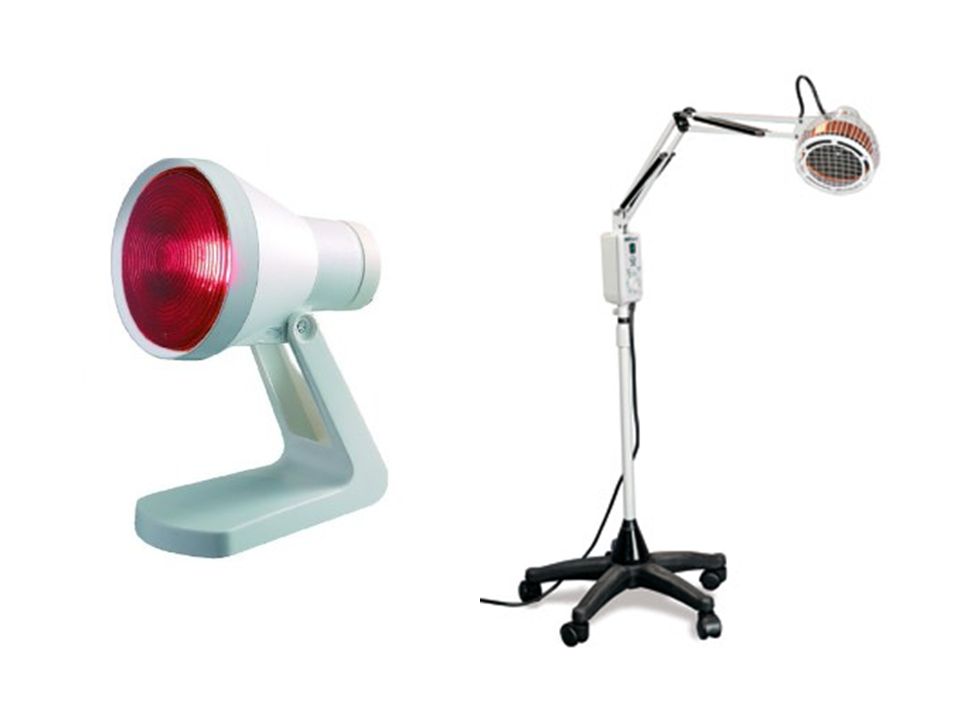
- The rays emitted from the Luminous generators are produced by one or more incandescent lamps.
- An incandescent lamp consists of a wire filament enclosed in a glass bulb.
- Which may be evacuated or may contain an inert gas at a low pressure.
- The filament is a coil of fine wire.
- A wire is made from tungsten.
- So that this material tolerates repeated heating and cooling.
- The exclusion of air prevents oxidation of the filaments.
- Which would causes an opaque deposit to form on the inside of the bulb.
- The passage of an electric current through the filament produces heat, infrared, visible, and a few ultra-violet rays.
- The front of the bulb is red to filter out the shorter visible and ultraviolet rays.
- Spectrum = form 350 to 4000 nm
- Wave-length = 1000 nm
Non-luminous generators:
Type -1:
- A simple type of element for producing rays consists of a coil of wire wound on a cylinder of some insulating material, such as fire clay or porcelain.
- An electric current is passed through the wire and produces heat.
- Infra-red rays are emitted from the hot wire and form the fire clay former, which is by conduction.
Type – 2:
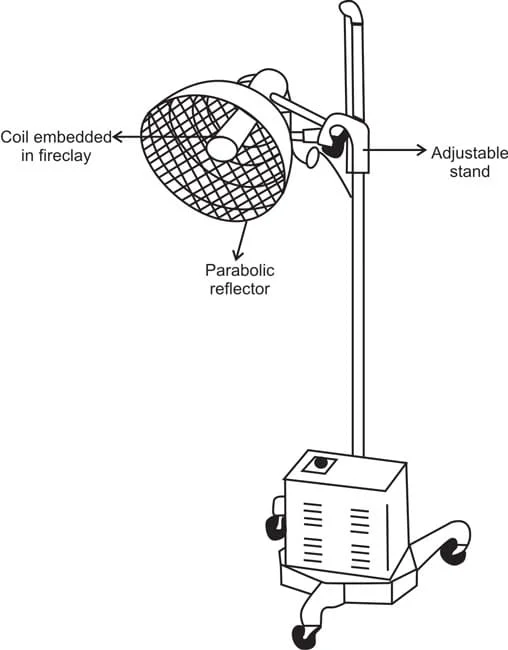
- The coil of wire is embedded in the fire clay or placed behind a plate of fire clay.
- The emission of the rays is entirely form the fire clay, which is commonly painted black, very few rays produced.
- Both elements are connected into the circuit by a screw -cap device and placed at the focal point of the parabolic or Gently curved spherical reflector.
- The reflector is mounted on a stand and its position can be adjusted as required.
Type – 3:
- In this type consists of a steel tube approximately 8 mm in diameter, within which is a spiral of wire embedded in some electrical insulator which is a good conductor of heat.
- Current is passed thought the central wire and produces heat.
- Which is conducted by the insulator to the steel tube which emits infra – red rays .
- The tube is bent into two or three large turns and mounted in a suitable reflector .
- Intensity = maximum
- Type 1 = 5 minutes
- Type 2 , 3 = 10 to 15 minutes
Difference between luminous and non luminous generators:
| NO | Luminous generators | Non luminous generators | |
| 1 | Sources | Electrically heated filament | Electrically heated resistance wire coiled |
| 2 | Gives | IR + visible rays | Only IR rays |
| 3 | Produce | Short IR | Long IR |
| 4 | Wavelength | 350 – 4000 nm [ max .= 1000 nm ] | 1500 – 12000 nm [ max. 4000 nm ] |
| 5 | Emission | 70 % near IRR 24 % far 5 % visible light 1 % UV | 90 % far IRR 10 % near IRR |
| 6 | Penetration | Epidermis , dermis & Subcutaneous tissue [ 5-10 mm ] | Epidermis & superficial dermis [ 2 mm ] |
| 7 | Heating | Deeply | Superficial |
| 8 | Uses | Chronic inflammation | Acute inflammation |
| 9 | Physiological effect | Pain reduction via counter – irritant effect | Pain reduction via sedative effect |
| 10 | Therapeutic effect | Heating | Sensory heating |
| 11 | Treatment time | 15 -20 minute | 20 -30 minutes |
| 12 | Distance | 40 – 60 cm form treated area | 75 -90 form treated area |
How Does Infrared Therapy Work?
- Infrared light has the ability to reach the muscles, nerves, and even the bones because it penetrates the inner layers of the skin up to a depth of 2 to 7 centimeters.
- Hence, it is among the most effective therapies used for healing inflammatory conditions.
- Infrared light gets absorbed by the photo receptors in cells which starts a series of metabolic processes, triggering natural processes of the body at a cellular level.
- It is estimated that the effectiveness of infrared light therapy may be due to nitric oxide.
- It is a molecule that is important for the health of the body’s arteries.
- Nitric oxide can help in relaxing the arteries, preventing platelet collection in the vessels, fighting free radicals to reduce oxidative stress, and regulating blood pressure.
- With all this, there is an increase in blood circulation that provides vital nutrients and oxygen to injured body tissues.
- Therefore, this therapy speeds up the repair and regeneration of injured tissues which in effect reduces pain and inflammation.
Depth of penetration of rays:
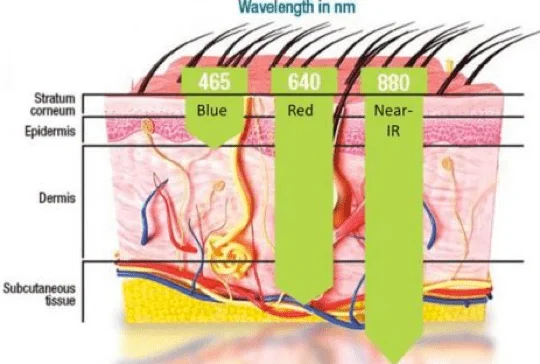
- It is of electromagnetic radiation depending on its wavelength and the nature of the material.
- The human skin will allow the passage of infrared, visible, and ultraviolet rays.
Absorption of rays in skin:
- Some radiations striking the surface of the skin will be reflected and some will penetration, scattered, refracted, and ultimately absorbed.
- Close to 95 % of the radiation applied perpendicular to the skin is absorbed.
- Water and proteins are strong absorbed to infra-red
- Any radiation entering into skin depends on structure, vascularity, pigmentation of skin, and wavelength of radiation.
Choice of apparatus for Infrared radiation Therapy:
- In many causes luminous and non luminous generators are equally suitable but in some causes one prove more satisfactory than the other.
- Acute inflammation or recent injury = non luminous generators
- Chronic injury = luminous generators
- One surface of body = single element mounted in a reflector is satisfactory
- Several aspects = tunnel bath
Preparation of the patient for Infrared radiation Therapy:
- Patient is placed in a comfortable position
- Clothing is removed form the affected part.
- First check the skin sensation [ hot + cold ]
- Instruction the patient for comfortable warmth if more excessive feel heat please inform the therapist and never touch the lamp
- Patient dose not move during treatment.
- Patient’s face is not exposed.
- Eyes must be shielded.
- Remove all metal objects like rings, safety pin, etc.
Arrangement of lamp and patients for Infrared radiation Therapy:
- The lamp is positioned so that it is opposite the center of the area to be treated.
- The rays strike the skin at the right angles, thus ensuring maximum absorption.
- Distance of the lamp form the patient = 75 or 50 cm
- Per-heated at least 5 minutes before heating
Application of Infrared radiation Therapy treatment:
- At the time of exposure = the intensity is low
- When vasodilation has taken place & increased the blood – flow = the strength of the radiation may be increased .
- It is achieved by moving the lamp nearer to patients or adjusting the variable resistance .
- End of treatment is skin should be red .
- After treatment patient should not rise suddenly form the recumbent position or go out into cold immediately .
Dosage of the Infrared radiation Therapy:
- Duration = 10 to 15 minutes
- During the day = several times
- Voltage of emitter of apparatus = 250-1000 Watt
- Wavelength = 800 nm to 1200 nm
Physical Effects of Infrared radiation Therapy
- Reflection
- Refraction
- Transmitted
- Absorption
Physiological Effects of Infrared Radiation Therapy
- Local cutaneous vasodilation = due to the release of a chemical vasodilator (histamine) as well as possible effect on the blood vessels, occurs after 1-2 mins
- Evident erythema = The rate and intensity of erythema depends on the rate and degree of heating.
- Reflex dilation of other cutaneous vessels = maintain normal heat balance
- Prolonged heating leads = sweating and eventually to cooling
- Sensation of warmth = due to stimulation of thermal heat receptor
- Increase in metabolism = According to Vant Hoff’s law, the chemical changes are accelerated due to heat, the heat produced by infrared radiation increases the metabolism due to which there is increased demand in the tissue for oxygen and foodstuffs which is maintained by an increased arterial flow.
- Nerve stimulation = Due to the effects of heating the thermal heat receptors in the skin are stimulated
Therapeutic Effects of Infrared Radiation Therapy :
- Pain relief
- Reduction of muscle spasm
- Joint stiffness
- Edema relief
- Skin lesion (psoriatic arthritis with psoriasis)
- Dermal ulcers (pressure ulcers)
- Increases the sensory nerve conduction velocity
- Increase in endorphins influencing the pain gate mechanism
- Increase the blood supply
- Increase the joint mobility
- Muscle relaxation
Benefits of Infrared radiation Therapy:
- Infrared light helps in cells regeneration and their repair.
- Infrared light can offer immense health benefits, ranging from pain relief to reducing inflammation.
- Ultraviolet light, which has damaging effects on the cells and tissues of the body, infrared light is safe.
- Infrared therapy technology in a way allows people to harness the benefits of sunlight, without getting exposed to harmful ultraviolet rays.
- Infrared light facilitates the circulation of oxygen-rich blood in the body, which can help in faster healing of deep tissues.
- It has been used extensively to reduce the pain caused by sports injuries, improve endorphin levels, and bioactivate neuromodulators.
- Infrared therapy has no side effects
- It is even used for infants in neonatal intensive care.
- Infrared radiations has proven to improve cardiovascular health.
- Its molecule nitric oxide plays an important part in keeping blood vessels healthy
- Infrared radiation physiotherapy has shown impressive health results in detoxifying the body.
- Major organs like kidneys, respiratory system, liver, and many others can be detoxified.
Indication of Infrared Radiation Therapy
- Osteoarthritis
- Bursitis
- Back pain
- Blunt trauma
- Muscle strain
- Neck pain
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sciatica
- Temporal mandibular joint pain (TMJ)
- Tendinitis
- Wounds
- Surgical incisions
- Spine injuries
- Sports injuries
- Tennis Elbow
Contraindications of Infrared Radiation Therapy
- Impaired cutaneous thermal sensations
- Defective arterial cutaneous circulation
- Dermatitis or eczema
- Tumors
- Skin damage due to ionizing radiation
- Fever
- Subjects with advanced cardiovascular disease.
- Hemorrhage
- Scar tissue or tissue devitalized by deep X-ray treatment or other ionizing radiations
- Superficial infections.
Dangers of Infrared Radiation Therapy
- Burns
- Skin irritation
- Eye damage
- Dehydration
- Low BP
- Electric shock
- Gangrene
- Headache
- Faintness
- Injury to the edge
Precautions of Infrared Radiation Therapy
- Pregnant women
- Hip or knee replacement
- Metal implants in their body.
- Photosensitive medicines





Please i need to know the Effect of IRR IN THE PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT OF ACL INJURY
I need more explanation of the effect of the IRR in the physiotherpy of ACL injury
Infrared light helps to relieve pain, swelling over the joint.