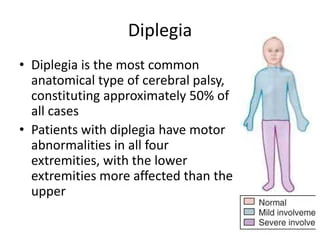
Diplegia
What is a Diplegia?
Diplegia is also called paralysis of both limbs mainly both lower leg or upper limb. In Diplegia symptoms like stiffness, weakness, and lack of mobility are the most commonly seen. It is usually affected by both upper limbs and/or lower limbs.
What are the Causes of Diplegia?
The most common cause of diplegia in the legs is called cerebral palsy.
paralysis in the legs may be also caused by trauma, injury, or genetics but it’s a rare case.
age of onset:
Diplegia is usually diagnosed after the age of 2 years the symptoms and signs of the earlier stages are typical and should enable the diagnosis to be made before the contracture has occurred. If parents suspect diplegia should take their child to the Pediatrician for an earlier diagnosis.
Facial diplegia:
Facial diplegia has affected both sides of the face (paralysis of both sides). one side of the face affected occurs when onset and the second side of the face affected occurs within a month.50%of patients affected with diplegia with Guillain barre syndrome.
Causes of facial diplegia:
facial diplegia is caused by traumatic, infectious, neurological, toxic, vascular, or idiopathic. 50% of cases affected one side of the face caused by an idiopathic condition. and less than 20% of cases affected both sides of the face caused by idiopathy. and most common cases of facial diplegia are caused by infection.
Diplegia of the arms:
Patients having diplegia in their arms have difficulties in reaching, pointing, grasping, releasing, and manipulating objects.
Causes of diplegia of the arm:
diplegia of the arm is very common in cerebral palsy patients. causes of diplegia of the arm are traumatic and event or injury.
Diplegia in the legs:
Diplegia in the legs is affected one side of the leg or both legs. diplegia in the legs are 3 types of severity. one is mild diplegia, the second is moderate diplegia, and the third is severe diplegia.
In mild diplegia, the patient can usually walk but has little difficulty in walking.in moderate diplegia, the patient can usually walk but with a slight bend in the knees. in severe diplegia, the patient can generally use crutches, a walker, or a wheelchair.
Diplegia in children of one or both legs has delayed the growth of leg muscles because of the shortening of the muscle. For children with diplegia, stiffness of joints and the range of motion decrease as the child grows.
Causes of diplegia in the legs:
Cerebral Palsy is the most common cause, however, Paralysis of both legs is also caused by trauma or injury.
Age of onset in diplegia:
The age of onset in diplegia usually occurs in 2 periods.
1 with newborn babies
2 full diagnoses usually between ages 2 to 5 years
Diplegia is usually diagnosed after 2 years
What are the symptoms of diplegia?
There are two types of symptoms of diplegia
- Physical symptoms
- Neurological symptoms
Physical Symptoms:
- Shortening of muscle
- Drooling
- Jerky reflexes
- Floppy muscle tone
- Gastrointestinal problems
- Incontinence
- Lake of coordination
- Problems swallowing or sucking
- Problems with movements on one side of the body
- Spasticity
Neurological Symptoms
- Hydrocephalus
- Behavioral problems
- Delayed motor skill development
- Difficulty with speech and language
- Sensory impairments
- Visual and hearing impairments
- Involuntary movements or tremors
What are the signs of diplegia?
- Gait abnormality
- Affected coordination
- Abnormal movement
- Abnormal posture
- Paralysis
- Weakness of upper limb or lower limbs or both limbs
- Spasticity
Treatment:
Different ages require different treatments which include therapy, braces, walker, wheelchair, and medication.
Medical:
medical treatment used in diplegia
Medication:
- Anti-inflammation
- Muscle relaxants
- Benzodiazepines
- Nerve blocks
- Botox
- Baclofen
- Anticholinergics
- Stool softeners
Physiotherapy Treatment:
Physical therapy can improve
- Coordination
- Balance
- Strength
- Flexibility
- Endurance
- Pain management
- Posture
- Gait
- Overall health
Equipment is used in delegate for physical treatment
- Exercise balls
- Thera band
- Hot and cold packs
- Weight cuff
- Electric stimulation
- Gripping exercise
- Physiotherapy treatment according to age:
- Birth to 1 year
- up to 3 years
- up to 6 years
- up to 12 years
- up to 18 years
Birth to 1 year:
Birth to 1-year patients has seen the development of many milestones. like head control, reaching out for a toy, sitting, starting to vocalize sounds and finger feeding. Most relatives want to be patient very fast but here is an upper and lower range development of early born babies it’s very hard to diagnose diplegia. The most common symptom of diplegia in children is stiff lower extremities. During this age, the patient is not moving their legs actively.
Up to 3 years:
Up to 3 years of age more noticeable symptoms of diplegia. mainly at this age patient with diplegia is not walking. At this age, it’s important for the child can participate in physical therapy and learn social skills. relatives should not force the patient to sit, crawl, or walk during this age. let the patient do comfortable and allow the therapist to correct this problem. if the therapist wants to help the patient walk more using walking aids.
Up to 6 years:
Up to 6 years of age patients with diplegia most significant physical improvement in motor function. During this time patient makes major improvements in motor function. then the patient is in a regular school and focuses on cognitive issues, not therapy. a patient using walking aids for mobility to move around.
Up to 12 years:
Up to 12 years physical improvement has leveled off in areas such as balance and coordination, and it’s a good idea to refocus the child’s attention away from additional physical improvement and toward intellectual learning.” During this time period, a child should lean away from physical therapy and do more outdoor or social exercises such as sports and adaptive. Usually, by age 8-10 a child has reached maximum walking ability. This will usually decrease a little when a child hits puberty and gains height and weight because walking becomes harder during this changing period. Any significant problems in walking should be addressed with surgery at this stage.
Up to 18 years:
“During this time period of a child’s development, a major issue is separating from the family.” Parents should learn how to cope with their children growing up and give them more freedom and independence. Teenagers need to make their own decisions and learn from them. One way to do this is for parents to compromise and let the child make smaller decisions so they feel important. Parents should also understand that their child may regress in walking some from the increase in height and weight. Going back to therapy during puberty is recommended so the teenager can adjust to the increase in height and weight and not regress as much.
Occupational therapy:
Occupational therapy is used by age one is a newborn baby second is young age and third is an older patient
In children, occupational therapy is used by toys, and games, to improve physical activities.
At a young age, patient occupational therapy is used by works on improving cognitive and physical activity. occupational therapy can also improve the child’s improvement the child’s performance in school.
Summary:
Diplegia is one type of palsy. It’s also called cerebral palsy. Cerebral palsy also starts in the lower limbs. Diplegia is affected by two ages. One is a newborn baby and the second is a young age.
In newborn babies, symptoms are seen by in a baby younger than 6 months, in a baby older than 6 months, and in a baby older than 10 months. Symptoms of diplegia are seen in two stages: physical symptoms and neurological symptoms. The physical symptoms are the shortening of muscles, jerky movements, and drooling. and neurological symptoms like delayed motor skill development, and difficulty in speech and language.
Signs of diplegia like gait abnormality, affected coordination, abnormal movement, and abnormal posture. Differential diagnosis in diplegia is Spasticity, Ataxia, Hypotonia, Cauda equina, and Vascular malformation.
Treatment is diplegia is medication, physiotherapy treatment, and occupational therapy. use of medication in the diplegia like Anti-inflammation, Muscle relaxation, Benzodiazepines, Nerve blocks, Botox, Anticholinergics, and Stool softeners.
Physiotherapy treatment for diplegia is start at two ages. One is a newborn baby and the second is a young age patient. physical therapy can improve Coordination, Balance, Strength, Flexibility, Endurance, Pain management, Posture, Gait, and Overall health. Equipment can use in diplegia for physiotherapy treatment such as Exercise balls, Thera bands, Hot and cold packs, Weight cuffs, Electric stimulation, and Gripping exercise.
Physiotherapy treatment is given in two stages one newborn baby patient and younger child patient. in the early delivered physiotherapy treatment is Resisted exercise, Balance board, Gait training, Electrical stimulation, Speech therapy, and Range of motion exercise. In the young age patient with diplegia physiotherapy treatment is Gait training exercise, Exercise ball, Resisted exercise, All joint approximation exercise, Gripping exercise, and Coordination exercise.
FAQ
What is the difference between diplegia and paraplegia?
Diplegia is weakness in both lower limbs. which is the upper motor neuron lesion type. the commonest cause is prematurity. And paraplegia is the paralysis of half the lower limb with the involvement of both legs. paraplegia caused by diseases or injury to the spinal cord.
What limbs are affected by diplegia?
In diplegia, both limbs are affected mainly both lower limbs and both upper limbs.
What are the early signs of cerebral palsy?
Delay development ( Slow to reach milestones like rolling over, sitting, crawling, walking).
Abnormal muscle tone( Body parts floppy or too stiff).
Abnormal posture.
Can people with diplegia walk?
ost individuals with spastic diplegia have normal cognitive abilities and can walk independently. more severe motor impairments may depend on walking aids such as a crutch, wheelchair, or walker.
What is the difference between diplegia and hemiplegia?
Diplegia usually indicates the lower limbs are affected more than the upper limbs. Hemiplegia indicates the upper limb and lower limb on one side of the body are affected


2 Comments