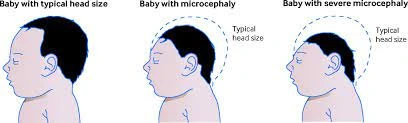
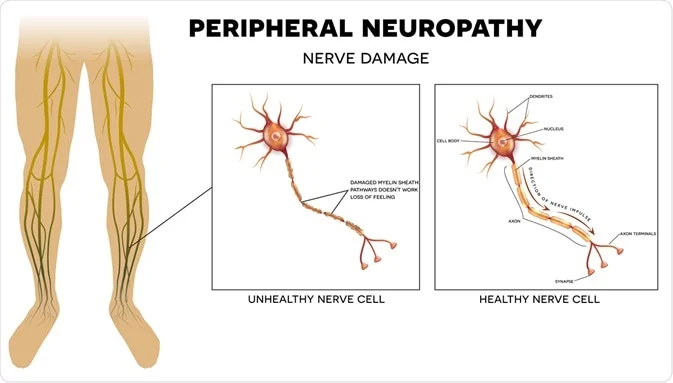
Lumbosacral plexopathy
Introduction Causes of Lumbosacral plexopathy Lumbar Plexus: Epidemiology Pathophysiology The pathophysiology of LS plexopathy differs based on the etiology: History & Physical examination Imaging Evaluation Electrodiagnostic Studies Laboratory Investigations Other Investigations Treatment of Lumbosacral plexopathy Rehabilitation Program Differential Diagnosis Prognosis Complications Deterrence & Patient EducationThe patient should be educated about the nature of the disease…