Reason for Knee Pain without Injury
What is the Reason for Knee Pain without Injury?
Exploring the Causes of Knee Pain Without Injury
A common condition that can significantly lower one’s quality of life is knee pain, which frequently brings to mind traumas from sports injuries, falls, or other traumatic experiences. Still, not every knee pain has an associated injury.
Understanding the underlying reasons for persistent knee pain is essential for successful management and therapy, as it affects many people without a history of trauma.
In this post, we’ll examine the several causes of knee pain that don’t include an injury as well as diagnostic tests, available treatments, and proactive steps like physiotherapy and exercise regimens.
Common Causes of Knee Pain Without Injury
Following are the conditions in which Knee pain occurs without any Injury.
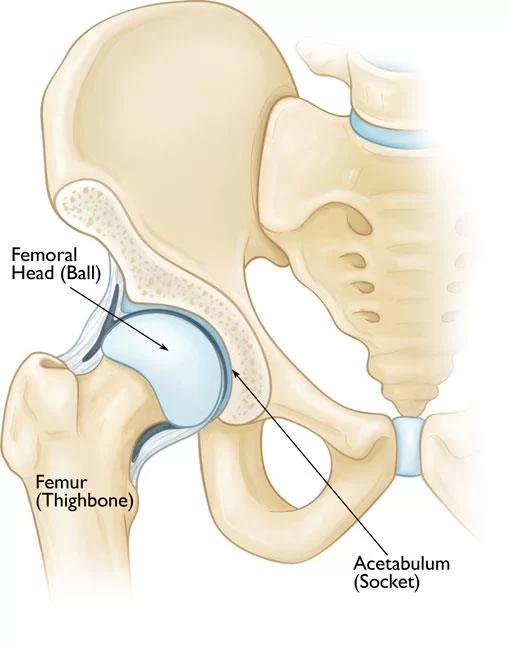
Osteoarthritis
Over time, knee pain may caused by osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease. It is caused by the cartilage in the knee joint breaking down, which causes discomfort and bone-on-bone contact. Obesity, aging, and genetics are common risks.
Physiotherapy can help manage osteoarthritis by increasing strength and mobility in the joints.
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
This problem, which is sometimes caused by overuse or kneecap misalignment, can hurt, especially while bending your knee. Physical examinations and imaging studies, such as X-rays, are the principal diagnostic tools. Exercises to address muscle imbalances and enhance joint alignment are frequently included in physiotherapy treatments for patellofemoral pain syndrome.
Tendinitis
Inflammation of the tendons around the knee is known as tendinitis. This illness may be exacerbated by age-related factors and overexertion. Anti-inflammatory drugs, rest, and ice are often used as forms of therapy. Rehabilitating the injured tendons with physiotherapy can aid in healing and pain reduction.
Bursitis
Pain may arise from inflammation of the bursae, which are tiny fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint when one bends the knee. Bursitis can be caused by repetitive motions or even an infection. With focused exercises, physiotherapy can help to improve joint function and reduce inflammation.
Gout
An accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joint caused by gout, a kind of arthritis, can cause knee pain. Genetic and dietary factors are major contributors to the development of gout. Exercises from physiotherapy can assist in preserving joint function and lessen discomfort in addition to medication.
Less Common Causes
Even though the above-mentioned reasons are more common, knee pain can also result from less common causes. The knee joint can be impacted by diseases such as psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, Lyme disease, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and nerve compression. For these diseases, physiotherapy can be used as part of the treatment strategy to increase joint mobility and lessen discomfort.
Symptoms of Knee Pain
Knee pain without a specific injury can manifest through various symptoms, including:
- Dull or sharp pain: Aching or stabbing sensations in or around the knee joint.
- Swelling: Visible or palpable swelling around the knee area.
- Popping or cracking sounds: Audible noises when moving the knee, indicating potential joint problems.
- Knee Joint Stiffness: Difficulty in moving the Knee joint such as extending or bending the knee.
- Redness and warmth: Inflammation can lead to visible redness and increased temperature around the knee.
- Instability: Feeling that the knee is giving way or unable to support your weight properly.
Diagnostic Procedures
Healthcare practitioners employ a number of diagnostic techniques to identify the underlying cause of knee pain in the absence of an injury:
Physical Examination: A comprehensive evaluation to evaluate knee function and symptoms.
Imaging tests: MRI and X-rays can be used to detect structural problems with the knee joint.
Laboratory testing: For diseases like gout or rheumatoid arthritis, aspiration of the joints and blood testing may be required.
Treatment Options
The precise cause and degree of non-traumatic knee pain determine the course of therapy. Typical therapeutic choices consist of:
- Medications: NSAIDs, anti-inflammatory medications, and, on rare occasions, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are recommended as pain relievers.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and physiotherapy can be very important for enhancing knee stability, strength, and mobility.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Exercise, weight control, and appropriate joint alignment and biomechanics are all critical to the long-term health of the knee.
- Injections: Hyaluronic acid injections can enhance joint lubrication, while corticosteroid injections may offer momentary respite.
- Surgical Interventions: In extreme situations, knee replacement surgery may be required.
When to Consult a Doctor?
If you are experiencing persistent knee pain without a clear cause, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. They can perform a physical examination, order imaging tests if necessary, and recommend appropriate measures to manage and alleviate your knee pain.
Prevention Strategies
There are several ways to avoid knee pain without getting hurt:
Keep Your Weight Normal: Excess weight puts additional strain on the knee joint.
Exercise and Strengthening: Physiotherapy exercises can assist in maintaining the knee joint’s strength and flexibility on a regular basis.
Appropriate Joint Alignment and Biomechanics: During physical activity, maintaining proper alignment and posture might help to lessen knee pain.
Dietary Modifications: Choosing the right foods is important while dealing with gout or other diet-related disorders.
Frequent Check-Ups: Early detection and treatment of knee problems can be achieved with routine medical check-ups.
Summary
Even though pain in the knee without an injury is a prevalent issue, it can frequently be effectively controlled with the right diagnosis, care, and addition of physiotherapy exercises. Maintaining knee health and stopping the development of diseases that cause knee pain need early action.
Through comprehension of the fundamental reasons and implementation of prophylactic actions, people can experience enhanced knee functionality and an enhanced standard of living. Physiotherapy is essential to the healing and rehabilitation process because it helps patients regain their comfort and mobility.
FAQs
How do you treat knee pain without injury?
Stay away from painful activities. Refrain from bearing weight on your knee. Utilise ice.
Can knee pain be normal?
Adults frequently complain of knee pain, which usually comes by regular wear and tear from daily activities including walking, bending, standing, and lifting. Athletes are also more prone to suffer from knee pain and issues if they run or participate in sports requiring rapid pivoting or jumping.
What disease causes knee pain?
In general, pain in the knee may be caused by bursitis, osteoarthritis, tears in the ligaments, or infection. Giving way, or instability, is yet another typical knee issue. Damage or issues with the meniscus, collateral ligaments, or patella tracking are typically linked to instability.
References
What is the Reason of Knee Pain without Injury? (2023, October 20). Orthopedic Treatment and Exercise. https://orthopedictreatmentexercise.wordpress.com/2023/10/20/what-is-the-reason-of-knee-pain-without-injury/https://orthopedictreatmentexercise.wordpress.com/2023/10/20/what-is-the-reason-of-knee-pain-without-injury/


2 Comments