Ischemic Heart Disease:
What is Ischemic heart disease?
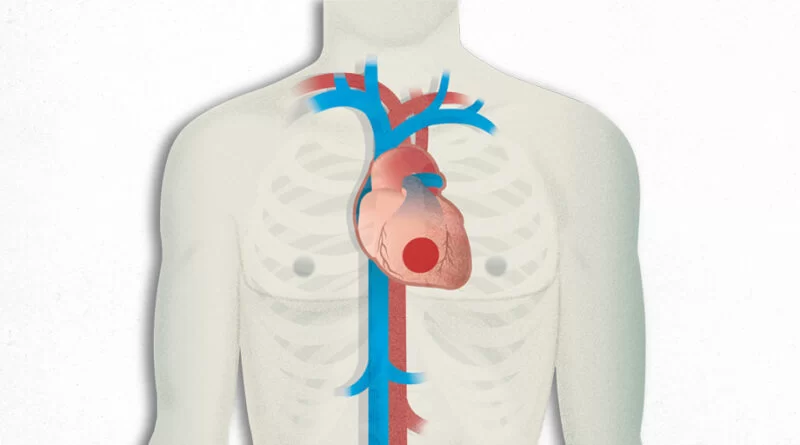
Ischemic heart disease, also known as coronary artery disease, is a condition in which the blood flow to the heart is restricted due to narrowed or blocked arteries. This can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and in severe cases, heart attacks.
Ischemic refers to a heart that is not receiving enough oxygen and blood. Heart disorders caused by blocked coronary arteries, commonly referred to as “ischemic heart disease,” “coronary heart disease,” “coronary artery disease,” or “coronary artery obstruction,” are characterized as feeding blood to the heart muscle.
Ischemic heart disease is a weakening of the heart caused by insufficient blood supply to the heart. Usually, coronary artery disease, a disorder that happens when your coronary arteries thin, is the cause of this decreased blood flow. Cardiac ischemia and ischemic cardiomyopathy are other names for ischemic heart disease.
Your heart needs to work harder as it ages to pump blood throughout your body. Your chance of developing blood clots, heart valve disease, heart failure, irregular heart rhythms, and other issues may arise as a result.
What are the symptoms of Ischemic Heart Disease?
- Chest pain, especially after physical exertion
- Dizziness or fainting
- Heart palpitations, which you could experience as your heart skipping or fluttering beats
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling in your feet or ankles
- Pain throughout the body
- Nausea
Causes of ischemic heart disease:
- When a buildup of fatty substances in the coronary arteries inhibits or interferes with your heart’s blood flow, it is referred to as coronary heart disease.
- Fatty deposits may ultimately form on the walls of your arteries. Atheroma is the fatty buildup, and atherosclerosis is the condition it causes.
- Atherosclerosis can be caused by lifestyle decisions including smoking and frequent drinking. Additionally, if you have diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, your chance of developing atherosclerosis increases.
Risk factors of Ischemic Heart Disease:
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol
- diabetes
- smoking
- being overweight
- not doing enough physical activity
- family history
- age
- ethnic background
How is ischemic cardiomyopathy diagnosed?
- catheterization of the heart to look for clogged arteries
- To examine your heart’s chambers and valves and how they are pumping blood, do an echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram to assess the electrical activity of your heart
- Using an electrophysiology test, you may assess the electrical activity in your heart in greater detail
- A chest X-ray, CT scan, or MRI are imaging tests that look at the architecture of your heart.
- Stress test to check the functionality of your heart during activity
- Treadmill test
- Radionuclide scan
- Coronary angiography
Epidemiology of ischemic heart disease:
Age:
Average: 64 years for men and 70 years for women
Gender:
High risk of males compared to female
Ethnicity:
Because of their relatively high-calorie diets, more sedentary lifestyles, and longer life expectancies, industrialized countries have the highest prevalence.
Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease:
The main goals of ischemic heart disease therapy are usually blood flow improvement and heart attack risk reduction. Our cardiologists and heart surgeons at Advocate Health Care offer the most recent therapies for ischemic heart disease utilizing a personalized, team-based approach.
Noninvasive treatments for Ischemic Heart Disease:
Depending on the severity of your symptoms, noninvasive therapies may help you increase blood flow. To manage ischemic heart disease and reduce your chance of developing new issues, your doctor may advise lifestyle modifications or drugs.
Medications:
- Lower cholesterol
- Lower blood pressure
- Treat underlying conditions, such as diabetes
- Reduce your risk of blood clots
Lifestyle changes:
- Eating a heart-healthy diet
- Getting better quality sleep
- Increasing activity levels
- Losing weight
- Lowering stress
- Participating in a cardiac rehabilitation program
- Quitting smoking
- Reducing alcohol intake
Surgery and minimally invasive procedures for the treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease:
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator
A tiny device called an implantable cardioverter defibrillator is inserted under the skin in the chest or belly. The implanted cardioverter defibrillator shocks your heart with tiny electrical charges to restore a normal rhythm when it notices an abnormal heartbeat. If you are susceptible to sudden cardiac death or life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, you may require an implanted cardioverter defibrillator.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy:
For those with heart failure, cardiac resynchronization therapy is a specialized treatment. Using a device known as a biventricular pacemaker aid in maintaining your heart’s regular beat. It consists of leads inserted into your heart and a pulse generator positioned in your chest just below the skin. The biventricular pacemaker aids in synchronizing your heart rhythm to improve the efficiency of your heartbeat and blood pumping.
Percutaneous coronary intervention:
A catheter-based treatment called a percutaneous coronary intervention is used to unblock an artery. Your doctor will insert a balloon into your coronary artery using a tiny catheter. Your artery is opened as the balloon expands, which compresses the plaque. Then they insert a stent—a mesh tube—into the artery. The stent, which has a pharmaceutical coating, offers assistance to keep your artery open over time.
Atherectomy:
A percutaneous coronary intervention may occasionally be ineffective because a blockage has calcified. In this situation, your doctor may use a catheter to place a tiny drill-like instrument or laser into your artery in order to dissect and remove the plaque.
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery:
Open heart surgery includes coronary artery bypass grafting. In order to circumvent one or more blocked arteries, your surgeon will use a blood artery from another region of your body throughout the treatment.
Preventing ischemic heart disease:
- eating a healthy, balanced diet
- being physically active
- giving up smoking
- controlling blood cholesterol and sugar levels
Summary:
Ischemic refers to a heart that is not receiving enough oxygen and blood. Heart disorders caused by blocked coronary arteries, commonly referred to as “ischemic heart disease,” “coronary heart disease,” “coronary artery disease,” or “coronary artery obstruction,” are characterized as feeding blood to the heart muscle.
Ischemic heart disease is a weakening of the heart caused by insufficient blood supply to the heart. Usually, coronary artery disease, a disorder that happens when your coronary arteries thin, is the cause of this decreased blood flow. Cardiac ischemia and ischemic cardiomyopathy are other names for ischemic heart disease.
Your heart needs to work harder as it ages to pump blood throughout your body. Your chance of developing blood clots, heart valve disease, heart failure, irregular heart rhythms, and other issues may arise as a result.
FAQ:
What causes ischemic heart disease most often?
Atherosclerosis is the most prevalent cause of myocardial ischemia. the bloody mass. Plaques associated with atherosclerosis may rupture and cause a blood clot. If the clot closes off an artery and produces severe, sudden myocardial ischemia, a heart attack might happen.
Can Ischaemic heart disease be cured?
Even though coronary heart disease has no known cure, medicines can help manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications like heart attacks.
What are the 2 types of ischemia?
restricted to one area of the brain: localized ischemia.
broad sections of the brain’s tissue are affected by global ischemia.
What are the ECG signs of ischemia?
A flat or sloping ST segment depression of at least one millimeter in depth is the most typical ECG indicator of myocardial ischemia. This research highlights other myocardial ischemia-related ECG symptoms that are far less typical yet may be just as significant.
What is the first-line treatment for ischemia?
Since beta-blockers are the only angiotensin-blocking drug with a survival benefit, they are regarded as first-line agents.



One Comment