9 Best Exercise for Lumbar Spondylosis
Exercise is the best therapy to recover from lumbar spondylosis naturally. Exercise helps to strengthen our lower back muscles and also improves the mobility of the spine. In this essay, we will discuss the exercises to relieve lumbar spondylosis symptoms. which you can do at home and or at the clinic.
Lumbar spondylosis impacts a substantial number of people worldwide. It is estimated that around 50-60% of individuals over 60 years old have some extent of lumbar spondylosis. The cause for its high prevalence is due to the natural agility process which induces wear and tear of the vertebral joints and discs in the lower spine. Other contributing factors have genetics, poor posture, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Fortunately, physiotherapy treatment can help relieve Lumbar issues and enhance overall back Strength.
What is a Lumbar Spondylosis?
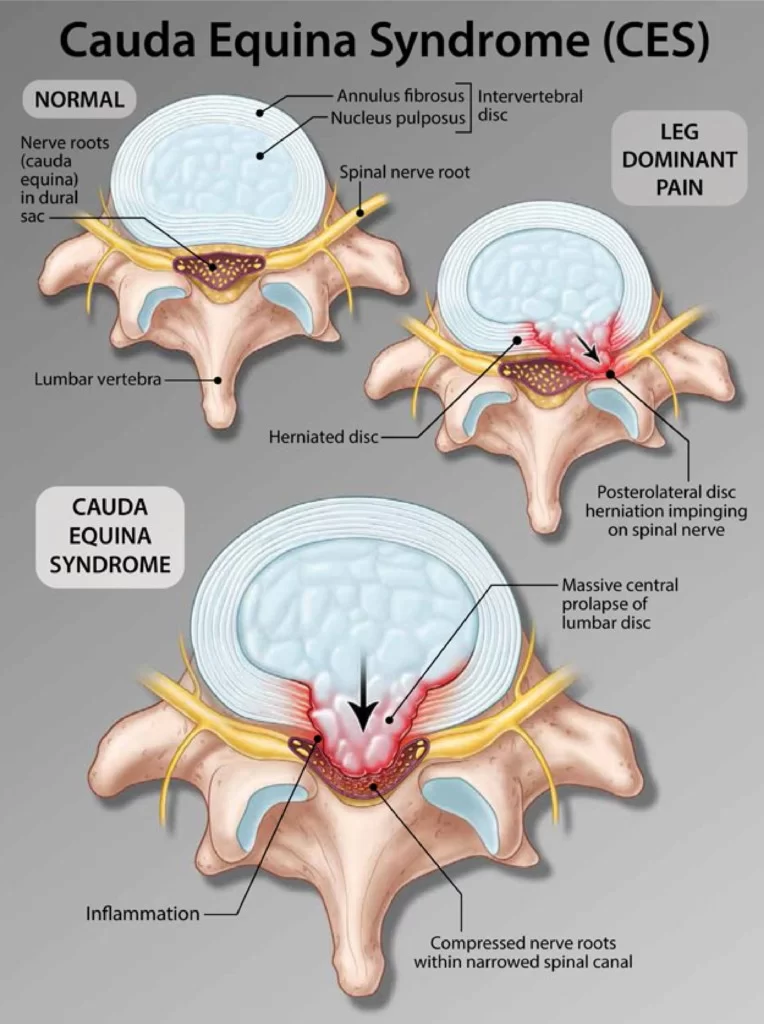
Lumbar spondylosis is a condition induced by degeneration of the lumbar disc or facet joints. It is a degenerative disease involving discs, vertebral bodies, and associated joints of lower vertebrae. These are progressive and irreversible changes in older patients and commonly occur due to orientation to mechanical strain.
Lumber spondylosis mainly occurs by wear and tear on the components of the spine. The typical risk factor for generating lumber spondylosis is age. In fact, by age 65 most people will display symptoms of spondylosis on investigations like X-ray or MRI.
According to the report, lumbar spondylosis now affects more than 85% of persons over the age of 40, up from 5% of people in that age group. About 20% of males and 22% of females between the ages of 45 and 64 and 30% of males and 28% of females between the ages of 55 and 64 have lumbar osteophytes, accordingly.
Lumber spondylosis is typical, but it is usually not severe. Lumbar spondylosis is mostly treated without surgery. Medical therapy options contain pain relief medicine, muscle relaxants, anti-inflammatory medications, and steroid injections. Physical therapy is very effective and has many exercises and hot- and cold therapy are also helpful in relieving pain.
Causes :
There have multiple causes of lumbar spondylosis, some of them include:
- Old-Age,
- Heredity,
- Back injury,
- Repetitious spine loading,
- Repetitious bending, lifting, twisting, and
- Prolonged postures can achieve.
Symptoms:
- Pain in the lower back.
- Feel Numbness in legs.
- Weakness.
- The lower back and leg are affected by neurological claudication whether somebody is standing or walking.
- Difficult in sitting and standing.
What Is The Physiotherapy Treatment Of Lumbar Spondylosis?
Lumbar back support:
Lumbar support with the use of braces is utilized for stabilization, reducing mechanical strengths, and determining spine exercise.
cold therapy is helpful to reduce swelling and pain.
Thermotherapy:
Thermotherapy is utilized to promote blood flow, decrease swelling, and release toxins.
Exercise therapy:
Exercise therapy contains muscle strengthening, muscle stretching, and aerobics exercises. The training programs vary in intensity, duration, and frequency.
Traction therapy:
Traction therapy is helpful in relieving chronic back pain. It allows to open intervertebral space and reduces spine lordosis.
Manual therapy:
Manual therapy is a hands-on technique that applies spinal manipulation and mobilization. It is helpful to break the adhesions, align the bones, and enhance mobility.
Massage therapy:
Massage therapy allows to reduce pain and swelling, breaks adhesion, and improves blood circulation.
Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS):
Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS) gives quick relief from aches.
Interferential therapy:
Interferential therapy is helpful to reduce pain and inflammation.
Laser therapy:
LASER therapy helps to improve the healing process, thus reducing pain and also improving mobility.
Kinesio-taping:
Kinesio-taping helps to reduce pain in the lower spine. It is helpful to enhance the range of motion and also to fix bad posture.
Strengthening exercises:
Strengthening exercises are used to strengthen back and core muscles which help to sustain the low back.
Stretching exercises:
Stretching exercises are performed to enhance the flexibility and pain-free range of movement of the back muscles.
Balance exercises:
These exercises are conducted for awareness to show the proper posture of the back while moving during various exercises.
McKenzie exercises:
McKenzie’s exercises concentrate on extension and help to control further degeneration of the lumbar spine.
How Can the Lumbar Spondylosis Pain Be reduced With These Exercises?
All exercises explain below focus on strengthening your spinal and core (abdominal) muscles. If the muscles around your backbone support and stabilize your back, you may have minor pain—and make a healthier spine for your body.
A powerful core is a key to back fitness and also Your core muscles work like your spine’s “front anchor.” When the spine’s supporting muscles are strong, you will likely feel reduced spinal osteoarthritis symptoms like joint pain and immobility.
Important Things to Consider for Lumbar Spondylosis Exercises
- All activities should be done within the pain-free range or evade pain-full movement while exerting.
- Do the movement two to three times daily.
- If you feel the movements are hard to do or can only move a little then slowly build up to the total number of repetitions over a few days or even a couple of weeks.
Best Exercises for Lumbar Spondylosis Video

Best Exercises for Lumbar Spondylosis
Lumbar Pelvic Rotations
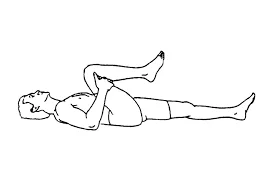
- Begin with lying on your back with both knees flexed and your feet flat on the ground and then Holding your knees together roll them to the right as far as is comfortable and then Return to the starting position in one smooth movement, moving as far to the left as is comfortable after that. .
- Do 10 repetitions of this exercise.
Single knee to chest
- Begin with Lying on your back and slowly bringing your knee upward to your chest and then Put both hands on the right knee joint and smoothly pull your until there is stiffness, bringing it closer to your chest.
- Maintain this position for ten seconds then gradually return to the beginning position you should Repeat this exercise with your opposite knee.
- complete 10 repetitions.

Double knee-to chest
- Begin with lying on your back and gradually bring both your knees up to your chest.
- keep your knees and gently pull them nearer to your chest until you feel tightness after that Keep this position for ten seconds then slowly return to the beginning position.
- complete 10 repetitions.
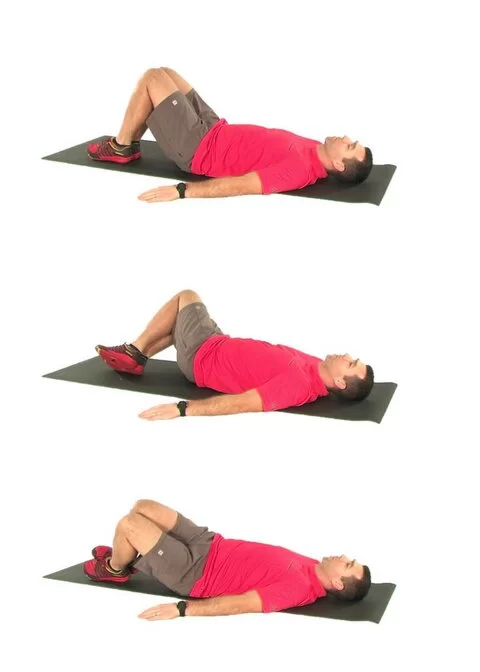
Bridging

- To perform bridge you have to take a supine lying position with both knees flexed and feet flat on the mattress and then Slowly raise your hips off the mattress as high as you can comfortably manage.
- Hold this position for 5 seconds and gently return lower back to the beginning position.
- Make sure the head and neck are held straight to evade strain on the neck joints.
- Do 10 to 15 repetitions.

Prone on elbow
- To perform this exercise you have to Lie down on your belly(take a prone lying position).
- Now, up yourself on your forearms with your shoulders just to your elbows.
- keep this position for 10 seconds.
- Bring down your upper body.
- Do this exercise 8 to 10 times.
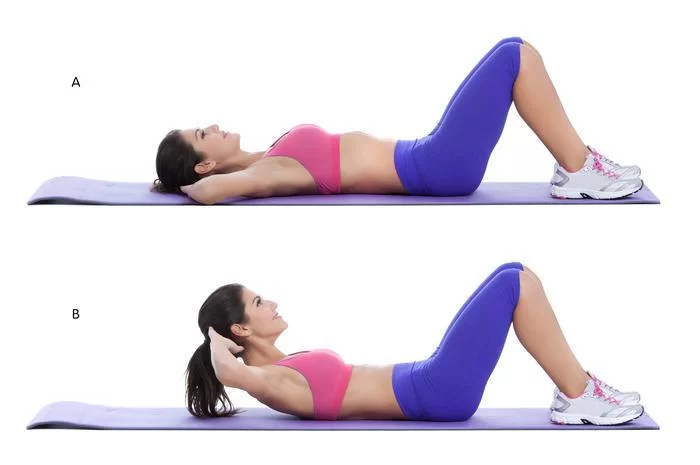

Modified sit-ups
- To do this exercise you have to Lie on your back on the mat. flexed one leg and leave the other one to stay extended and flat. Put your palms underneath the arch of your lower back to preserve the natural curve.
- Gradually lift your chest, shoulders, and head as one unit off the bed without twisting your lower back, but placing pressure on your hands. The range of movement is short – your head does not lift very far off the ground.
- Hold the position for 2 seconds while breathing deeply.
- Then gradually return to the initial position.
- Do this exercise for 10 repetitions then switch legs for another set.
- Do this exercise 10 times.
Hamstring stretch

- To perform a hamstring stretch you have to take a supine lying position.
- Slowly raise one leg off the floor, maintaining it straight.
- Hold your hands behind your thigh or calf and slowly pull the leg towards you until you feel a stretch in the posterior of your thigh.
- Hold this stretch for thirty seconds.
- Release and repeat on the opposite leg.
- You can also perform this stretch with a towel or resistance band looped around your foot to help deepen the stretch. Be sure to breathe greatly throughout the stretch and evade jerking or bouncing motions.
- If you feel any pain or discomfort please avoid this activity.
Pelvic Tilt
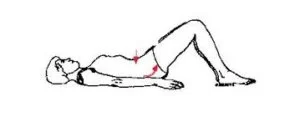
- To perform pelvic tilt Lie on your back with your knees flexed
- Constrict your tummy muscles and push your lower back toward the ground.
- Keep for 5 seconds.
- Do this ten times.
Cat-camel

- To do this exercise take a quadruped position place your wrists just below your shoulders, and place your knees just below your hips.
- Your shoulder, spine, and, hip should be in one line.
- Keep the spine in a neutral position.
Breath in for Cat Pose
- Inhale and try to take your back down towards the mat.
- Then you raise your neck towards the roof.
- Now sticking your tailbone out to make a turn with your spine. Exhale at the same time.
Breath out for Camel Pose
- Now Tuck in your chin and tailbone in
- Try to upward your spine towards the roof you have to look over the base.
- Make a hunch over your spine if you can.
- Repeat the Cat-Cow Stretch per breath in and breath out, coordinate the move to your breath.
- Do this exercise 15 times with both cat and camel pose.
Can Exercise with Lumbar Spondylosis hurt me?
Your physician should allow you before you start any new stretching or exercise schedule and if any movement seems harmless, it can cause further damage if done without any suggestion from your doctor.
Your physician knows your specific medical history or condition so he or she may direct you to a physical therapist (PT) or another trainer to show you how to complete any stretches and exercises that eliminate your specific lumbar spondylosis diagnosis. Last but not least, regulate yourself when you exercise.
Lumbar spondylosis is painful sufficiently—listen to your body, and tell your spine specialist if you feel any kind of pain or any other symptoms like tingling or numbness during physical activity.
Which exercise should be avoided?
- Heavy lifting,
- Excessive bending,
- Twisting,
- Stooping,
- Avoid engaging in any work or recreational activities that strain the lumbar spine.
- Avoid workouts that require quick, jerky movements.
- Any exercise that hurts or makes you uncomfortable should be avoided.
- Stay away from high-impact sports like sprinting and jumping.
Patient Education
The patient is educated about the disease and lumbar anatomy, correct posture, and ergonomics, and given proper back exercises. The patient is recommended to avoid activities that aggravate the pain.
FAQ
What effect does exercise have on spondylosis?
For those with spondyloarthritis, regular practice can help enhance posture, immobility, pain, fatigue, breathing capacity, and therefore general function. Remember that it is your doctor’s job to help control the pain, inflammation, and immobility so that you can maintain a healthy exercise schedule.
Which activity is most suitable for lumbar spondylosis?
Pelvic Tilt
Knee To Chest
Cat-Cow Stretch
Hamstring Stretch
Bridging
Which positions can be avoided with lumbar spondylosis?
When you sleep on your stomach, your spine is more likely to move into an arched posture, which places additional strain on your lumbar spine. That is why lying on the belly tends to be the worst sleeping position for spondylosis patients. Side-sleeping with flexed knees involves less compression of the lumbar spine.
Can physiotherapy heal lumbar spondylosis?
Lumbar spondylosis is arthritis of the lumbar spine which typically affects people over the age of sixty. Physiotherapy can decrease symptoms of lumbar spondylosis.
How much time take to recover from lumbar spondylosis?
This can be healed in between 6-12 weeks with good rest, anti-inflammatory medications, exercise modification, and physical therapy.
Which are the risks of spondylosis?
Spondylosis is induced by wear and tear on the elements of the spine. The main risk factor for acquiring spondylosis is age. In fact, by age 60 many people will show signs of spondylosis on X-ray.
Which precautions should be taken for spondylosis?
You can not be able to stop spondylosis, but these steps may decrease your risk:
Stay physically involved.
Utilize good posture.
Avoid spine injuries by constantly utilizing the right equipment and adopting the correct form whether working out or playing sports.
Avoid concussion to your neck.
Which exercises should be avoided with lumbar spondylosis?
Avoid exercises like full sit-ups and heavy weight lifting that impose an excessive amount of strain on the lower back. Avoid exercises that induce pain or discomfort. Exercise should be stopped right away if it is causing pain, and a medical professional should be consulted.