Periodontal Abscess
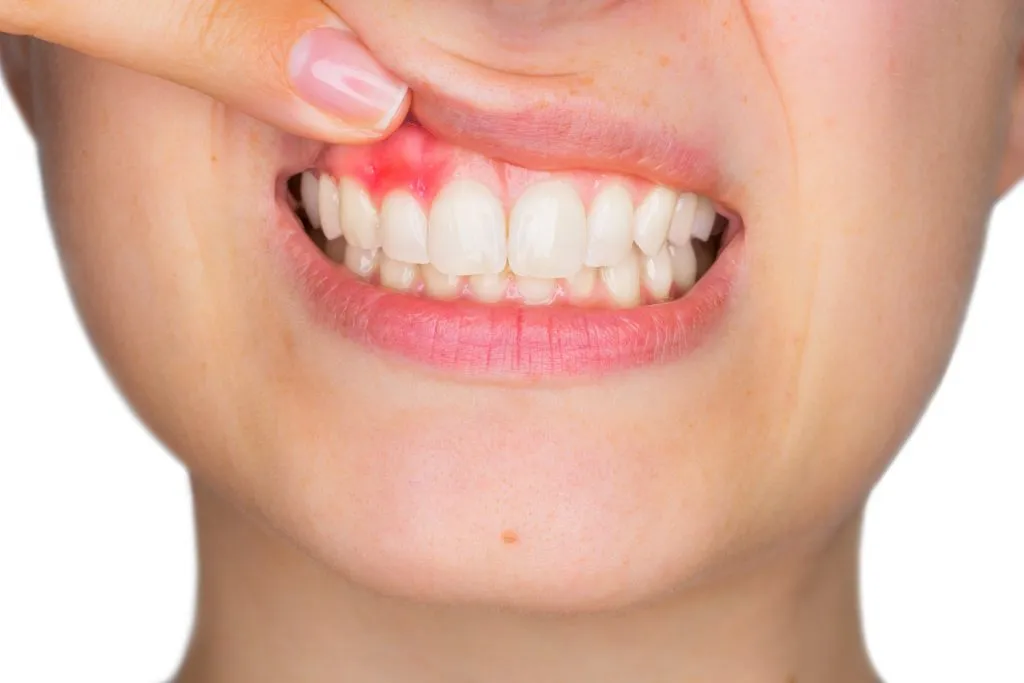
A periodontal abscess is a pus-filled pocket seen in the gum tissues. It seems to be a tiny red ball coming from the inflamed gum tissue. Serious gum disease (periodontitis), which pulls the gums away from the teeth, can result in an abscess. Deep spaces are left for germs to proliferate in as a result.
A periodontal abscess is an infected pocket that develops in your gum tissue. Periodontal abscesses can affect anyone, however, those who practice poor oral hygiene are more likely to have them. If left untreated, the infection from a periodontal abscess can cause difficulties by spreading to other parts of your body and mouth.
What is a Periodontal Abscess?
- A periodontal abscess is a pus-filled pocket seen in the gum tissues. It seems to be a tiny red ball protruding from the inflamed gum tissue. Serious gum disease (periodontitis), which pulls the gums away from the teeth, can result in an abscess. Deep spaces are left for germs to proliferate in as a result.
- A pocket of pus that can form on any area of your body, including the inside of your mouth, is called an abscess. A tooth abscess that affects the surrounding tissue might occur in certain people. However, an abscess on the gums might occasionally develop.
- Periodontal abscesses, also known as gum abscesses, are excruciating infections that can have life-threatening consequences. It’s critical to understand the warning indications of a Periodontal abscess and to get medical attention if one appears.
- An abscess in the periodontal region resembles a pimple or boil on the gums. It appears bloated and is typically darker than the surrounding gum tissue. There are several levels of edema.
Causes of the Periodontal Abscess
- An infection in the area between the gums and teeth is what leads to a periodontal abscess. Mouth germs are the source of this. Poor oral hygiene leads to periodontal disease, which is the cause of several periodontal abscesses.
- Plaque buildup behind the gum line causes periodontitis disease, an inflammatory disorder of the gums. Plaque is a colorless, sticky layer of microorganisms. If it isn’t eliminated from teeth by routine tooth brushing and flossing, the surrounding tissue may become infected. A periodontal abscess may grow as a result of this.
- An extensive periodontal pocket may also be the cause of a periodontal abscess. A periodontal pocket is an area where gum disease has spread around teeth. This area can support bacteria.
- Bacteria can proliferate here if food and plaque get stuck. Because a weakened immune system is less able to fight off infections, it can potentially worsen periodontal abscess. Your body’s defenses may be weakened by conditions like fatigue, stress, or a long-term sickness.
- If you have any of the following conditions, you are more prone to develop a periodontal abscess:
- Bruxism: a condition in which teeth are constantly clenched and grinding.
- Teeth that have been injured or traumatized.
- Restorations that are broken or damaged, such as dental fillings, crowns of gold, or bridges
Symptoms of the Periodontal Abscess
In their early stages, some oral disorders affecting the gums and mouth can go undiagnosed and present with minimal symptoms. A gum abscess does not behave in this manner
In the affected location, these abscesses may cause painful, constant pain. You might also see redness and swelling if you open your mouth and examine the region.
An additional symptom of a gum abscess is:
- Fever.
- Sensitive to temperature changes in food as well as beverages.
- Discomfort when chewing.
- A tooth that is loosened.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth caused by pus discharge.
- Pus discharge.
- Halitosis (bad breath).
- You have lymph nodes in your jaw and swollen neck.
- Chewing causes pain.
Risk Factor of the Periodontal Abscess
- Poor oral hygiene is one of the risk factors for periodontal abscess. The greatest risk factor is this one.
- If you do not remove tartar and plaque from your teeth regularly, your gums will become red and swollen. These symptoms are early warning signs of gum disease.
- Gum disease, if left untreated, can lead to tooth abscesses and bone loss.
- A diet heavy in sugar. Sugary meals and drinks raise your risk of cavities and gum disease.
The following are other Periodontal Abscess risk factors:
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Hepatitis C
- Arthritis, and Heart disease.d
- Alterations in hormones (in females).
- Some illnesses.
- Several drugs that interfere with salivary flow.
- Genetics.
Complications of the Periodontal Abscess
- Untreated, gum abscess can lead to various oral health problems, including destruction of the ligaments and soft tissues around your teeth.
- Your jawbone is weakening.
Tooth Loss. - According to research, germs from your mouth can spread to other body regions. In some situations, a periodontal abscess may be connected with Sepsis (blood infection).
- Inflammation of the heart.
- Pneumonia.
- An abscess in the brain.
If you suspect you have a gum abscess, contact your dentist straight once. The importance of emergency care in preventing complications cannot be overestimated.
Diagnosis of the Periodontal Abscess
Reviewing symptoms. A dentist will determine the presence of a gum abscess by reviewing your symptoms. Your dentist will ask you about your symptoms, including the duration of the abscess.
Performing a periodontal examination. They will take measurements of the pockets around the damaged tooth. This informs them whether or whether you’ve lost any bone in the region, and how much.
Taking dental X-rays. X-rays of the afflicted tooth will be taken by your dentist. This demonstrates the severity of the abscess and the extent of the infection.
Treatment of The Periodontal Abscess
An urgent oral issue that needs to be treated quickly is a periodontal abscess. Treatments for periodontal abscess include:
- Drainage of a periodontal abscess. The abscess required to be drained by a dentist. They will create a tiny incision (cut) in the gums and then use pressure to drain the infection.
- Treatment for gum disease. To cure the infection, your dentist might suggest gum surgery or scaling and root planing, which is a deep cleaning of the teeth.
- Antibiotics. your dentist may prescribe antibiotics in addition to treating the diseased region to lessen your chance of re-infection. This medication can also help to prevent the recurrence and spread of the illness to other parts of your body. If you are in discomfort, your dentist can prescribe pain relievers.
- Root canal therapy. If a periodontal abscess extends to a tooth and infects it, root canal therapy may be required to save the tooth.
A gum abscess cannot be treated at home. To relieve discomfort and sensitivity until you can visit a dentist, rinse your mouth with warm salt water or take an anti-inflammatory medicine like ibuprofen.
How to Prevent a Periodontal Abscess
- Maintain adequate dental hygiene to avoid a gum abscess.
- Brushing and flossing your teeth regularly are part of this. Make sure to brush your teeth twice a day, ideally just after eating.
- This minimizes the amount of plaque that builds up on your teeth and behind your gum line. Also, floss at least once a day to eliminate food and plaque that has been lodged in the gums.
- Make an appointment for frequent dental cleanings. Once every six months, have your teeth cleaned by a dentist.
- Your dentist can monitor the condition of your teeth and gums and detect oral issues early on to help you avoid illness and infections.
- Brush your teeth with fluoride toothpaste and a toothbrush made of soft bristles.
- Purchase toothbrushes and dental floss.
Summary
A periodontal abscess has a good prognosis if treated early. Your dentist can remove the infection and drain the pus, lowering the chance of problems. However, if left untreated, a gum abscess can grow and lead to a potentially fatal infection. Consult your dentist if you experience gum discomfort, swelling, or discharge.
FAQs
Will a periodontal abscess heal on its own?
An abscess in the periodontal region won’t go away by itself. It required medical attention.
What is the severity of a periodontal abscess?
Most periodontal abscesses are not fatal. However, because the illness might spread, it is critical to treat it as soon as possible. Though uncommon, an untreated periodontal abscess can lead to sepsis and other potentially fatal complications.
When should I make an appointment with my doctor?
Schedule an appointment with a doctor if you have a swelling, painful lump on your gums. They can offer advice for therapy and validate your diagnosis.
Is it possible to spread a periodontal abscess?
While an abscess is not transmissible, the bacteria that causes it can move from person to person. Bacteria can be transmitted by direct contact with contaminated saliva. You should avoid sharing cups, dining utensils, and other personal belongings if you have a periodontal abscess.
What is the last stage of a dental abscess?
Sepsis. If you do not get treatment for an abscessed tooth, the germs may move to your bloodstream and cause sepsis, a potentially fatal illness. If you have Chills or fever symptoms, you should get medical attention right away.
Is it possible to cure a periodontal abscess at home?
A periodontal abscess cannot be treated at home. While certain home cures (such as warm saltwater rinses) might provide temporary relief, they cannot heal the illness.
References
- Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.-b). Periodontal abscess. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24573-periodontal-abscess
- Higuera, V. (2023, February 24). Gum abscess. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/gum-abscess
- Johnson, J. (2020, January 27). Gum abscess: Everything you need to know. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/gum-abscess#summary
- NHS inform. (2023, December 5). Dental abscess | NHS inform. NHS Inform. https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/mouth/dental-abscess/