11 Best Exercises If You Have Diabetes
Exercise is useful for everyone, especially important if you are suffering from diabetes. Exercise can give all benefits to you, like decreasing your blood sugar and blood pressure, increasing your energy, and assisting you to sleep better. If physical, high-impact exercises are not for you, there have many other options to do.
Introduction:
If you are suffering from type 2 diabetes, exercising daily can help you manage your blood sugar levels and weight. It can also help you lower your risk of heart attack and stroke, lower cardiovascular risk factors, and boost overall health and well-being. Practice can also help to prevent the effect of diabetes in people who have prediabetes. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) promotes people to get at least 160 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity in a week.
Exercise benefits are independent of weight loss. However, observation with an exercise program has to be even to see ongoing results. It was a good idea to speak with a doctor before starting an exercise program if your lifestyle is sedentary to ensure there are no limitations or special precautions. It is always a good idea to initiate slowly and build up to your individual goal.
- If you are a male above 40 or a female over 50 years of age or have not exercised in over a year, then you should get medical permission to exercise from your doctor.
- If you operate a pedometer to count the number of steps taken per day, starting, you should seek to increase up to an extra 2400 steps/day. You can adjust this every week by just adding a few more steps until the target of 12,000 steps per day is reached.
- do exercise with a partner it could be a family member, friend, child, or grandchildren. Keeping a partner through this exercise journey can assist you on track and motivated.
- Select an exercise training you would enjoy. Ultimately, you are more likely to attach to that. You can accomplish any form of activity like aerobics, strength training, swimming, yoga, dancing, tai chi, or Zumba, just as long as you locate them interesting.
Importance of exercise for Diabetes:
- Activity reduced HbA1c values by 0.7% points in individuals of other ethnic groups with diabetes who lived taking additional medications and following a combination of diets and this progress occurred even though they did not reduce any weight.
- Resistance, aerobic, or combining the two types of exercise (combined training) were all equally effective at bringing down HbA1c levels in diabetics.
- Previously inactive older individuals with abdominal obesity who are at risk for diabetes can lower insulin resistance through both resistance training and aerobic exercise. Mixing the two types of training proved more useful than doing either one alone.
- Individuals with diabetes who walked at least 2 hours a week were slightly more likely to die of heart disease than their sedentary counterparts, those who exercised three to four hours per week further reduced their risk.
- females with diabetes who engaged in moderate exercise (including walking) or physical activity for at least 4 hours per week had a 30% lower chance of getting heart disease than those who did not exercise. These advantages stayed even after researchers adjusted for confounding factors, including BMI, smoking, and additional heart condition danger factors.
In general, one to three hours after eating, when your blood sugar level may be higher raised, is the best time to exercise. If you take insulin, it is necessary to test your blood sugar before a workout. Prior to exercising, if your blood sugar is below 100 milligrams per deciliter, eat a piece of fruit or a little snack to increase it and help you prevent hypoglycemia. Testing also done after 30 minutes later will indicate whether your blood sugar level is stable. Checking your blood sugar after any especially strenuous exercise or activity is also a fantastic idea. If you are taking insulin, your risk of producing hypoglycemia can be most increased 6 to 12 hours after the workout. Additionally, experts advise against exercising if your blood sugar is extremely high (over 250), as a workout may occasionally lead blood sugar to rise even higher.
How does exercise affect Blood Sugar?
When you do work out, your body requires extra energy from blood sugar, also named glucose. When you perform some activity,such as runt to catch the bus, your muscles uses glucose for fuel. The workout usually lowers your levels. If you take insulin or diabetes medications, increasing the intensity or duration of your workouts may need you to change your diet, your prescription, or both. Consult your physiotherapist before starting exercise to confirm which exercise is good for you.
The big gain comes when you do average exercise for a more extended time, like a hike. When you do that, your muscles absorb significantly more glucose. This helps lower your blood sugar levels. After engaging in vigorous exercise, your blood sugar levels may briefly increase.
Overly challenging exercise might increase blood sugar by making it more difficult for your muscles to use insulin. Exercise allows pump you up by forcing small tears in muscle fibers. When they recover, your muscles are stronger. However, if you aren’t used to performing physically demanding activities, such as HIIT (high-intensity interval training), they can cause such severe damage that it may take days for you to feel like moving again. During that time, your muscle cells can not use insulin well, and that will increase your blood sugar.
It may also rise if you skip workouts. If you are so sore you can not make your next gym session, you probably need to dial it down. There has no rush: It is better to make intensity gradually as you get used to a new routine.
How frequently should People with type 2 diabetes work out?
Available policies suggest that people with Type 2 diabetes do aerobics and strength training exercises per week. You can control your blood sugar by doing aerobics or strength training. But a mix of the two may be even more useful. According to these policies, you should aim for 180 minutes of aerobics and 2 to 3 strength training sessions every week.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends everyday exercise to meet these goals. But if that does not work with your program, they suggest not skipping your workout more than two days in a row. These suggestions are not appropriate for everyone with Type two diabetes. For illustration, weight lifting or high-intensity aerobics may not be safe if you have certain medical conditions in addition to diabetes. So it is best to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any regimen.
The insulin in your body can function more effectively if you practice at least 30 minutes of aerobic exercise five days a week. We are talking about exercise that gets your heart and lungs moving and kicks your blood flow into a more elevated supply. If you have not been active in a while, start with five to ten minutes a day and build up over time.when you want to start exercise, first consult your doctor and let him know about your exercise program.
Best Exercises for Type 2 Diabetes Management:
A well-rounded exercise practice should include a combination of exercises. These workouts can help you enhance and maintain your fitness, strength, and mobility.
Walking
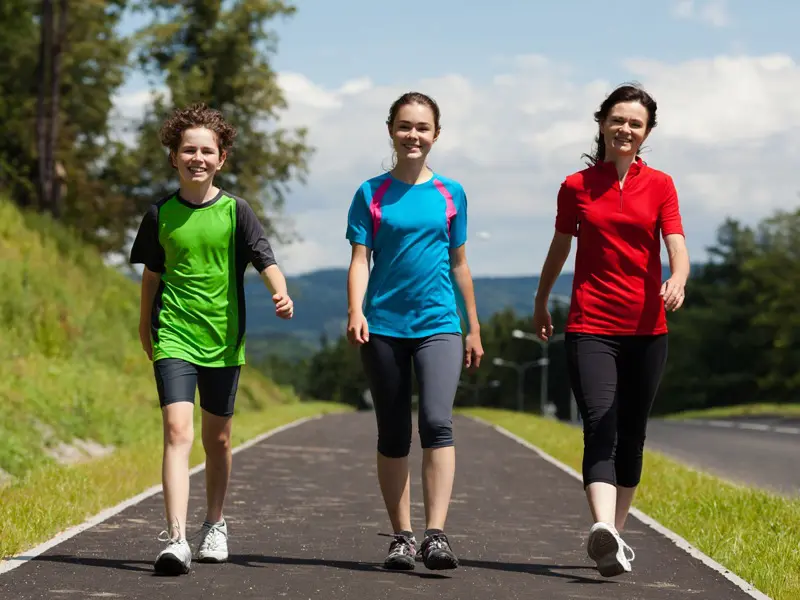

Walking is a low-impact exercise that multiple people like. Getting your steps can enhance your blood pressure, glucose, and cholesterol levels. And thirty minutes of fast walking or about a hundred steps a minute is a great way to meet the American Diabetic associations advice for everyday aerobic exercise.
You can also increase the intensity of your walks by adding exercises like stair climbing. But if you were not active before your diabetes was confirmed, consider beginning slowly and gradually upping the speed.
Running
With proper movement and your physician’s approval, you can work your way up from brisk walking to running. A lower risk of hypertension, high blood sugar, and high cholesterol has been associated with this faster-paced training.
Cycling

There has a purpose the stationary cycle has become so popular. Everyday bicycling can enhance everything from your heart and lung health to your balance and posture. But you do not require an expensive wellness bike to get initiated. You can hold an old bicycle and hit the outdoors or try a stationary bicycle at your local gym. And the study shows that cycling can enhance health outcomes for individuals who have diabetes.
Dancing
Adding dance to your practice can make your exercises more fun. Dancing is a heart-healthy exercise that can also enhance your fitness and blood sugar levels. One analysis saw that people with T2D who participated in a dance schedule were more motivated to stick to a routine than those who did another fitness schedule.

Water aerobics
There are a lot of reasons to take your training to the pool. Aquatic exercises like swimming are easy on the joints and may decrease blood sugar levels. They may also increase overall fitness, strength, and heart fitness in people with Type 2 Diabetes.
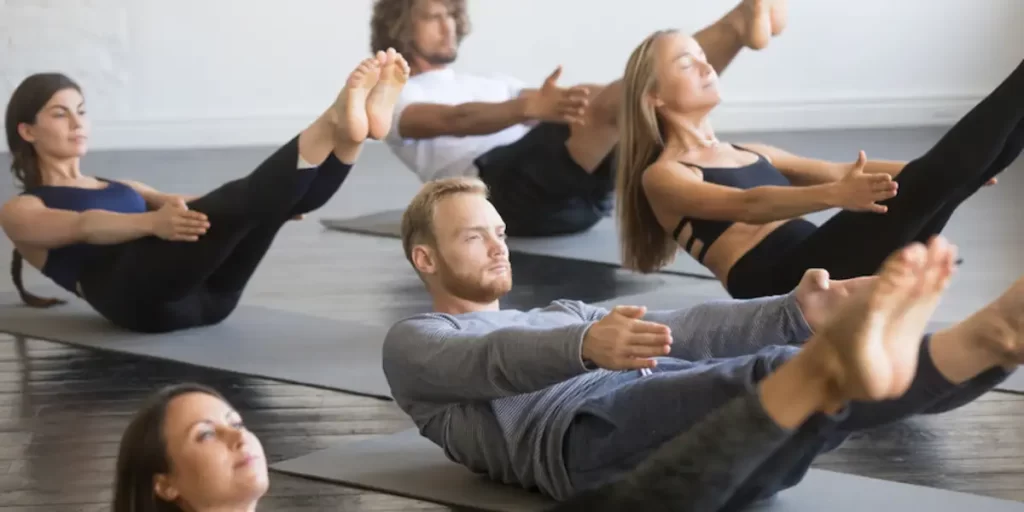

Pilates
Another low-impact form of training, Pilates deserves a spot on this list for good reason. It utilizes repetitious activities and breath control to support your core and enhance your balance and posture. An analysis showed that practicing Pilates helped players with Type two diabetes control their blood sugar.
Climb Stairs
This can be a beneficial and comfortable way to burn calories and reach your heart and lungs functioning faster, particularly if you have type 2 diabetes. Going up and down stairs for three minutes about a 1 hour or two after a meal is a good practice to burn off blood sugar. You can accomplish it anywhere there has a staircase, like when you require a break from work.
Strength Training
You perform this with free weights or resistance bands. Your blood sugar can be lowered, and it can also strengthen your bones and muscles. You get the most out of it if you do it two times a week in addition to your aerobic stuff. You can do multiple of these exercises at home, like:

Push-ups:
- To perform a push-up you are reaching to get on the ground on all four limbs, placing your hands slightly wider than your shoulders.
- Do not lock out the elbows; hold them slightly flexed. Set your feet hip-width apart and straighten your legs until you are standing on your hands and toes. when you come to this position.
- you have to Contract your abdominals and tighten your core by pulling your tummy button toward your spine.
- Take a deep breath in as you slowly bend your elbows and lower yourself to the ground until they are 90 degrees apart.
- breath out while contracting your chest muscles and pushing back up from your hands, returning to the initial position.
Sit-ups:

- Sit-ups are an awesome core muscle exercise that targets your core muscles, quadriceps, and lower back. Sit-ups won’t cause back pain if performed slowly and correctly, however, they can help digestion, build muscle, and improve posture over time.
- To do sit-ups you have to lie down on your back.
- flexed your knees and put your feet firmly on the floor to stabilize your lower body.
- Cross your hands to opposing shoulders or position them behind your ears, without tensing on your neck.
- Curl your upper half up toward your knees. breathe out as you raise. gradually lower yourself down, returning to your initial point. breathe in as you lower.
Squats:

- To do squatting exercise you have to Stand with feet a little wider than hip-width, toes facing front.
- Push your hips back flexing at the knees and ankles and pushing your knees slightly open as you.
- Keep your heels and toes on the floor, your chest up, and your shoulders back as you squat down.
- Aim to eventually reach parallel, meaning knees are flexed to a ninety-degree angle.
- Push into your heels and extend your legs to return to a vertical upright position.
Lunges:

- To do this exercise you have to stand in a split stance with the left foot roughly 3 to 4 feet in front of the right foot.
- Your trunk is straight, your shoulders are back and down, your abdominals are contracted, and your hands are relaxing on your hips. Flex the knees and drop your body until the back knee is a few inches from the ground.
- The back thigh should be parallel to the ground, the back knee should be pointing down, and your weight should be evenly distributed between both legs.
- Go back up to the initial position, supporting your weight on the heel of the front foot.
Gardening
If the idea of formal exercise is not for you, do not worry. Gardening time counts as both strength training and cardiovascular exercise. It brings your blood going (since you are walking, kneeling, and bending). It even builds muscles and allows your bones (since you are digging, raising, and raking). You are also outside, where your anxiety levels can be lower.
Yoga

It has been effective for about 5,000 years as a gentle exercise that can increase your strength and flexibility. Yoga can also assist with balance. The actions, poses, and focus on breathing may also ease anxiety and help build muscle. This may help to maintain regular blood sugar levels.
Tai Chi
This ancient Chinese practice uses deep breathing, visualization, and slow, controlled movements to increase strength. Additionally, it can improve flexibility, balance, and mobility. Your stress level may also be reduced by this moderate workout. It could help in preventing foot nerve injury.
Watch for Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar:
Check your blood sugar every 30 minutes if you’re planning a long workout, especially if you’re trying a new exercise or increasing the duration or intensity of your current routine. Reviewing almost every half-hour enables you to determine whether it is safe to continue exercising and whether your blood sugar level is normal, rising, or declining.This may be difficult if you are participating in outdoor workouts or sports. But until you are aware of how changes in your workout habits affect your blood sugar, you must use this safeguard.Blood sugar levels that drop during exercise can be dangerous.
Discontinue exercising if:
- Your blood sugar is 60 mg/dL (3.8 mmol/L) or more down
- You feel unstable, weak, or dizzy
- To raise your blood sugar levels, consume or drink something that has about 20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as Glucose pills or gel (see the label to see how many grams of carbohydrates these contain.
- 1/2 cup (4 ounces/118 milliliters) of standard (NON-diet) soft drink
- Check the label to determine how many grams of carbohydrates are in hard candy, jelly beans, or candy corn.
Recheck your blood sugar 15 minutes later, if it’s still too low, and consume another serving of 15 grams of carbohydrates. To obtain a blood sugar level of at least 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), repeat as necessary. Once your blood sugar levels stabilize, you can resume your workout if you didn’t previously.
Tips for exercising safely :
- To train your body for the workout, you should always do some kind of warm-up for 5 to 10 minutes, which gently increases your heart rate and gets your muscles heated before your primary workout.
- If you are exercising alone, including accomplishing heavy housework, recognize to start the exercise gently and build up.
- Cool down following a workout to avoid feeling fuzzy and dizzy; cooling down after an exercise helps your body return to a resting state.
- Finish 5-10 minutes by repeating the movements done in the warm-up.
- Sharpness and complete your efforts in dieting too.
Which exercise you should avoid?
- Avoid Very strenuous exercise
- Avoid heavy lifting or straining
- Avoid isometric exercises
- Avoid training in extreme heat or cold.
- Avoid breath-holding while lifting or pushing
- Avoid High-Impact activities.
FAQ
Which exercise is best for lowering blood sugar?
Usually over time, regular exercise can lower blood sugar. Exercises like mild cycling, walking, and other low-impact activities can be beneficial.
Which exercises should people with diabetes avoid?
Exercises to avoid if you have diabetes will depend on any complications you are experiencing as a result of your condition.
For example, those with hypertension should avoid harsh activity and heavy lifting.
Can diabetes be cured by exercise?
Some persons with diabetes can get their condition under control with diet and exercise. 2020 found that 60 percent of participants with early diabetes who underwent a highly controlled 1-year intensive lifestyle that included a low-calorie diet and regular exercise no longer met the criteria for diabetes.
How much exercise can reduce diabetes?
There has two new types of research accomplish that exercise for 30 minutes a day decreases your risk of diabetes by 30 percent, and walking for ten minutes after meals reduces your blood sugar by 20 percentage
How many times should diabetics exercise?
The plan is to get at least 140 minutes a week of moderate-intensity physical exercise. One way to perform this is to try to fit in at least 25 to 35 minutes of exercise every day. Include exercises that target all main muscle groups (legs, hips, back, abdomen, chest, shoulders, and arms) on two or more days per week.
When is the best time for diabetic patients to exercise?
The best time to exercise is typically one to three hours after eating because your blood sugar is more likely to be increased during this period. If you use insulin, it is important to test your blood sugar before a workout.
Which effect does exercise have on glucose levels?
Sugar stores in your muscles and liver are utilized when you work out. Your body uses blood sugar to refuel these reserves as it rebuilds them. Your blood sugar will be affected for a longer period with more intense exercise. Even four to eight hours after exercise, low blood sugar is still possible.
Is a physical workout more important than diet management for diabetes?
Even while individuals frequently compare the advantages of exercise, calorie restriction, and weight loss, it seems that each of these strategies may have unique advantages that add up to managing type 2 diabetes risk.
Which types of diabetes are helped by exercise?
A vital part of lifetime therapy for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes (T2D) is exercise. These suggestions are supported by research showing beneficial relationships between physical exercise and T2D morbidity and mortality as well as prevention and therapy.