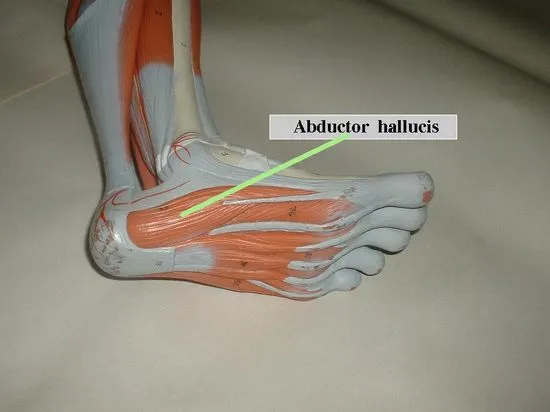
Abductor Hallucis Muscle
What is Abductor hallucis muscle?
Abductor hallucis is a fusiform muscle found superficially and medially in the foot. Abductor hallucis, along with flexor digitorum brevis and abductor digiti minimi, make up the first (most superficial) layer of plantar foot muscles, observing the variety of superficial to deep muscles. On the further hand, if the foot muscles are inspected by groups from medial to lateral, this muscle belongs to the medial plantar muscles of the foot together with the flexor hallucis brevis and adductor hallucis.
The role of this muscle is to abduct and flex the first toe. These actions contribute to the stability of the foot during walking by maintaining the central position of the first toe and keeping the medial longitudinal arch of the foot.
Origin of Abductor hallucis muscle
The flexor retinaculum and the medial process of the posterior calcaneal tuberosity
Insertion
It inserts on the medial part of the base of the proximal phalanx of the first toe.
Relations
The abductor hallucis muscle is the most medial muscle of the foot, running medially to the flexor hallucis brevis muscle. Plantar aponeurosis surrounds the muscle’s plantar surface, while its dorsal surface is connected to the flexor digitorum longus tendon, medial plantar artery, and nerve. A space known as the porta pedis is built by the beginning fibers of abductor hallucis and calcaneus. This space acts as a tunnel via which lateral and medial plantar nerves and vessels pass.
Innervation
The medial plantar nerve (root values S1-S3), which is the larger of the two tibial nerve terminal branches, innervates the abductor hallucis muscle.
Blood supply
The blood supply for the abductor hallucis muscle arrives from two arteries;
The first plantar metatarsal artery and the medial plantar artery supply the Abductor Hallucis.
Function of Abductor hallucis muscle
As the name of this muscle suggests, its main motion is the abduction of the first toe at the first metatarsophalangeal joint. This motion keeps the central position of the first toe during walking, and if it’s delayed it may result in deformities of the toes like hallux valgus.
Together with flexor hallucis longus and flexor hallucis brevis muscles, abductor hallucis helps the flexion of the first toe. The muscle also assists in keeping the medial longitudinal arch of the foot while walking.
Clinical relevance
As an intrinsic muscle of the foot, the Abductor Hallucis plays an essential part in stabilizing the medial longitudinal arch of the foot.
Abductor hallucis muscle pain
The abductor hallucis muscle is located in the foot and is responsible for the movement and stabilization of the big toe. When this muscle becomes painful, it can be due to various reasons. Here are a few possible causes and treatment options for abductor hallucis muscle pain:
- Overuse or strain: Excessive or repetitive use of the muscle can lead to strain and pain. This can happen due to activities that involve prolonged standing, walking, or running. Resting the foot and applying ice packs can help alleviate the pain. Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain and gradually reintroducing them as the muscle heals is recommended.
- Muscle imbalances: Muscle imbalances in the foot or lower leg can put extra stress on the abductor hallucis muscle, leading to pain. Stretching and strengthening exercises can help correct these imbalances. A physical therapist can provide guidance on specific exercises that target the abductor hallucis muscle.
- Plantar fasciitis: This is a condition characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes. The abductor hallucis muscle plays a role in maintaining proper foot mechanics, and if the plantar fascia is affected, it can cause secondary pain in the abductor hallucis. Treatment options for plantar fasciitis include rest, ice, stretching exercises, orthotic inserts, and in severe cases, medical interventions.
- Nerve compression: Nerves running through or near the abductor hallucis muscle can become compressed or irritated, leading to pain. This can occur due to conditions like tarsal tunnel syndrome or nerve entrapment. Treatment options may include physical therapy, stretching, anti-inflammatory medications, and in some cases, surgery.
If you’re experiencing persistent or severe abductor hallucis muscle pain, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional such as a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment based on your specific condition.
Abductor hallucis muscle exercises
Gentle activities can be done to reduce strain on the abductor’s muscle. Sitting in a chair, cross your legs. Take hold of your first (big) toe and gently stretch it upwards. Maintain the position for 20 seconds then return toe to the starting position. Rest the toe for roughly 10 seconds and repeat another two times.
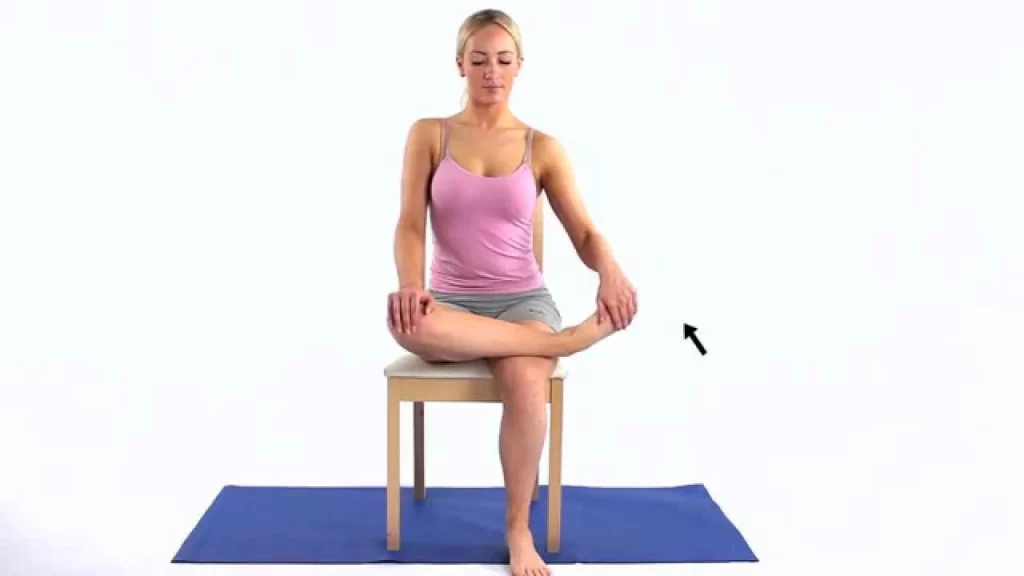

Toe spread
This is a toe abduction activity that is used for motor control. This activity can be completed while seated, standing, weight-bearing, or non-weight bearing.
FAQ
How do you treat abductor hallucis pain?
Use cold treatment or ice as soon as possible. Ice can be used for 10 minutes every hour initially for the first few hours decreasing frequency as pain and swelling go down to 2 or 3 times per day.
What are abductor hallucis pain symptoms?
Aches, swelling (edema), redness (erythema), and swelling (hematoma) along the medial portion of the longitudinal curve of the foot may be signs of this muscle strain. Pain is present even when the body is at rest, and it gets worse when a specific muscle or a joint around that muscle is used.
Where is abductor hallucis pain?
Abductor hallucis tendinopathy is a condition that causes heel pain on the inside and bottom of the heel, which can spread to the arch. This illness is very generally misdiagnosed, frequently mistaken for plantar fasciitis heel ache because the two share the same origin at the heel, leading to comparable symptoms when damaged.
How do you massage abductor hallucis?
Sit erect and put your foot on a tennis ball. Rotate the ball gently across the sole to gently massage the foot. Continue for two minutes, stay for 10 seconds, and then repeat.
What causes abductor hallucis?
AHT is generally an overuse injury. When the tendon is overloaded from extra or repetitive strain and pressure, micro-tears and damage result, and painful symptoms and inflammation starts.



2 Comments