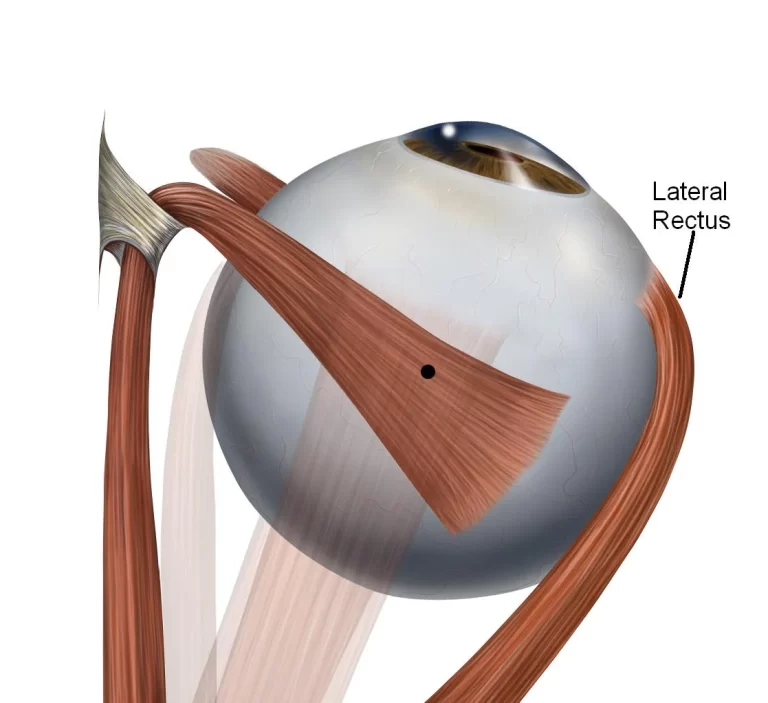
Lateral rectus palsy
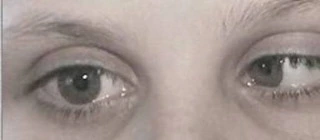
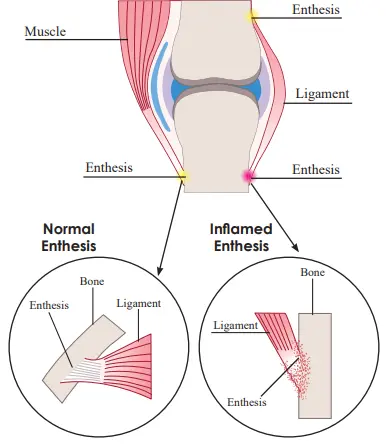
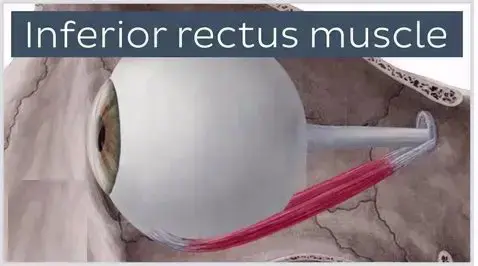
What is Lateral rectus palsy? Sixth cranial nerve palsy involves the lateral rectus muscle, damaging eye abduction. This is also called lateral rectus palsy and abducens nerve palsy. Abducens (sixth cranial) nerve palsy is the most familiar ocular motor paralysis in grown-ups and the second-most familiar in kids. The abducens nerve regulates the lateral rectus…