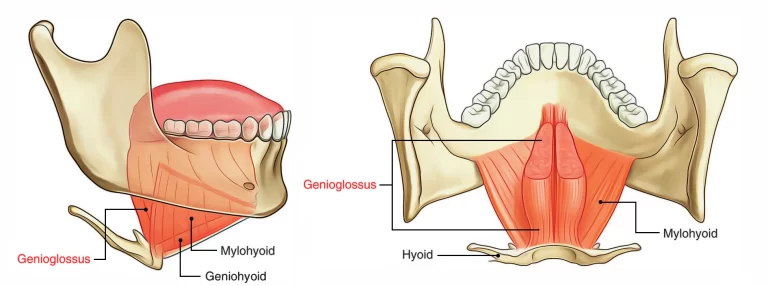
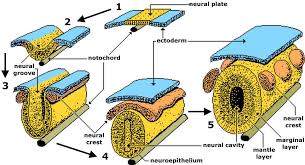
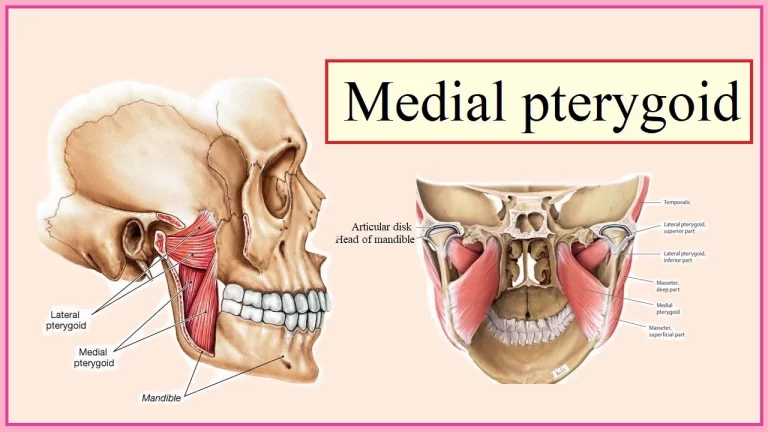
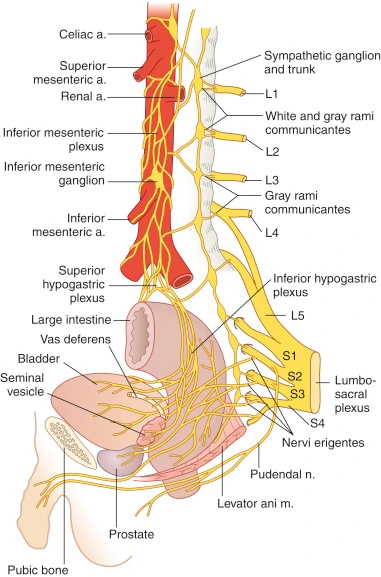
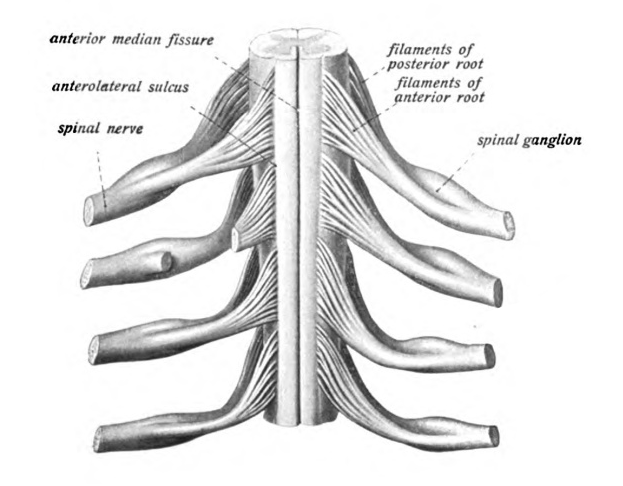
Hindbrain
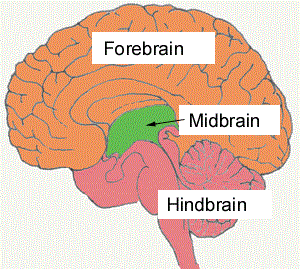
What is a Hindbrain? The hindbrain (developmentally obtain from the rhombencephalon) is one of the three major areas of the brain, situated at the lower back part of the brain. It comprises most of the brainstem and a dense coral-shaped composition called the cerebellum. The brainstem is one of the very important parts of the…