Matsyasana
What is Matsyasana?
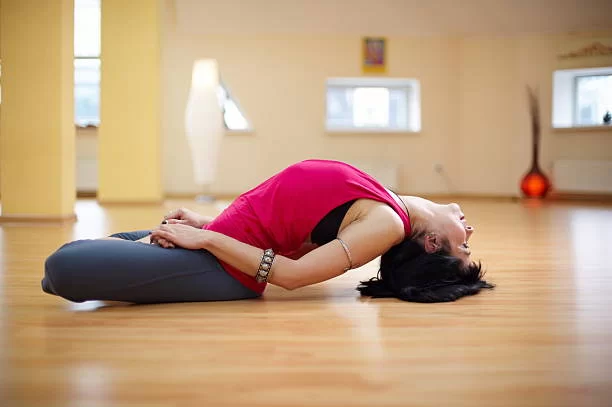
Matsyasana (Fish Position) is normally taught as a counter position to the inversion Shoulderstand (Sarvangasana), but it can be a forceful posture in it is right. Matsya means “fish” and Asana means “posture” or “position”. This asana is pronounced as mut-see-ahs-ana. It is traditionally designated as a back-bend, a position in which you expand your spine — in other words, arch your back. These types of positions are accepted to be stimulating.
Since Padmasana is beyond the capacity of most starting students, here we will work either with the knees folded, feet on the ground, or with the legs straight depressed against the ground. Fish Position (Matsyasana) stretches out the same upper body muscles that Shoulderstand (Salamba Sarvangasana) taxes. That is why, if you are doing an inversions series, you might follow Shoulderstand with Ear Pressure Position (Karnapidasana) and Fish Position. The fish position, if transferred out in the water, allows the body to stream quite simply like that of a fish; therefore the name.
Fish pose is a complete asana for elasticity and muscle strength. Yoga specialists advise matsyasana for thyroid functions, digestion, respiratory problems, posture improvement, and replacing stress. Fish Position is a bit of a chameleon (or maybe we should say cuttlefish since the cuttlefish is often known as the “chameleon of the sea”). You can modify it to whatever level of severity you are seeking and whatever requires your separate body may have.
For example, the Classically Fish Position is achieved with the legs in Padmasana (Lotus Position). A few newfangled yoga educators will add Lotus Position (Padmasana) to the legs, while others dial the severity way back with the use of props. The key benefits of this position come from the enormous arc in the upper spine, so whatever way you do it does not genuinely matter as long as your chest is well raised.
This position is a back-bend where the trainee lies on their back and raises the heart chakra by lifting on the elbows and drawing the shoulders back. The neck is lengthened, and the top of the head, the Sahasrara Chakra, is sharped backward. As the arch of the back deepens with exercise, and the heart and throat open further, and the top of the head may brush the floor. Fundamentally, no weight should rest upon the head.
What are the Health Benefits of Matsyasana?
Matsyasana helps in diminishing back pain. Along with that, this amazing yoga position can give you several benefits for a healthy body. We have jotted down some of the most common and successful matsyasana benefits you should be aware of in this position. Read and conduct fish position yoga every day.
As with any practice, it is best to consult a doctor ahead of your start, to avoid any sort of injury. Exercising this asana is a good way to increase the energy levels of one’s body and say goodbye to all that stress, anxiety, and fatigue caused by a frenetic daily schedule. Matsyasana or fish position is best for women’s reproductive organs, reproductive disorders, and patients agonizing from asthma, bronchitis, cervical spondylitis, hemorrhoids, and back pain. One must achieve this position frequently for maximum benefits.
Fish Position stretches the anterior of your body, counting the chest, abs, hip flexors, neck, and back, and captures parts of the body that are often mistreated, even within yoga’s asanas. Fish is a good counter position because the chin is lifted, the neck is curved back, and the spine is in extension, while in Shoulderstand, the chin is powerfully pushed, the neck is expanded, and the spine is in a position of flexion.
From a chakra stance, Fish has a lot of possibilities because it stimulates two important areas that are hard to extend. First is the vishudda (throat) chakra, which connects to transmission and self-expression. This is often condensed as speaking your truth, so if this area is blocked it means you keep things bottled interior that would be greater let out. There are not that many yoga positions where the throat is opened as it is in Fish. Fish The position also conducts observation of the Sahasrara (top) chakra on the top of your head. Again, there are not many yoga positions that put pressure on the top, which is restrained to intelligence and knowledge.
Improves Spinal Health:
As we have mentioned in advance, the fish position is a type of back bend that stretches the muscles of the back. Now, when you do that, your spine obtains strengthened and stabilized. It can also upgrade body position. Matsyasana strengthens back muscles and the spine. To continue correctly posture, maintaining the back is necessary while performing this position.
Tones Glutes:
Your glutes are fabricated of Gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus. Each of them plays a vital role in safekeeping your lower body healthy and in shape. The raised hip version of Matsyasana supplies extra stretch to the gluteal muscles. This not only makes them powerful but also tones the glutes.
Beneficial for Thyroid:
When you do matsyasana, you also stretch your neck toward a deep curve. In the occipital part of the neck, you have the thyroid gland, which is accountable for the construction of thyroid hormones that command how the body uses energy. The neck movement in matsyasana stimulates the thyroid gland empowering it to create several thyroid hormones.
Beat the Stress:
Sitting all day long at the desk with poor posture frequently conducts to stress in the back and neck muscles. Matsyasana helps in positioning the spine, relaxing the back and opening the lungs. All this helps stimulate the body-mind and decreases the stress in muscles. The matsyasana helps in stress reduction through significant breathing and better respiration. exercising matsyasana daily can help those with anxiety feel calm and restful.
Regulates Anxiety and Stress:
This position helps to control emotions and stress.
The flexibility of the Upper Back:
The replicated exercise of Matsyasana, with flexion of the neck, upgrades the flexibility of the neck. This flexibility in the neck helps in the exercise of various other yoga positions that are of forwarding level.
Improves Mood:
Another one of matsyasana’s benefits is its capacity to reduce your mood. When your back moves into the arch, your heart is raised and the muscles of the ribs obtain stretched. This eases more oxygen absorption and the delivery of pent-up emotions across the heart. This finally betters your mood.
Keeps Diseases at Bay:
Not many people know but matsyasana is known as the Desecrater of all Diseases. Regular exercise in this yoga can help in good digestion. It also relieves menstrual discomfort, withdraws the body, and helps you feel healthy and bright all day long.
Weight Loss:
If you try the leg-lifted variation of matsyasana, you can lock up some extra kgs by burning calories. When you lift your legs, the abdominal and obscure body muscles get attached. This further serves in the discharging of undesired fat from the stomach, waist, thighs, and hips.
Matsyasana for Thyroid:
Yoga specialists suggest mastaysana for thyroid disorders. Matsyasana causes the back to arch and expands the blood flow to the thyroid gland. The fish position stretches the neck and throat, thus refreshing the thyroid gland.
Promotes Respiration:
Matsyasana benefits those with respiratory issues. It helps control issues like asthma and bronchitis.
Benefits to women’s health:
The fish position benefits women’s reproductive systems. It helps command the menstrual flow and manages menstrual pain.
Improves Posture:
Matsyasana’s strategy focuses on enlarging the chest, strengthening the spine, and upgrading your posture. It arrested the body from bending ahead.
Stronger Neck And Abs:
The fish position benefits the muscles in the abs and thighs. It helps keep the spine flexible and upgrades blood circulation. Stretches the deep hip flexors (psoas) and the muscles (intercostals) connecting the ribs. Stretches and restorative the muscles of the belly and front of the neck. Stretches and restoratives of the organs of the belly and throat. Strengthens the muscles of the upper back and back of the neck.
Stretches Neck and Shoulders:
Fish position (Matsyasana) opens and stretches the neck muscles and shoulders.
Detoxifies the Body:
Matsyasana helps withdraw the body by safely keeping the bowels clean.
Reduces abdominal fat:
The leg lifted variation of the matsyasana position helps burn abdominal fat by manufacturing you raise the leg upward with a perfect arched back.
Benefits to endocrine glands:
Matsyasana restoratives the pituitary and pineal gland while also increasing blood flow to the brain.
Relieves constipation:
Achieving the fish position consistently helps manage constipation and regularise bowel movement.
Improves Digestion:
Matsyasana’s command stretches the abdominal and core muscles. This results in a gentle movement of the internal organs, upgrading digestion.
Opens the Chest:
Helps in opening the chest and rectifies round shoulders too.
Increases Lung Capacity:
This position supplies comfort from respiratory disorders by inspiring deep breathing, hence Fish Position (Matsyasana) increases lung magnitude to a great expanse.
Strengthens Back Muscles:
This position, with the spine, curved and bent backward, supplies a great way to strengthen the back muscles with the formation of the arch.
Increases Supply of Blood to Glands:
There is an expanded supply of blood to the cervical and thoracic regions of the back that helps tone the parathyroid, pituitary, and pineal glands.
Eases tensions at the Neck and Shoulders:
The exercise of Matsyasana conducts down the tensions and the rigidity at the neck and the shoulders. Fish Position also helps in curing the starting stages of spondylitis with the advice of an accomplished yoga teacher.
May reduce symptoms of hypothyroidism:
The same study establish a tremendous enhancement in contributors to hypothyroidism markers, stipulating yoga’s usefulness in handling hypothyroidism.
May improve quality of life (QOL) for people with chronic conditions:
Several studies propose that yoga is a successful alternative treatment for chronic health conditions. One of the more remarkable benefits may be the development in QOL.
May benefit people with rheumatoid arthritis:
A review found that yoga may help upgrade physical function, and disease activity, and hold strength in people with rheumatoid arthritis.
Can help subteens with self-esteem and learning capacities:
Fish Position every day, was unbelievably beneficial for upgrading self-esteem and increasing observation and learning.
Can improve mindfulness and self-compassion:
While these can be observed as common goals for many yoga practitioners, these benefits seemed to be especially significant in a high-stress population.
Anecdotally, many supporters report feeling animated after doing back-bends.
This position is also sometimes classified as a “heart opener” in classes.
What are the Preparatory poses for Matsyasana?
While Sarvangasana is not entirely a preparatory position, Matsyasana is often coursed as a counter-position after Shoulderstand. Though the fish the position is not as difficult, starters may essential to exercise some positions to finally ace Matsya asanas. Other preparations for this position might include:
- Baddha Konasana or the Butterfly Position
- Bhujangasana or the Cobra Position
- Virasana or the Hero Position
- Salabhasana or the Locust Position
- Dhanurasana or the Bow Position
- Setu Bandha Sarvangasana or the Bridge Position
- Supta Virasana or the Reclining Hero’s Position
- Urdhva Mukha Svanasana or the Upward Facing Dog Position
- Surya Namaskar or Sun Salutation
- Pavan Muktasana or Wind Release Position with Head Up
- Virasana
How to Perform Matsyasana?
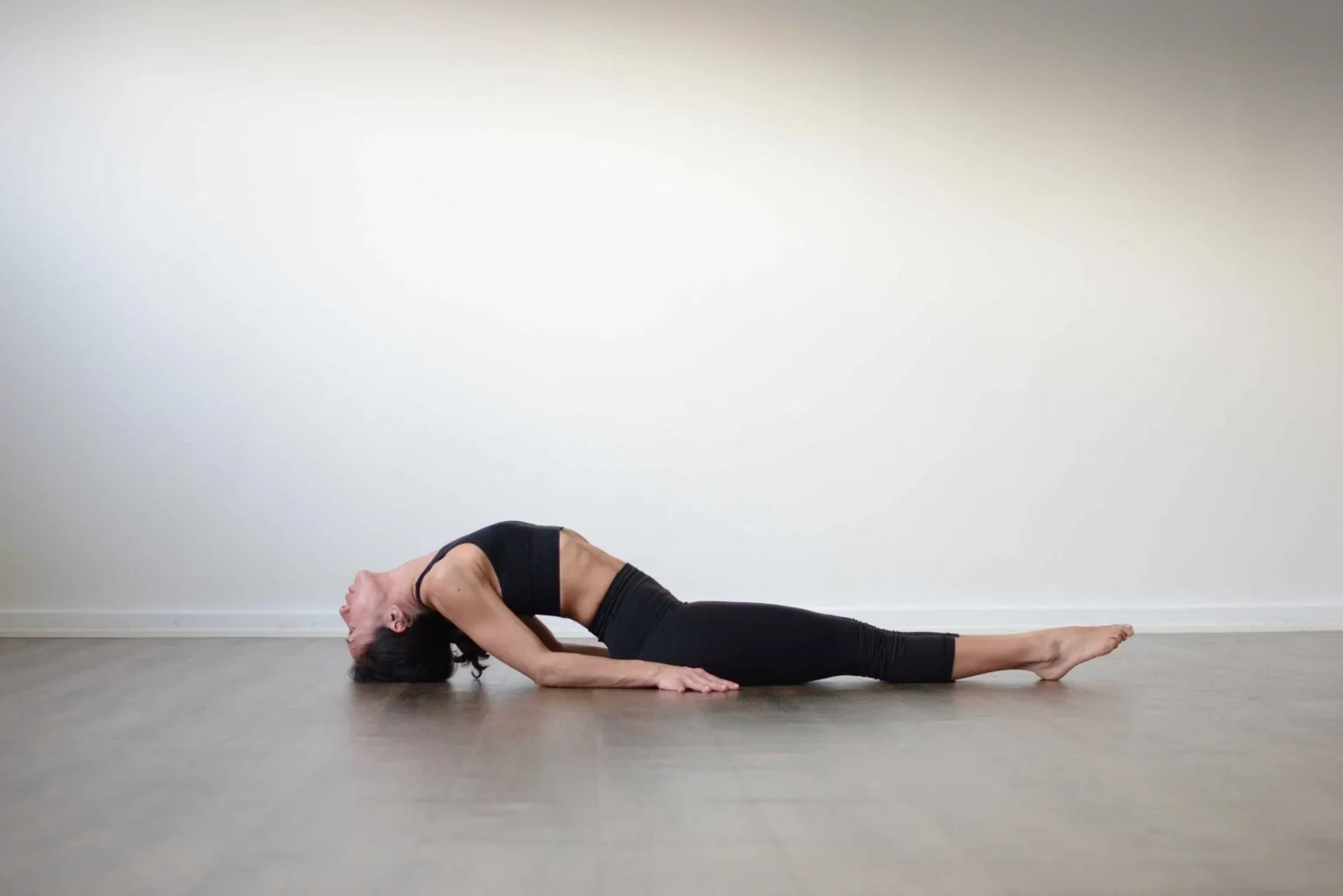
Start Fish Position (Matsyasana) by lying down in Savasana (Corpse Position). Stretch arms and legs out, modify the body and take a few breaths here.
Conduct your hands below the hips, palms facing down, and fold the arms at the elbows. Place the elbows on the ground close to your body.
Inspire and lift the full upper body (from the lower back to the neck) and slowly place the top of the head on the ground and twist the head backward.
Expire here when placing the top of the head on the ground.
Breathe out and push the elbows down into the ground, bend the body back and as you lower the top of the head onto the ground, arch the back lifting the chest upwards.
The lower body (across the buttocks to the heels) should be close to the ground and not lifted.
Apply the abdominal muscles, take the torso deeper first upwards and then downwards and make certain the weight of the body is not on your neck and head, but evenly diffused at the hips, elbows, and core.
Hold the position for as long as it is comfortable, taking moderate long breaths in and out. Modify this posture with every expires with eyes closed.
To deliver from Matsyasana or Fish Position, gently lift the head, lowering the chest and head to the floor and bring the hands back along the sides of the body.
Make certain the head is at complete rest and the lower spine is close to the ground. Modify in Savasana (Corpse Position) and take a few breaths here.
When ready, go back into the position afresh and detain it for a longer time and take the position deeper with every expiration.
How to perform Matsyasana by Watching a Video?
What are Follow up poses for Matsyasana?
- Matsyasana Variation with Padmasana or Fish Position with Lotus Position
- Camel Position (Ustrasana)
- Supta Virasana with Elbows (Reclined Hero Position with Elbows)
- Gomukhasana
- Setu Bandha Sarvangasana
- Supta Virasana
- Ustrasana
- Virasana
What are the Beginners tips in Matsyasana?
- If starters find it hard to adopt this position, they can start by lying on their back with their face upward and then folding their legs. Starters sometimes strain their neck in this position. If you feel any stiffness in your neck or throat, either lower your chest slightly toward the ground or put a thickly folded blanket below the back of your head.
- Make certain to raise your chest first, ahead of taking your head back.
- Your throat should be soft. Your neck should not be twisted back like a Pez dispenser. Rather, you should be able to speak in the position. Try saying your name.
- Circumvent turning your head when you are in the full expression of this position.
- If you are applying your forearms on the ground, the more you press down into them, the higher your chest will rise.
- Keeping your legs active and lengthening will help ease compulsion on your lower back.
- If you ever get dizzy or breathless, that is a clear sign to back off and come out of the position early.
- Make certain that you are on the top of your head. Defective locating of the head may lead to neck injuries or pain.
- Examine modifying this position during pregnancy or instantly postpartum, because modifying can disconnect the joints throughout your body. As such, most yoga teachers do not propose placing weight on your head through this time.
What is the Breath Awareness in Matsyasana?
- Inspire and Expire: Stretch the legs out in Savasana (Corpse Position) and expire relaxing the body.
- Inspire: Place the palms under the lower back raising the lower back a bit and conduct the elbows to twist.
- Expire: Twist the elbows and expire.
- Inspire: Lift the upper body away from the ground as you inspire conducting the head and shoulders up.
- Expire: Slowly conduct the head up and back and place the top of the head on the ground as you expire, and enlarge the chest out completely.
- Inspire and Expire: While continuing in this yoga position, start slow inspiration and expiration, and as you expire directly the chest out and conduct the head deeper down.
- Inspire: Slowly inhale and conduct the head up and release the head and shoulders.
- Expire: Bring the full body to relax as you exhale and stretch the whole back down to the ground or mat and take a few breaths.
What are the Variations of Matsyasana?
As mentioned above this position is typically achieved with the legs in Padmasana, a position that’s behind the capacity of even many accomplished students. Here’s a challenging variation of the position as described above. Achieve the position with the legs straightened on the ground, as described. Then with an expiration lift the legs off the ground to an angle of 45 degrees relative to the ground. Hold for 15 to 30 seconds, serious assiduously through the heels. Finally, lower the legs to the ground with expiration, and put the torso and head on the ground.
Fish on elbows, keeping head raised:
Lie down on your back with your legs symmetrical.
Twist your elbows back so your forearms endure on the ground. On an inspire, start to raise your chest toward the roof.
Thrust your forearms actively into the ground.
Deliver your head back but keep any weight off it. Rather, work the raising of your chest.
Actively reach across your legs and extremity your toes.
Secure your neck on the way down by inserting your chin ahead and lowering down.
Folded blanket below the top of your head:
Roll a blanket to about 3 inches in diameter and put it horizontally at the top of your mat.
Lie down on your back with your legs straight and the back of your head on the blanket.
Twist your elbows, open your shoulders, keep your forearms down, and raise your chest toward the roof.
Place the top of your head on the blanket. If it is too high, simply come down and regulate.
Lengthen across legs and point toes.
Secure your neck on the way down by inserting your chin ahead and lowering down.
Supported Fish with blocks:
Place two blocks at the crown of your mat, in a vertical line (parallel with your mat), 3–5 inches apart. The upper block should be on its elevated setting, and the second can be on medium. Feel free to play with heights to discover what works for you. Some people such as having both blocks on the same level, as it can increase the opening in the upper back.
begin with your knees twist and feet on the ground hip-width apart.
Lie down so your shoulder edge rest on the base block and the crown block supports the back of your head.
Modify arms by your sides with palms facing up.
You may straighten your legs, but if you feel any pressure in your lower back, simply re-fold your knees or regulate the blocks to a lower height.
If you find that the conventional form of Matsyasana is hard to accomplish, you can employ a prop such that it is simple for you to do. Variations of Matsyasana has been examined.
Matsyasana with Palms set Closer to Shoulders: Here you are essential to place your palms closer to your shoulders as they supply your neck with supplemental support.
Matsyasana with a Blanket Under your Head: You can place a blanket under your head such that your lower back and neck are not as strenuously-stretched.
Matsyasana with Bolsters Under Lower Shoulders: Practitioners can place bolsters under their lower shoulders such that they can push their heads back with facility and still, be able to stretch their neck and shoulders.
Matsyasana with Blankets Under Hips: This variation involves blankets being placed under the hips to diminish the strain they might otherwise experience.
Ardha Matsyasana: This variation of Matsyasana translates to the half lord of the fish’s position. It requires the practitioner to be seated and bend his / her body such that his/ her posture upgrades.
Below are some common variations of the yoga position Matsyasana with the base position as Fish Position (Matsyasana):
- Fish Position
- Fish Position Bolster
- Fish Position Bolster Variation Head On Floor
- Fish Position Blocks
- Fish Position Block Upper Back
- Fish Position Blocks Knees Positions
- Fish Position Flow
- Mountain Brook Position
- Fish Position Block Lower Back
- Fish Position Blocks Knees Bent
- Raised Legs Position
What are the Types of Matsyasana?
There are 3 types of Matsyasana.
- Vajra Matsyasana (Thunderbolt Fish Position)
- Vajra Padma Matsyasana (Half Thunderbolt Fish Position)
- Ardha Matsyasana (Half Lord of the Fishes Position)
Vajra Matsyasana
What is Vajra Matsyasana?
Vajra Matsyasana is also known as Thunderbolt Fish Position. Vajra means Thunderbolt, Matsya means Fish, and Asana means Position or posture.
What are the Health Benefits of Vajra Matsyasana:
- As per Vajrasana and Matsyasana, it extends the knees and abdomen.
- Quality for leg muscles and abdominal organs.
- The dorsal around is fully expanded, lungs are well extended, and neck muscles are strengthened.
- Thyroid and parathyroid are corrective.
- Helps construct digestive ailments and constipation.
- Spinal nerves are competent.
- Asthma and bronchitis.
- Redirects sexual energy to the brain for spiritual motivation.
- Legs are disconnected for meditative asanas.
- intellect and creativity are increased.
- For Women: Tones pelvic region. Separate pelvic congestion. Hypo Thyroids, Reproductive problems, Weak digestion.
What are the Preparatory poses for Vajra Matsyasana:
- Vajrasana
- Matsyasana

How to Perform Vajra Matsyasana?
In the sitting position, twist your left leg and conduct the foot to the left buttock. Twist your right leg and point the right foot next to the left foot.
Transfer the weight ahead onto the toes. Conduct your knees to the floor, toes together, heels apart, and sit connecting your heels in vajrasana variation.
Inspire and while expiring lean back slowly, take the support of the elbows one after another, and region the top of the head on the floor.
Keep the hands on their separate thighs or hold the feet.
Modify in the asana, breath normally, The back is arched, and the pelvis, abdomen, chest, and throat are extended.
The thighs should be together but if it’s awkward some detachment can be there.
To deliver the asana, conduct your hands to the floor and support your upper body with your elbows.
Slowly deliver the head from the floor, straighten the neck and lift your body from the hips.
Lift your knees and transfer your weight onto your toes. Straighten the left leg.
Adjust the right leg and lower the buttocks to the floor replace to the sitting position.
What are Follow up poses for Vajra Matsyasana:
- Advanced Vajrasana Series
- Supta Vajrasana
What are the Variations in Vajra Matsyasana:
If one cannot sit connecting the heels one can sit on top of the heels, as per normal vajrasana.
One can different the knees if it is heavy.
What are the Precautions and Contraindications for the Vajra Matsyasana:
Circumvent if there is knee or back pain.
What are the Dos and Don’ts in vajra Matsyasana:
Do’s:
Sit connecting the heels if practicable (sitting on top is a variation).
Keep your mouth shut.
Don’ts:
Overstretch and tension the neck or other parts of the body.
What are the Therapeutic applications for Vajra Matsyasana:
- Hypothyroidism.
- Reproductive problems.
- Weak digestion.
- Asthma and bronchitis.
Vajra Padma Matsyasana
What is Vajra Padma Matsyasana?
Vajra Padma Matsyasana is known as a Half Thunderbolt Fish Position. Vajra means Thunderbolt, Padma means Louts, Matsya means Fish, Asana
means Posture or position.
What are the Health Benefits of Vajra Padma Matsyasana:
- Stimulates the Vishuddhi Chakra and consequently restorative function of the thyroid gland.
- Extends the throat and chest muscles and builds up the neck and back.
- Thoughtful for asthma, bronchitis, and a rounded back.
- Good extends for the abdominal region and upgrades the digestion.
- Upgrades function of thyroid and thymus gland.
- Extends the pelvic region.
- Extends and strengthens the knees and ankles.
- Opens the chest and upgrades respiration.
What are the Preparatory poses for Vajra Padma Matsyasana:
- Vajrasana series.
- Padmasana preparatory movements.
- Paschimottanasana
- Naukasana
- Ardha Matsyendrasana,
- Bhujangasana
- Veerasana
- Matsyasana are all helpful

How to Perform Vajra Padma Matsyasana?
Lie down on the back.
Put the leg in Vajrasana, heel exterior the buttock.
The legs are straight, the arms are parallel to the body.
With the help of the elbows lift the chest far sufficient from the ground so that the crown of the head rests on the ground.
Apply the elbows for support, arch the back and lower the top of the head onto the floor.
Put the left foot on the right thigh close to the hip joint and comparably the right foot on the left thigh.
Hold the feet forcefully with the hands.
Inspire deeply across the nose and slowly expire between the mouth.
Endure 1 minute in the position. A leisurely return to the starting position.
Constant on both sides.
What are Follow up poses for Vajra Padma Matsyasana:
- Shavasana
What are the Variations in Vajra Padma Matsyasana:
Sit in Padmasana position. With the help of the elbows twist the upper body back slowly until the crown of the head rests on the ground. Conduct the palms together in the anterior of the chest. Endure 1/2 – 1 minute in the position inhaling deeply across the nose and slowly exhaling between the mouth. With the help of the elbows restore to the starting position. One does not have to follow the required order of the series. If some positions are not suitable then one can quit them out or change them everywhere.
What are the Precautions for the Vajra Padma Matsyasana:
Hip, knee, or ankle ailments, begin with caution. Circumvent if you have heart disease, ulcers, hernia, or other serious illnesses.
General Precautions for the complete series:
Circumvent if there is the knee, ankle, or back pain.
Ardha Matsyasana (Half Lord of the Fishes Pose)
What is Ardha Matsyasana?
Half Lord Of The Fishes Position (Ardha Matsyendrasana) is a transitional level seated twisting position. This position is a good stretch for the neck and shoulders. The English name, Half Lord of the Fishes Position, comes from the Sanskrit words Ardha means Half, Matsya means Fish, Asana means Position or Posture. This yoga position has other variations and can be mentioned as Half Spinal Twist Position or Vakrasana (which means twist). This yoga position usually emerges as a seated spinal twist with many variations. In this yoga position, the spine acquires its maximum twist at the upper back with the thighs resting over each other and with the support of the arms, the torso gets its bend.
Ardha Matsyendrasana (Half Lord of the Fishes Position/Seated Twist Position) is a deep, recuperative twist that is both strengthening and recharging. Your full torso twists in the position, which improves circulation, helps with digestion, and upgrades spinal mobility.
It accepts me to feel like my total body is start wrung out after I have been animated and warmed up from previous positions. When I was younger—ahead. I even realize what yoga was. I used to exercise this position after running all over the area during soccer exercises. It is one that’s been a strength to me all my life.
One of the considerable things about yoga is that it puts you in positions you normally do not do in the normal course of your day. operating in dissimilar ways approach places where you did not even acquire you were holding tension. This is certainly true of deep twists, such as Half Lord of the Fishes.
What are the Health Benefits of Ardha Matsyasana?
Half Lord of the Fishes is good for stretching the side body, your outer hips and thighs, upper back, and neck, and upgrading spinal mobility, opening
your shoulders and chest, structure strength in your upper back, enlarge your spine, and stretching the front of your thighs. It can also help restorative digestion. It is important to keep these areas insecure and mobile to check pain from repetitive stress injuries. Bends such as this can also help constipation. Mainly good if you have been functional at a desk all day. Can replace tension in the thoracic (mid) spine. Massages the abdominal organs and increases the digestive liquid making it useful for waste of appetite and constipation. Applicable for diabetics, with a concentration on the pancreas. Adjusts the secretion of bile and adrenaline.
Exercise of Half Lord Of The Fishes Position has a spinal twist while the arms are bound together. The benefits of this position are mentioned below:
Stretches, Strengthens and Lengthens:
Exercise of Half Lord Of The Fishes Position will stretch the neck muscle, back muscles, hip muscles, leg muscles, and upper abdominal muscles to the maximum. This stretching upgrades the elasticity of the muscles and gives them a toned look. This yoga position is a good hip opener and can be part of the exercise of hip opener series of yoga positions. This position flexes the lower part of the body making the hip powerful and toned. Stretches
and animate the spine. Stretches the muscles on one side of the body during compressing the muscles on the other side.
Flexibility and Range of Motion:
Half Lord Of The Fishes permits the spine to adjust from the base of the spine to the very top. It quality the spinal nerves and ligaments. Also conducts more blood to the spine. This increases the elasticity of the spine thereby improving the range of motion of the spine to construct the practitioner for advanced-level positions. Increases elasticity, mainly in the hips and spine. Increases the flexibility of the spine, tones the spinal nerves and improves the functioning of the spinal cord. disconnect the hip joints, and often stiffness.
Chest, Diaphragm, and Breath:
With the bend in the spine, this position also inspires the neck, shoulders, and chest opening. With the upper body and chest beginning up, the professional will be able to breathe deeper and better. With deeper breathing, it becomes simpler to hold the position for a longer duration of time without acquiring exhaustion or feeling breathless. Opens the chest and expands the oxygen supply to the lungs. Ardha Matsyendrasana is very beneficial for opening your chest muscles and checking cardiovascular disorders. Half Lord of the Fish Position benefits people who agonize from respiratory problems. It helps arrest and control conditions such as COPD and asthma.
Awareness and Focus:
In this position the body upgrades with the consciousness of the breath, the breathing helps to move the body and this position helps to conduct that recognition of the breath. As the inspire happens the spine moves up and out and with every expiration the spine twists you down and in.
Alignment and Posture:
To obtain the Half Lord Of The Fishes Position, various folds are essential. Each fold has its significance. Therefore, they need to be performed with accuracy. The correct adjustment will help the practician obtain into the posture correctly. When the position is achieved correctly, it is simple to hold it without any inessential injuries.
Energizing, De-stressing, and Relaxing:
Twisting of the spine in Half Lord Of The Fishes Position will help obtain rid of the miserliness in the muscles about the spine, neck, shoulders, lower back and upper back. Acquiring rid of the rigidity in this area will have the practitioner feel modified and refreshed. Deliver profusion of heat and toxins from organs and tissues. Deliver tension in the arms, shoulders, upper back, and neck.
Stimulation and Organs:
Twisting the spine with the hands in a secure inspire the compression of the stomach. It communicates with the abdominal muscles. Communication of the abdominal organs help in replacing constipation. The digestive system upgrades and the functioning of the liver and pancreas improves. The internal organs like the liver, heart, lungs, kidneys, and spleen are restorative and cleansed. The twist also helps in delivering a profusion of heat and toxins from organs and material. Tones and build-up abs and obliques. Decontaminate the internal organs. Restorative the abdominal area and can help digestion and erasure of wastes. Restorative Agni, the digestive fire in the body. Helps to continue the spine’s natural range of motion.
Therapeutic, Healing, and Ailments:
Exercise in this position softens symptoms of backache, fatigue, menstrual discomfort, and sciatica. Therefore yoga teachers can use the position as a part of the therapeutic yoga series.
Balance and Emotions:
Half Lord Of The Fishes Position is an asymmetrical position. Exercise of asymmetrical positions conducts balance in the body. Apply, one side of the the body is stiffer than the other. Thus, the exercise of asymmetrical positions helps conduct balance in the body by decreasing stiffness. Also, This position balances the body well and conducts peace of mind during nervous disorders.
Others:
Women who have problems connected to their menstrual cycle can benefit from the exercise of Ardha Matsyendrasana as the twist helps to keep the reproductive organs active, thus delivering unwanted energy. Increases the circulation to the pelvic region and therefore given (that) fresh blood, nutrients and oxygen, improving the health of the reproductive organs as well as the urinary system. Useful for arresting urinary tract disorders. Beneficial for menstrual disorders. Those who have symptoms connected to perimenopause or menopause too can benefit from this, as it helps keep hormones in balance. Increases absolution of the blood as well as the internal organs. Delivers symptoms of back pain, tension, fatigue, menstrual discomfort and sciatica. Delivers stiffness from between the vertebrae. Delivers tension that may have constructed up in the back from forward and back twisting asanas. Useful for slipped disc.
Preparatory Poses:
Half Lord Of The Fishes Position can be a preparation position for advanced positions like Marichi Position D and Full Spinal Twist Position.
What are the Preparatory poses for Ardha Matsyasana:
For the exercise of Ardha Matsyendrasana (Half Lord Of The Fishes Position) which is a seated twist position, that is exercised along with the locking of the arms, essential opening of the shoulders, hips, and lower back. For the same, the given positions can be exercised as part of the preparation, these are:
- Leg movements
- Vakrasana Type 1 and 2
- Two knee spinal twist | Jathara parivartanasana
- Revolved child position | Parsva balasana
- Head to knee position | Janu sirsasana
- Dhanurasana (Bow Position)
- Parivrtta Parsvakonasana Hands-On Floor (Revolved Side Angle Position Hands-On Floor)
- Bharadvajasana I (Torso Stretch Position I)
- Bharadvajasana II (Bharadvaja Twist Position II)
- Ardha Matsyendrasana Variation Hand Down (Half Lord Of The Fishes Position Variation Hand Down)
- Uddiyana Bandha
- Marichyasana (Sage Twist Position)
- Marichyasana I (Marichi Position I)

How to Perform Ardha Matsyasana?
Sit on the ground, with your legs extended straight in front of you.
Twisting the left knee and conducting the left foot under the right thigh, while raising the right leg a bit and placing it close to the right hip tucking it deepunder the right seated bone.
Conduct the right leg with the knee bend and conduct the right foot over the left thigh and place it close to the outside of the left hip on the ground, placing the right knee close to your upper body.
Taking a deep breath and bending the upper body towards the right, conduct the right palm and place it on the ground just beyond you with a twist.
The bend should be more from the inside of the right thigh and the palm placed close to your lower back beyond you.
With the left arm, placing the outer elbow close to the outside of the right knee grasp the right foot. Pull your anterior torso and inner right thigh amply together.
After complete expiration twist the torso more towards the right and moderately place the right hand on the hips trying to hold the left side of the lower back.
The bending of the body should be simple and slow, making certain the neck and the shoulders too are in alignment. Here the chest, shoulders and the the face is in perfect adjustment.
With every inspiration raise a little more through the sternum, pushing the right fingers deep into the left upper thighs to help bend deeper. And twist a little more with every expiration.
Be certain to distribute evenly as this position is all about maintaining the body balance. The full length of the spine gets twisted evenly.
Make certain that both sit bones are on the ground to secure the body is balanced well at the hips.
Stay in this position for as long as one is comfortable and modify the position and stretch the legs out in anterior of you and moderate.
Repeat this position with the twisting of the right leg and taking the left foot over and twisting towards the left side complete the position and stay as long as it is comfortable. Deliver from the position and stretch the legs out in anterior of you and modify in Dandasana.
What are Follow up poses for Ardha Matsyasana:
The exercise of Ardha Matsyendrasana is a seated hip opening with a bending action of the spine, and some of the common follow-up counters or
modifying positions that yoga teachers can consider are mentioned below:
- Poorna Matsyendrasana
- Baddha Konasana (Bound Angle Position)
- Paschimottanasana (Seated Forward Fold Position)
- Staff Position Variation Side Bend (Parsva Dandasana)
- Staff Position Hands Back (Dandasana Hands Back)
What are the Beginners tips in Ardha Matsyasana:
Exercising Ardha Matsyendrasana is a great way to detoxify and soothe your full body. Keep the following information in mind when exercising this
position:
- Let the back of your neck be sloppy. Balance your head considerately over your spine. Never lead the bend with your head. Rather, let your head be the
- last part of your body to turn.
- Keep your belly sloppy throughout the bend.
- Keep your buttocks grounded all around the position.
- Never attack or force the position. Progress with your breath. Inspire to lengthen your spine, and expire to considerately rotate deeper.
- Bend to the right first. Doing so will place a demand on the ascending colon. Bending to the pressure of the left place on the descending colon. This right-left order caricature the flow of digestion and helps upgrade detoxification. Reversing the series and pressing on the descending colon first may cause aggravation, constipation, bloating, and intestinal discomfort.
What is the Breath Awareness in Ardha Matsyasana:
The twist on the spine, abdomen, and modified breathing mostly focuses on chest breathing.
What is the Variation of Ardha Matsyasana:
- To deepen the bend, move to a wall. Make certain your back is facing the wall, and set a foot or so away from it, hang on on the length of your arms.
- When bending, use the wall as an opposing force to help move the anterior of the torso as opposed to the thigh.
- If it is heavy to hold the foot or endure in the position some other variations can be used to start with.
- The right leg can be kept straight rather of enclose around the body and/or the left foot can be placed a little further aside from the body, closer to the right foot.
- Rather the holding the left foot with the right hand the feet can be lifted, closer to the hands.
- Rather than holding the toes, the right arm can be twisted with the hand pressed against the left shoulder or the left knee can be held by both arms.
- If it is difficult to balance the left hand can be placed close to the body with the palm on the floor to carry the torso rather than wrapping it beyond the back.
- If one wants to get more extended between the shoulder blades then one can wrap the right arm under the left leg and beyond the body, grasp the left hand.
- If there is discomfort sitting on the floor around then one can sit on a pillow.
Under are some common variations of the yoga position Half Lord Of The Fishes Position with a base position as Half Lord Of The Fishes Position (Ardha Matsyendrasana).
- Half Lord Of The Fishes Position Variation Hand Up Leg
- Twisted Position
- Sage Marichi Position C
- Chair Seated Twists
- Half Lord of the Fishes Position
- Half Lord Of The Fishes Position Variation Hand Up
- Sage Marichi Position C Variation
- Sage Twist Position
- Sage Twist I Position Variation
- Half Lord Of The Fishes Position Variation Hand Down
- Marichi Position C I
- For a deeper twist, try Ardha Matsyendrasana, Rather.
What are the Modifications and Variations in Ardha Matsyasana:
If you find the move heavy at first, there are modifications you can use. Once you are adept at the position, you can make it more demanding.
Ardha Matsyendrasana will increase spinal elasticity, improve digestion, and calm your mind. This position is suitable for most starters but only goes as deeply into the bend as it feels safe. Try these simple changes to find a variation that works best for you:
If you are disagreeable sitting flat on the ground, prop yourself up on a folded, firm blanket or extra yoga mat.
Those with less elasticity in the hips can keep the bottom leg increasing.
If it is heavy to place your opposite-side elbow to the outside of your lifted leg, hug the thigh with your hands, rather. In time, your elasticity will increase and you will be able to wrap your full arm around your thigh. Once that is pleasant, you will be able to place your elbow to the outside of the knee in the full version of the position.
For variety in the neck stretch, you can otherwise turn your head in the direction of the bend, or the opposite direction. Gaze softly at the horizon with otherwise variation.
More elastic students can bind the arms. This variation is known as “Baddha Ardha Matsyendrasana” (Bound Half Lord of the Fishes Position):
Achieve steps 1-3 as listed in the Instructions, above.
Twist your left elbow and thread your left arm below your right knee. Conduct your left hand toward your left hip. Reach your right arm around beyond your body. Clutch your hands together or hold your left wrist with your right hand. Keep elongating your spine, relieve your left shoulder, and turning into the bend.
Deliver and come back to the center. Repeat the bound bend on the opposite side.
What are the Precautions and Contraindications for the Ardha Matsyasana:
Contraindications of Half Lord Of The Fishes Position are mentioned below:
Injury and Surgery:
People who agonize from severe back or neck pain should exercise with caution, and with close supervision. Those with slip disc problems should circumvent this position completely. Those with internal organ issues may find this position difficult and painful. Recent or chronic hip, back or shoulder injury or inflammation.
Lack of Body-Breath Connections:
As discussed in the benefits, while achieving intermediate positions, the coordination between the body movements i.e. different folds and the breathing while achieving those folds is necessary. Lack of this coordination might lead to various unnecessary injuries and supporters might find themselves having difficulty security the position for longer.
Others:
Exercise of this position shall be avoided by Senior Citizens having weak joints also this exercise should be avoided by pregnant women as it can press the fetus. Should be avoided during pregnancy and menstruation due to the powerful bend in the abdomen. Protection should be taken for those with peptic ulcer or hernia. Those with severe spinal problems should avoid and those with the mild slipped disc can advantage but in severe cases, it should be avoided. You should avoid this position if you have back problems, had recent surgery. It might not be pleasant during menstruation.
What are the Dos and Don’ts in Ardha Matsyasana:
Do:
With the right hand, carry the left big toe from the left of the left knee. If it is difficult to hold the toe then one can hold the ankle or lift the toes keeping
the heel on the floor.
Surround the lower back with the left arm, palm facing outwards. Turn to the left side of the spine; turn the shoulders and head to the left.
Try to keep both of the buttocks mightily on the floor. Only bend as far as you can and keep your back and neck straight.
Don’t:
Raise either of the buttocks off the floor or sit on the heel. Let the twist leg fall away to the side. Let the back or neck twist. Sit on the right heel.
Overstrain the knees and hips. Raise the left sole from the ground.
What are the Common Mistakes in Ardha Matsyasana:
Keep your back straight and vertebrae stacked during this bend, not rounded.
What are the Modifications in Matsyasana:
The back bending position in Matsyasana can be hard for starting students. Achieve the position with your back supported on a thickly rolled blanket.
Be certain your head rests adequately on the ground and your throat is soft.
- Palms Closer to Shoulder: Placing palms close to the shoulders is a good different to give support to the neck if one lacks confidence.
- Blanket underneath Head: Place a blanket underneath the head to give a tender stretch to the lower back and neck.
- Bolsters underneath Lower Shoulders: Place bolsters below your lower shoulders to take your head back with ease and still allow the same stretch to the neck and shoulders.
- Blanket under Hips: Place a blanket under your hip to decrease stress on the hips in Fish Position (Matsyasana). This will simplify the lower back too.
These Matsyasana modifications will help you perform this yoga position without placing too much strain on your muscles.
What are the Precautions and Contraindications for the Matsyasana:
There are some precautions for Matsyasana:
As introduced, get in touch with your doctor or a yoga expert ahead you start any asana. You should mainly avoid exercising matsyasana or fish position if you agonize from health conditions like migraine, high or low blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, serious lower back or neck injury, knee injury or pain in the knees, osteoporosis, or insomnia.
While achieving matsyasana is a great way to have a healthy body and mind, it can be injurious if not done the right way. Therefore, make certain you
follow all the tips and precautions so that it does not end up giving you trouble. Some of the necessary ones are as follows:
- Do not achieve matsyasana if you are agonizing over any heart diseases, counting high Blood Pressure and low Blood Pressure.
- If you have a neck injury or have harmed any part of your lower back, you should not venture into the fish position.
- Individuals who oppose a migraine should avoid venture this position.
- If you agonize from severe spondylitis, you should not exercise Matsyasana.
- Pregnant women should not venture to do this yoga position.
- Outstanding the fact that this yoga position is essential for you to breathe deeply it should be circumvented by those who have underlying heart conditions.
- Avoid this position if you have a neck or back injury or if you have a headache.
- When you are a recruit, achieve matsyasana under the close observation of an accomplished yoga teacher.
- If you have been constantly any surgery, avoid matsyasana exercise until the doctor suggests it.
- Never rush during the matsyasana steps as it can conduct to muscle stress or strain.
- Never perform matsyasana after having a meal. Make certain you do it at least 2 hours ahead or after eating your food.
There is some Contraindication for Matsyasana:
Avoid this position if you have high or low blood pressure. Migraine and insomnia patients should also abstain from doing the Fish Position. Those who
have had serious lower-back or neck injuries are strongly approve not to exercise this position.
Avoid doing matsyasana if you have any of the following conditions:
- Abnormal Blood Pressure: Individuals who agonize from high or low blood pressure should avoid this position.
- Neck Injury: Neck injuries or any part of the lower back or middle back can make it heavy to exercise this Fish Position and hence should be circumvent.
- Migraine: Migraine patients may find this position challenging but, if exercised, should be done leisurely with the advice of a yoga teacher.
- Spondylitis: Care should be taken if exercised by someone who is agonizing from spondylitis. Ideally should be avoided if it is severe. But if spondylitis is in starting stages then with proper advice from a yoga teacher Fish Position (Matsyasana) can be exercised.
- Pregnant: Women who are pregnant should not venture into this yoga position.
- Tightness in Neck or Back: If at the time of exercise of Matsyasana, one feels any kind of tightness around the lower neck and upper back, one should instantly stop doing the yoga position and modify in Corpse Position (Savasana).
- General Heart Ailments: Since breathing in this yoga position is deep, it may not be pleasant for someone who agonizes from heart ailments.
- Others: High or low blood pressure, Migraine, Pregnancy, Heart problems, Spondylitis, Insomnia, Serious lower-back, Serious neck injury.
What are the Common Mistakes in Matsyasana:
- To get the most out of this position, check your performance to avoid these errors.
- Too Much Pressure on Head: Make certain to root into your forearms, heels and unavailable thighs to create a raise in the upper body so that your head
- and neck is safe and assist.
- Straining the Neck: Your neck and back should be in a constant arch. Imagine relaxing the center of your top on the ground, not your forehead.
The Bottom Line
Fish Position offers benefits, but it is analytical that you learn to do the position accurately to minimize the strain on your neck. No position is ever
substance risking neck injury, no matter how magnificent it may look.
There are many amazing variations of Fish Position that can give you the same (and sometimes even more) benefits without threatening your spine.
Remember that all advanced positions are examined as such not just because of the physical essential but because of the care needed to do them safely. If you have questions about this position or how to do it safely, it’s best to work with a certified yoga trainer.
Once you can exercise Fish Position safely, enjoy producing the benefits of this powerful backbend.




2 Comments