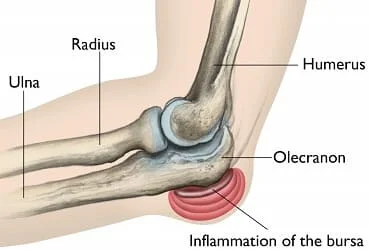
Olecranon Bursa
Olecranon Bursa Anatomy
The olecranon bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that lies between the olecranon process, the bony tip of the elbow, and the skin. It acts as a cushion and helps to reduce friction between the bone and the skin.
The bursa’s roof is in contact with the surrounding subcutaneous tissue, while the bursa’s floor rests on the triceps brachii tendon and olecranon. It is a synovium-lined sac with a thin wall and just a very little amount of fluid inside of it typically.
Development
The purpose of this bursa, which forms between the ages of 7 and 10, is to facilitate frictionless motion when the elbow is bent by the triceps brachii tendon and olecranon process, which are deep to the bursa.
Clinical Significance
The bursa may become inflamed, leading to olecranon bursitis, in reaction to direct trauma, infection, repeated injury, or inflammatory illnesses (such as gout, rheumatoid arthritis, or pseudogout).
In more severe cases, the doctor may drain the fluid from the bursa or inject it with steroids.
With proper treatment, most cases of olecranon bursitis resolve within a few weeks. However, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to prevent the condition from recurring.


One Comment