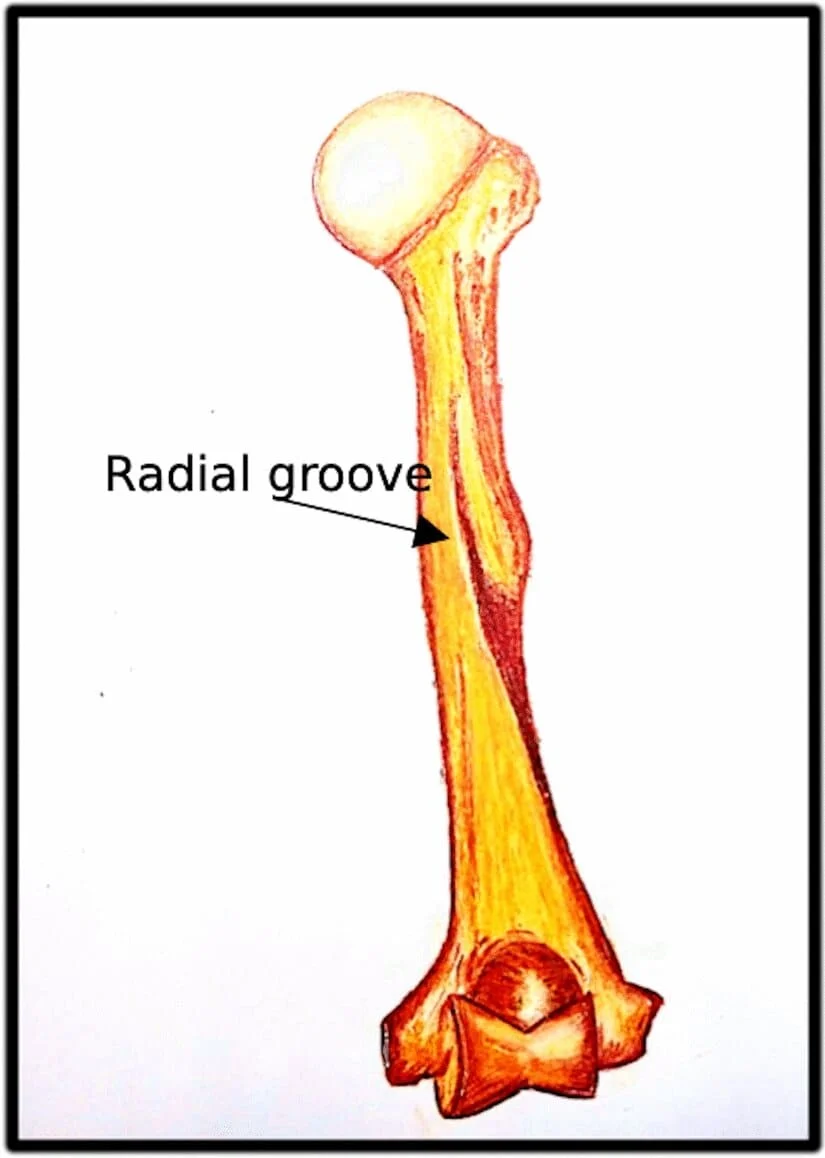
Radial Groove
In human anatomy, the radial groove, also known as the radial sulcus or spiral groove, is a shallow groove located on the posterior (back) aspect of the humerus bone. The humerus is the bone of the upper arm, and the radial groove is one of its distinctive features.
The deep brachial artery and radial nerve are located in the radial groove, often referred to as the musculospiral groove, radial sulcus, or spiral groove. It is situated in the middle of the humerus bone’s lateral edge. It begins at the inferior edge of the deltoid tuberosity and runs parallel to its posterior margin.
Here are some key points about the radial groove:
Location
The radial groove runs diagonally down the posterior surface of the humerus, specifically along the posterior shaft of the bone. It starts at the junction of the upper and middle thirds of the bone and extends downward toward the elbow.
Function
The primary significance of the radial groove is that it provides a pathway for the radial nerve. The radial nerve is a major nerve of the upper limb that arises from the brachial plexus, a network of nerves originating from the cervical and thoracic spinal nerves. The radial nerve innervates a number of muscles in the arm, forearm, and hand, and it also provides sensory innervation to parts of the forearm and hand.
Clinical Relevance
The radial nerve is relatively exposed in the radial groove, making it vulnerable to injury in cases of trauma or fractures of the humerus bone. Fractures or dislocations of the humerus can potentially lead to compression or damage to the radial nerve, resulting in symptoms such as weakness, loss of sensation, and pain in the arm and hand.
Surrounding Structures
The radial groove is located between the lateral and medial heads of the triceps brachii muscle, which is the primary extensor muscle of the forearm. The groove provides a distinct landmark for identifying the location of the radial nerve during surgical procedures.
In summary, the radial groove is a notable anatomical feature on the posterior aspect of the humerus bone. It serves as a pathway for the radial nerve, which is a crucial nerve for the innervation of various muscles and sensory areas in the upper limb.
FAQs
What is a radial groove of the humerus injury?
The spiral groove of the humerus is where radial nerve damage frequently happens. Compression of the nerve by the operating table’s edge and the humerus, arterial pressure cuffs, compression against the patient screen, or an arm board that is positioned incorrectly, causing a step, can all result in injury.
Is spiral groove and radial groove the same?
Important landmarks in connection to the radial nerve in the arm are the intermuscular septum and the spiral groove, commonly referred to as the radial groove.
Is the radial groove anterior or posterior?
Posterior.
Into a shallow depression on the back surface of the humerus (the radial groove), it travels obliquely downward into the posterior side of the arm, between the bellies of the medial and lateral head of the triceps.




One Comment