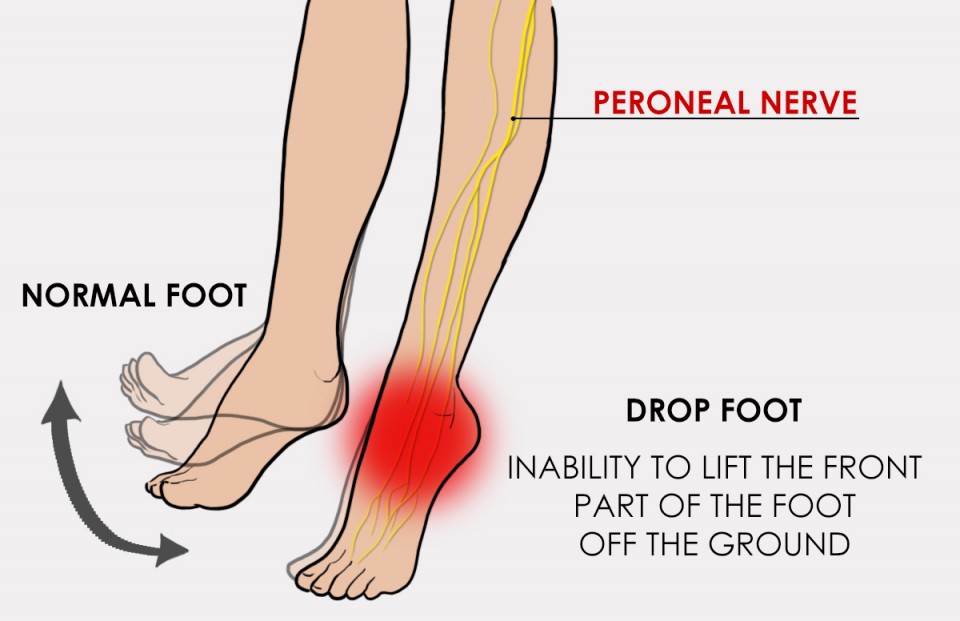
Foot Drop
What is Foot Drop?
A foot drop are used to describe somebody having an issue or inability to lift the front part of their foot.
Alternative Names
Peroneal nerve injury – foot drop; Foot drop palsy; Peroneal neuropathy
Introduction:
Foot drop is the inability to elevate (dorsi flexion) the foot because of weakness or dysfunction of the dorsi flexors (especially tibialis anterior) muscle
that raises the foot. If you have a foot drop, the front of your foot might drag on the ground once you walk…foot drop can happen to one foot or both feet at the same time. It will strike at any age. It will have several different causes. Treatment for foot drop is very consistent with the cause. drop foot will have an effect on young and old, men and women, and it can be so debilitating that even the most simple tasks will become difficult.
Relevant anatomy:
The common peroneal nerve is the smaller and terminal branch of the nerve that consists of the posterior division of L4, L5, S1, and S2. The nerve is often palpated behind the top of the fibula because it winds around the neck of the fibula. Commonly, with harm to the common peroneal nerve, there’ll be a weakness of the tibialis anterior and different key dorsiflexors of the foot.
Sciatic Nerve
The Sciatic Nerve is the thickest and largest Nerve within the body. It begins in the lower back and runs through the buttocks and lower limb with a root value of L4 until S3. It supplies biceps femoris,semitendinosus, semimembranosus, and adductor magnus muscle in the lower thigh just above the back of the knee sciatic nerve divided into two nerves which are tibial and peroneal nerve. those two nerves innervate different parts of the lower leg.
Peroneal nerve
It begins from L4, L5, S1, and S2 nerve roots and joins the tibial nerve to the sciatic nerve common peroneal nerve travels anteriorly around the fibular neck common peroneal nerve divides into the superficial and deep peroneal nerve. deep peroneal nerve innervates in the tibialis anterior muscle responsible for the ankle’s dorsi flexion.
Causes of foot drop
-Compression of nerve by a tight plaster cast
-Lumbo sacral plexus injury due to pelvic fracture
-Sciatic nerve injury, hip dislocation
-Injury to the knee, knee dislocation
-Fracture of the neck of the fibula
-Neurodegenerative disorder of the brain, Multiple sclerosis, Stroke, cerebral palsy.
-Motor neuron disorder
-Polio and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
-Injury to the nerve roots, spinal stenosis
-Peripheral nerve disorder acquired peripheral neuropathy.
-Damage to the peroneal nerve.
-Spinal cord injury.
-lumbar radiculopathy is also a common cause of foot drop.
Level of a lesion in sciatic nerve injury:
-High lesion(above the knee)both tibial and peroneal nerve is paralyzed.
-Low lesion (below the knee) spared peroneus longus and brevis muscle.
Type 1 Deep peroneal nerve injury
Lost-tibialis anterior, extensor halllucis longus,extensor digitorum longus and peroneus tertius.
Type 2 Superficial peroneal nerve injury
Spared-all above muscle innervated by deep peroneal nerve
Lost-peroneus longus & brevis
Sensation-over outer leg and foot
Symptoms of foot drop:
Difficulty or inability to lift the foot
abnormal gait which drags the front of the foot on the ground during walking (steppage gait)
an exaggerated swinging hip motion
tingling, numbness & slight pain in the foot
muscle atrophy in the anterior & lateral side of the leg
Clinical features:
-Unable to do dorsi flexion
-wasting is seen over the anterior aspect of the leg
-sensation lost over the lateral side of the leg, web space between the great and
second toe.
The gait of foot drop:
-High steppage gait
-the patient lifts the knee-high and slaps the foot to the ground on
advancing to the involved side.
Risk factors:
the peroneal nerve runs near the surface of the skin on the side of the knee, activities that compress this nerve can increase the risk of foot drop.
examples include: crossing the legs-people who habitually cross their legs can compress the peroneal nerve on their uppermost leg.
-prolonged kneeling occupations that involve prolonged squatting or kneeling, such as picking strawberries or laying floor tile can result in foot drops.
-wearing leg cast-plaster casts that enclose the ankle and just below the knee can exert pressure on the peroneal nerve.
Diagnosis:
-It occurs throughout examination wherever patients notice it’s difficult to walk on their heels.
-Subjective History: emphasis on any knee trauma, recent spinal or peripheral limb surgery, or family history of neurological disease
-Assessment of dorsiflexion
-neurological examination
-gait assessment
-plain x-ray
-magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) This test uses radio waves and a powerful magnetic field to elaborate detailed images.
-electromyography(EMG) is a test in which electrodes are placed within the muscles of the legs to see their electrical activity (how well they transmit signals and sensations)
-Nerve conduction study to examine how the nerves are functioning.
-SD curve
-Blood tests to check blood sugar levels, and to look for any potential toxins (poisons) that could be causing the condition.
Treatment of Foot drop:
treatment for foot drop will depend on the cause. early treatment may improve the chances of recovery.
Medical treatment-
Alternative treatments are amitriptyline, nortriptyline, duloxextine,pregabalin, and gabapentin. Local treatment with transdermal capsaicin or diclofenac can also reduce symptoms. Even if there is significant pain, narcotic medications should be kept to a minimum.
-conservative treatment shows a high incidence of recovery, keeping the ankle in a neutral position for nighttime. in daytime walking is allowed by using a ‘foot drop appliance’.
Physiotherapy treatment of Foot drop:
Physical therapy is used to strengthen foot and leg muscles.
Treatment might include:
Exercises to reduce tightness in dorsiflexors muscles.
Exercises to maximize and strengthen the muscle activity among the ankle/leg
Mobilization to the foot to boost the ability to movement
orthotics used to maintain the foot within the correct position throughout walking.
Gait re-education to reduce the result of compensations
Balance exercises to strengthen balance reactions and reduce the risk of falling
Benefits of physiotherapy for foot drop
- Reduced risk of falls
- Improved confidence
- Improved muscle strength
- Reduced muscle stiffness
Electrical stimulation (IG): Electrodes are placed on the lower leg and connected to a little pack that the patient wears on his or her hip. The pack sends impulses to the electrodes to cause the shortening of nerves inside the lower leg, which helps raise the leg. stimulating the nerve that lifts the foot.
Passive movement
stretching care of anesthetic foot
Deep tissue release
splintage-varieties of foot drop appliances used
- foot drop splint
- Dorsi flexion assist device
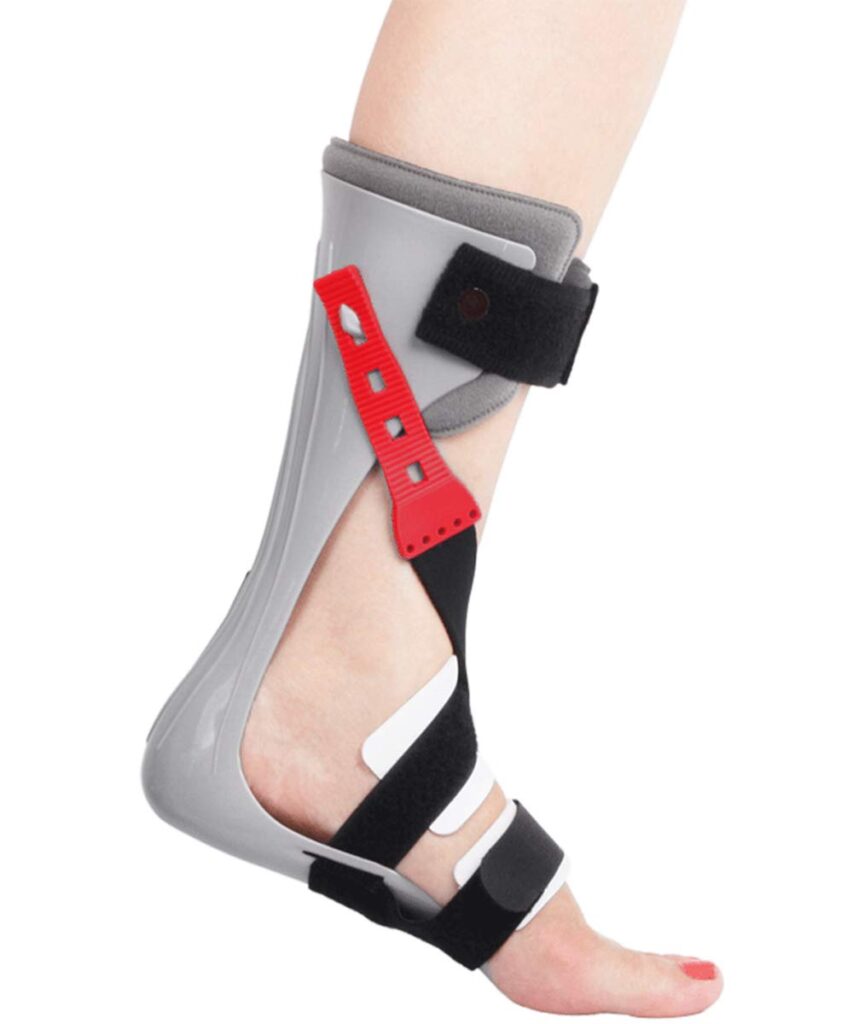
-ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) supports the foot with lightweight leg braces and shoe inserts.
Self-exercise to strengthen the lower leg muscles:
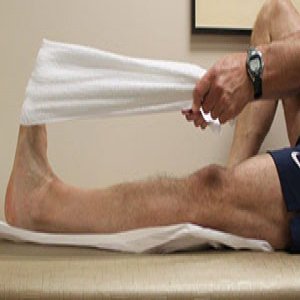
1-Towel Stretch
the patient should Sit on the ground with each leg straight and go in front of you. Loop a towel or exercise band around the affected foot and hold onto the ends with your hands. Pull the towel or band towards the body. Hold it for thirty seconds. Then relax for thirty seconds. Repeat three times.
2-Toe to Heel Rocks
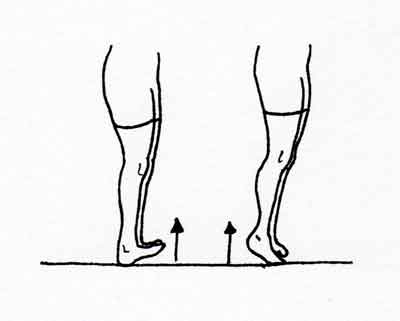
Stand in front of a table, chair, wall, or another study object you’ll hold onto for support. bend forward and rise up onto toes. Hold this position for five seconds. Next, bend backward onto your heels and raise your toes off the bottom. Hold for five seconds. Repeat the sequence six times.
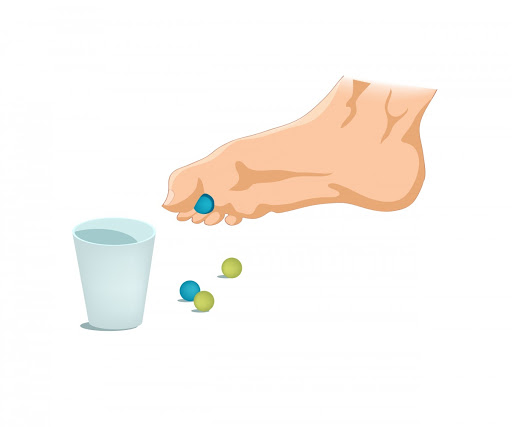
3-Marble Pickup
Sit in a very chair with each foot flat on the ground. Place twenty marbles and a bowl on the ground before you. Using the toes of the affected foot, pick up every marble and place it within the bowl. Repeat till you have got picked up all the marbles.
4-Ball raise
Sit in a very chair with each foot flat on the ground. Place a little round object on the ground before you (about the size of a tennis ball). Hold the object between your feet and slowly raise it by extending your legs. Hold
for 5 seconds then slowly lower. Repeat ten times.
Surgical treatment-
surgery is done if conservative treatment fails, repairs or decompresses a broken nerve fuses the foot and ankle joint, or transfers connective tissue from a stronger leg muscle.
-choice of surgery tendon transfers, for mobile foot drop tibialis posterior is used to substitute for the tibialis anterior.
In extreme cases, tibialis posterior may be transposed to regain active dorsiflexion by using the tendon not innervated by the common peroneal nerve, this surgery has been shown to be a lot of successful than nerve repair.




5 Comments