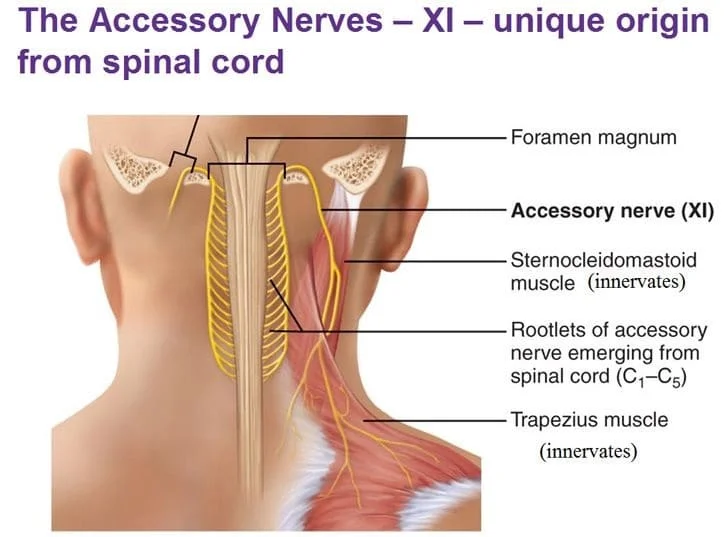
SPINAL ACCESSORY NERVE
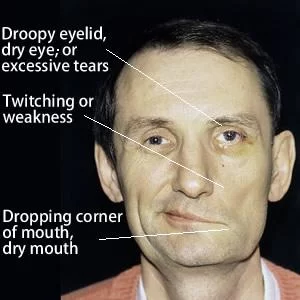
Introduction The accessory nerve is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is considered the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerves, or simply cranial nerve XI, as part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain. The accessory nerve divides it into a spinal part and a cranial…