Under Eye Swelling
Introduction
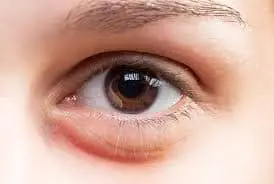
Under-eye swelling, sometimes referred to as “under-eye bags,” is a build-up or retention of fluid that delays the lymphatic system’s ability to evacuate lymph fluid, aiding in the body’s fluid balance.
The swelling is brought on by this under-eye bag, which is frequently the result of too much skin and tissue. As you age, the tissues around your eyes deteriorate, including some of the muscles that support your eyelids. As a result, fat that normally supports your eyes may migrate into your lower eyelids, giving them a puffy appearance.
This is why it happens more frequently. Because of the extremely thin skin on the underside of the eyelid, any fluid retention makes any vascular abnormalities or fat protrusion more noticeable. The orbicularis oculi muscles visible beneath the skin and/or blood breakdown products are frequently to blame for the purple appearance of under-eye bags.
Causes of Under Eye Swelling
Medical Conditions
Under-eye swelling can be caused by several illnesses that impact bodily tissues, including dermatitis, dermatomyositis, renal failure, and Graves’ disease. For instance, eyelid edema, or swelling around the eyes, can be brought on by renal illness, which damages the kidneys and causes high levels of protein leakage into the urine.
About 33% of those with Graves’ disease, an autoimmune illness that affects 1 in 100 Americans and can result in hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid), experience visual issues.
When your immune system targets the tissues and structures surrounding your eyes, it can result in Graves’ ophthalmopathy, which causes swelling and puffiness.
Allergies can also result in eye swelling because an external irritant can cause swelling of the conjunctiva, the protective layer that covers your eyelid.
Infections
Under-eye swelling is frequently caused by infections such as blepharitis (inflamed eyelids), conjunctivitis (eye infection caused by bacteria or a virus), and periorbital cellulitis (soft tissue and skin infection surrounding the eye).
Fatty Bags
Orbital fat pads, also referred to as fatty bags, are cushions that encircle and support the eyeball in the socket. It may result in puffiness and swelling around the lower eyes.
Vascular Circles
Under-eye puffiness could be caused by vascular rings, which are caused by dilated veins surrounding the eyes. Darker rings and blue-tinged edema result from these veins’ dilatation, and these effects worsen with age and facial volume loss.
Structural Shadows
Your facial anatomy may also contribute to the swelling under your eyes. Although exophthalmos, a disorder in which your eyes shift forward and seem to pop out, can also cause enlarged eyes, significant shadowing is not the only condition that can give the appearance of swelling in the eyes.
Under-Eye Hollows
Volume loss in the upper face can be brought on by aging. The lower eye area appears larger and swollen as a result of the tear trough, or under-eye, hollowing.
Diet
Certain factors, including smoking, meals heavy in fat, salt, or both, and excessive alcohol use, might result in eyelid edema, a swelling caused by vascular [The system of blood vessels in the body] congestion.
Symptoms of Under Eye Swelling
Swelling may accompany other symptoms in some illnesses, such as:
- eye discoloration
- itching
- bruising
- tearing
- discharge
- Puffiness: The most typical symptom is this one, which manifests as a prominent swelling of the skin beneath the eyes. It may be minor or severe, affecting one or both eyes.
- Discoloration: Depending on the reason, the skin under the eyes may seem red, blue, or yellow.
- Itching: Skin diseases or allergies can cause swelling around the eyes, which can be accompanied by itching.
- Tearing: Certain conditions that induce swelling, like allergies or clogged tear ducts, might result in excessive tearing.
- Pain: Injuries, infections, and more serious illnesses can all be indicated by painful swelling.
- Vision problems: Severe swelling occasionally presses against the eyeball, resulting in double or blurry vision.
Risk factors
Lifestyle
- High-sodium diet: Overeating salt can cause fluid retention, which can cause puffiness beneath the eyes.
- Lack of sleep: Lack of sleep can lead to fluid buildup under your eyes, which makes them puffy.
- Smoking: Smoking can aggravate under-eye puffiness because it irritates the eyes and increases fluid retention.
- Alcohol consumption: Alcohol can cause the body to become dehydrated and disturb sleep, two factors that can exacerbate puffiness around the eyes.
Allergies:
- Seasonal allergies: Histamines are released in response to allergens such as dust mites, pollen, or other substances, and this can result in swelling and inflammation around the eyes.
- Allergic reactions: Allergies to drugs, cosmetics, or other materials may also result in swelling under the eyes.
Medical conditions:
- Thyroid problems: One of the many signs of Graves’ disease, an overactive thyroid, is swelling under the eyes.
- Kidney disease: Fluid retention can occur anywhere in the body, including under the eyes, as a result of renal issues.
- Sinus infections: The face tissues may become inflamed and swollen as a result of sinus infections, potentially affecting the area under the eyes.
- Dermatitis: Eczema and atopic dermatitis are two skin disorders that can produce redness and swelling around the eyes.
Other factors:
- Crying: Because crying increases blood flow to the area, it might temporarily produce swelling under the eyes.
- Genetics: Some people just have genetic predispositions that make them more likely to develop under-eye puffiness.
- Aging: The skin surrounding our eyes loses elasticity and collagen as we age, which increases the likelihood that it will sag and puff.
Differential diagnosis
Inflammatory causes:
- Allergies: Histamine release can be triggered by allergic reactions to dust mites, pollen, cosmetics, or even drugs.
- This can result in inflammation and puffiness around the eyes.
- Conjunctivitis: Viral, bacterial, or allergy-induced pink eye can inflame the conjunctiva, resulting in redness, irritation, and occasionally swelling around the eyes.
- Blepharitis: Eyelid inflammation resulting from Demodex mites or bacterial overgrowth can produce redness, irritation, and swelling in the vicinity of the affected areas.
- Dermatitis: Eczema and atopic dermatitis are two examples of skin disorders that can cause redness, swelling, and itching around the eyes.
- Styes or chalazia: These are little lumps on the eyelid that are brought about by clogged meibomian glands or diseased eyelash follicles, respectively. They may manifest as painful, red swellings beneath the eyes.
- Cellulitis: Severe swelling, redness, pain, and warmth around the eye are the symptoms of this dangerous infection of the tissues that line the eyelids. Emergency medical attention must be given.
Fluid retention causes:
- High sodium intake: Consuming too much salt can cause fluid retention, which can appear as puffiness beneath the eyes, especially in the morning.
- Lack of sleep: Lack of sleep can lead to fluid buildup under the eyes, which results in puffiness.
- Menstrual cycle: Temporary fluid retention, especially under the eyes, might result from hormonal variations during the menstrual cycle.
- Crying: Because crying increases blood flow to the area, it might temporarily produce swelling under the eyes.
Other causes:
- Trauma: Eye injuries can result in discoloration, bruising, and swelling around the eyes.
- Dental problems: Facial swelling that reaches the under-eye region may be caused by infections or abscesses in the jaw or teeth.
- Sinus infections: Swelling beneath the eyes may result from sinus inflammation pressing on the surrounding tissues.
- Thyroid disorders: Under-eye puffiness and protruding eyeballs are two indications of Graves’ disease, an overactive thyroid.
- Kidney disease: Fluid retention can occur anywhere in the body, including under the eyes, as a result of renal issues.
Diagnosis
- Gathering information: Talking about your recent activities, symptoms, medical history, and any medications you are taking are all included in this. Your nutrition, lifestyle, and sleeping patterns will probably be discussed with the doctor as well.
- Physical examination: Examining the swollen area and looking for signs of redness, warmth, or soreness is part of this process. Your throat, nose, ears, and eyes may also be examined by the doctor to check for any indications of further illnesses.
- Blood tests: to examine kidney, thyroid, or allergy functions.
- Allergy testing: to pinpoint certain allergies.
- Imaging tests: To rule out underlying disorders involving the teeth, sinuses, or the eye itself, similar to CT or MRI scans.
Treatment of Under Eye Swelling
Dietary Changes
As was already mentioned, some foods, such as meals high in sodium, might influence how your body eliminates fluid through the lymphatic system. Put differently, diets heavy in salt have the potential to cause water retention and an excessive accumulation of bodily fluids, including on your face.
Face Massage
Fluid accumulation around the eyes can be released by massaging the face. shrinking enlarged blood vessels or lymphatics, use a cooling facial roller that offers a firm, chilly touch, or massage the area while applying moisturizer every day.
Fillers
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring moisturizing ingredient in dermal fillers are becoming a more and more common cosmetic surgery. Fillers restore volume and prevent the shadowing effect that causes under eyes to appear swollen, puffy, and weary. They also diminish the appearance of capillaries and are the most useful for structural shadows and other reasons that cause swelling under the eye.
Medications and Ointments
Allergy drugs and healing ointments like Aquaphor and CeraVe, which lessen itching and irritation, can often be used to treat allergies that cause swelling in the eyes. A dermatologist might prescribe medicine to treat irritated eyes that result in frequent rubbing.
Prevention
There are a few simple techniques for minimizing swelling beneath the eyes. Daily changes include reducing fluid consumption completely before bed, abstaining from smoking, and getting enough sleep. Consider limiting your exposure to allergens if you have allergies, and consider natural therapies like applying cucumber slices over your eyes to relieve swelling.
If an allergy is the cause of the swelling in the eyes, antihistamines also have anti-inflammatory qualities. Reduce or stay away from processed foods and salt in your diet. Excess sodium intake can result in water retention that collects and shows on the face, torso, and under the eyes. recommended consuming foods high in potassium instead, such as yogurt, bananas, potatoes, and dried apricots. While more water consumption can aid in the removal of extra sodium, potassium enhances urine output and lessens the effects of salt.
Applying cold ice compresses to the eye can help reduce redness and puffiness by vasoconstriction, or the narrowing of the blood vessels surrounding the eyes.
Conclusion
There are several reasons why under-eye puffiness might occur, from benign ones like allergies and sleep deprivation to more significant ones. Finding the underlying reason necessitates a physician’s experience and possibly more testing.
Diagnosing oneself is not advised. It is essential to see a doctor as soon as possible to ensure that you get a proper diagnosis and treatment to address the underlying problem and reduce swelling.
FAQ
Why is the under of my eye swollen?
Many illnesses, from minor ones like allergies or clogged tear ducts to more serious ones like organ failure, can cause swelling behind the eyes. Anyone experiencing puffy or swollen eyes, breathing difficulties, or excruciating pain should get medical attention right once.
What deficiency causes under-eye swelling?
One main cause of swollen eyes is believed to be a deficiency in either vitamin K or B12. To ensure you are getting all the vitamins and minerals you need, make sure your diet is rich in fruits and vegetables as well as water. Cut back on the salt you eat. Smoking is not only bad for you, but it may also cause puffiness and under-eye circles.
Can vitamin D deficiency cause eye swelling?
Studies have demonstrated that low serum vitamin D levels are associated with increased ocular surface inflammation and pro-nociceptive components in tear fluid.
Why are my eyes puffy and swollen?
Allergies, ocular trauma, and pink eye are a few more conditions that can result in puffy eyes. Home cures and lifestyle modifications such as using a cold compress, getting enough sleep, and cutting back on sodium frequently alleviate puffiness. Fluid accumulation around or near your eyes might result in puffy eyes.
How long does a swollen eye last?
Usually, within a day or two, eyelid swelling goes down on its own. See your eye doctor if, after 24 to 48 hours, it doesn’t improve. You should consult a doctor straight away if you experience any of the following symptoms: fever, double vision, vision loss, or abnormal protrusion or bulging of one or both eyes.
REFERENCE
Jesner, L. (2023, September 12). Under-Eye Swelling: Causes, Symptoms And Treatments. Forbes Health. https://www.forbes.com/health/eye-health/under-eye-swelling/