Elbow Flexors- Anatomy and Exercise
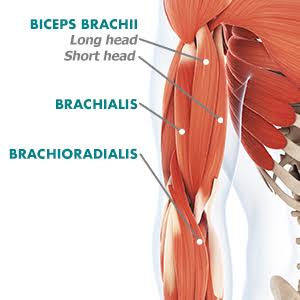
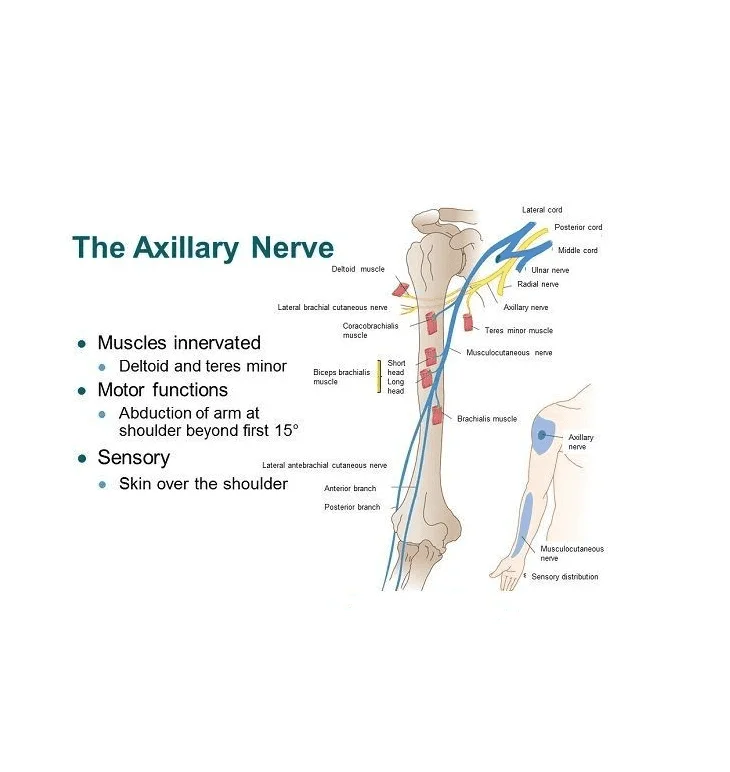
Introduction to Elbow Flexors The flexor group – including the brachialis, biceps brachii, and brachioradialis bend the arm by decreasing the angle between the forearm and upper arm. The brachialis is the primary flexor of the elbow and is found mainly in the upper arm between the humerus and the ulna. Superficial to the brachialis…