CHRONIC SHOULDER INSTABILITY
What Is Chronic shoulder Instability?
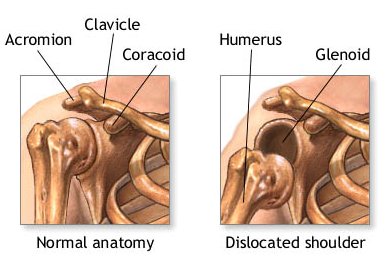
Chronic shoulder instability is a condition characterized by the repeated subluxation of the shoulder joint, or partial dislocation. It is often associated with sports that involve throwing, such as tennis or baseball. The shoulder joint is made up of three bones: the humerus, clavicle, and scapula. The humerus is the long bone in the upper arm that connects to the elbow joint, and it is also where the rotator cuff muscles are located. During a subluxation, this muscle group fails to hold the humerus in its proper position, which causes pain and discomfort.
It is often caused by a previous injury to the shoulder, and is characterized by repeated episodes of dislocating. Chronic shoulder instability can occur in any type of joint, but it most commonly occurs in the glenohumeral joint due to its wide range of motion.
It is characterized by pain, popping, and instability in the arm. Treatment options for chronic shoulder instability include physical therapy and last option is surgery.
- The shoulder joint is the most moveable joint in your body. It helps you to lift your arm, to rotate it, and to reach up over your head. It is able to turn in many directions. This greater range of motion, however, can cause instability.
- Shoulder instability occurs when the head of the upper arm bone is forced out of the shoulder socket. This can happen as a result of a sudden injury or from overuse.
- Once a shoulder has dislocated, it is vulnerable to repeat episodes. When the shoulder is loose and slips out of place repeatedly, it is called chronic shoulder instability.
- Shoulder dislocations can be partial, with the ball of the upper arm coming just partially out of the socket. This is called a sub-luxation. A complete dislocation means the ball comes all the way out of the socket.
- Once the ligaments, tendons, and muscles around the shoulder become loose or torn, dislocations of shoulder can occur repeatedly. Chronic shoulder instability is the persistent inability of these tissues to keep the arm centered in the shoulder socket.
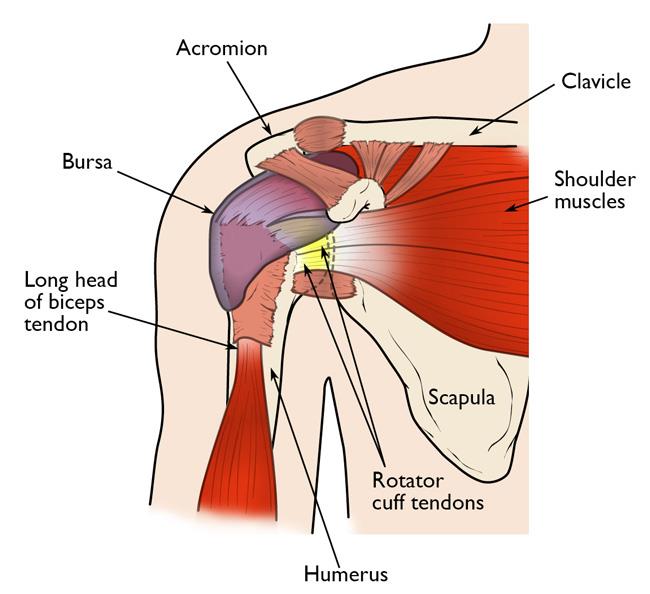
Anatomy Of The Shoulder Joint
- Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
- The head, or ball, of your upper arm bone fits into a shallow socket in your shoulder blade. This socket is called the glenoid.
- Strong connective tissue, called the shoulder capsule, is the ligament system of the shoulder and keeps the head of the upper arm bone centered in the glenoid socket. This tissue covers the shoulder joint and attaches the upper end of the arm bone to the shoulder blade.
- Your shoulder also relies on strong tendons and muscles to keep your shoulder stable.
What Are The Causes?
- Shoulder instability may have traumatic or atraumatic cause. There is a high recurrence rate after a primary shoulder dislocation, which is greatest in individuals < 20 years old
There are three common causes that a shoulder can become unstable:
Shoulder Dislocation
- Severe injury, or trauma, is often the cause of an initial shoulder dislocation. When the head of the humerus dislocates, the socket bone (glenoid) and the ligaments in the front of the shoulder are often injured.
- The labrum — the cartilage rim around the edge of the glenoid — may also tear. This is commonly called a Bankart lesion.
- A severe first dislocation can lead to continued dislocations, giving out, or a feeling of instability.
Repetitive Strain
- Some people with shoulder instability have never had a dislocation. Most of these patients have looser ligaments in their shoulders.
- This increased looseness is sometimes just their normal anatomy. Sometimes, it is the result of repetitive overhead motion.
- Swimming, tennis, and volleyball are among the sports that requiring repetitive overhead motion and that can stretch out the shoulder ligaments. Many jobs also require repetitive overhead work.
- Looser ligaments can make it hard to maintain shoulder stability. Repetitive or stressful activities can challenge a weakened shoulder. This can result in a painful, unstable shoulder.
Multidirectional Instability
- In a small minority of patients, the shoulder can become unstable without a history of injury or repetitive strain.
- In such patients, the shoulder may feel loose or dislocate in multiple directions, meaning the ball may dislocate out the front, out the back, or out the bottom of the shoulder. This is called multidirectional instability.
- These patients have naturally loose ligaments throughout the body and may be “double-jointed.”
Symptoms
Common symptoms of chronic shoulder instability include:
- Shoulder Pain caused by shoulder injury
- Repeated shoulder dislocations
- Repeated instances of the shoulder giving out
- A persistent sensation of the shoulder feeling loose, slipping in and out of the joint, or just “hanging there”
How It Can Be Diagnose?
- Doctor discuss your symptoms and medical history with you, after that your doctor will examine your shoulder.
- Specific tests help your doctor assess instability in your shoulder.
- Your doctor may also test for general looseness in your ligaments. For example, you may be asked to try to touch your thumb to the underside of your forearm.
Imaging Test:
Your doctor may order imaging tests to help confirm your diagnosis and identify any other problems.
- X-rays: These pictures will show any injuries to the bones that make up your shoulder joint.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This provides detailed images of soft tissues. It may help your doctor identify injuries to the ligaments and tendons surrounding your shoulder joint.
- MR arthrogram: To better visualize the labrum cartilage, a dye can be injected into the shoulder prior to doing an MRI. If shoulder instability is suspected, then an MR arthrogram should be performed instead of a plain MRI.
TREATMENT
Chronic shoulder instability is often first treated with nonsurgical options. If these options do not relieve the pain and instability, surgery may be needed.
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENT (CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT)
- Your doctor will develop a treatment plan to relieve your symptoms. It often takes several months of nonsurgical treatment before you can tell how well it is working. Nonsurgical treatment typically includes:
- Activity modification. You must make some changes in your lifestyle and avoid activities that aggravate your symptoms.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication. Pain relieving Drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen reduce pain and swelling.
- Physiotherapy: Strengthening shoulder muscles and working on shoulder control can increase stability. Your therapist will design a home exercise program for your shoulder.
SURGICAL TREATMENT
Surgery is often necessary to repair torn or stretched ligaments so that they are better able to hold the shoulder joint in place.
Surgical repair of a Bankart lesion:
- Bankart lesions can be surgically repaired.
- Sutures and anchors are used to reattach the ligament to the bone.
Arthroscopy:
- Soft tissues in the shoulder can be repaired using tiny instruments and small incisions.
- This is a same-day or outpatient procedure.
- Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgery.
- Your surgeon will look inside the shoulder with a tiny camera and perform the surgery with special pencil-thin instruments.
Open Surgery:
- Some patients may need an open surgical procedure.
- This involves making a larger incision over the shoulder and performing the repair under direct visualization.
Rehabilitation:
- After surgery, your shoulder may be immobilized temporarily with a sling.
- When the sling is removed, exercises to rehabilitate the ligaments will be started.
- These will improve the range of motion in your shoulder and prevent scarring as the ligaments heal.
- Exercises to strengthen your shoulder will gradually be added to your rehabilitation plan.
Be sure to follow your doctor’s treatment plan. Although it is a slow process, your commitment to physiotherapy is the most important factor in returning to all the activities you enjoy.
Physiotherapy Treatment
I. TREATMENT WITHOUT SURGERY
Non-operative physiotherapy management will vary in a case-by-case situation and each patient’s care should be individualised to target their specific goals. Physiotherapy management is largely impairment-based and response-driven as there is little high-level evidence to assist decision making but commonly includes:
- Education to prevent recurrence
- Postural re-education
- Motor control training of specific muscles during functional activities (rotator cuff muscles, scapular stabilisers)
- Strengthening in particular the deltoid, rotator cuff muscles and scapular stabilisers
- Stretching in particular posterior shoulder structures, pectoralis major and minor and any other muscles with flexibility impairments
Manual therapy targeting impairments of mobility in the glenohumeral, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular joints and cervico-thoracic spine.
EXERCISE THERAPY:
Physiotherapist will teach you some exercises which improves the strength of your shoulder muscles.
Treatment also depends upon symptom’s of the joint.
Pain relieving electrotherapy modalities like IFT (Interferential therapy), Ultrasound therapy, TENS.
Muscle strengthening exercise to strengthen weak muscle and stretching of tight muscle. Stretching exercise require extra care while strengthening exercise are given more importance to strengthen shoulder joint stability. (Exercise must be pain-free)

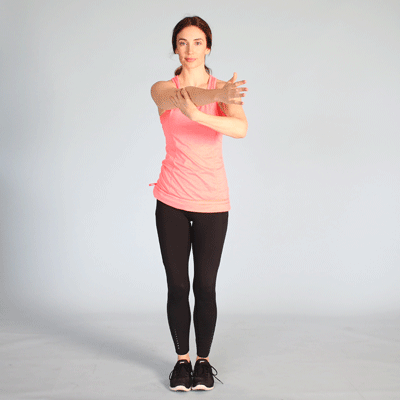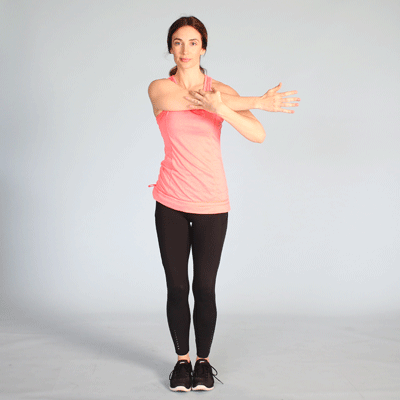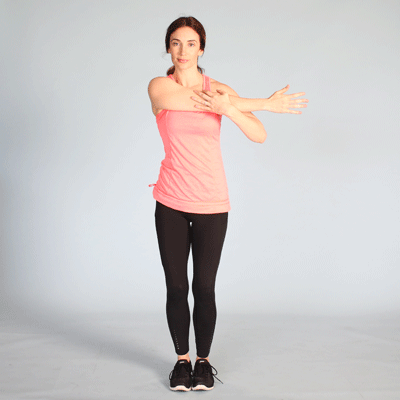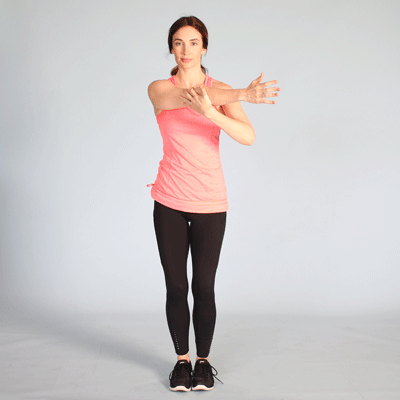


II. Post-Operative Treatment:
Rehabilitation after surgery should be based on each individual patient’s case with consideration to the type of surgery and surgeon’s preference where surgery is undertaken.
Thus, the post operative physiotherapy treatment depends on:
- Surgical procedure
- Surgeon’s protocol
- Mechanism of injury
- Concomitant injuries
- Tissue quality
- Impairments noted at evaluation




6 Comments