Forearm Exercises for Beginners, Intermediate, and Advanced Athletes
Forearm Exercises are an important part of your overall fitness program that helps to improve the strength and flexibility of the forearm.
Introduction
The forearms often go overlooked in many fitness routines, overshadowed by the focus on bigger muscle groups like the chest, back, or legs. However, neglecting your forearms can limit your overall strength and hinder your performance in various activities, both inside and outside the gym. Strong forearms not only contribute to a balanced physique but also play a crucial role in enhancing your grip strength, which is essential for activities like lifting weights, and rock climbing.
In this article, we will explore the importance of forearm strength, its benefits, and the various exercises you can incorporate into your workout routine to develop powerful forearms. Whether you’re an athlete looking to improve your performance or someone seeking to enhance your functional strength, these exercises will help you achieve your goals and build forearm muscles that not only look impressive but also serve you well in your daily life. Let’s dive into the world of forearm training and discover the exercises that will help you unlock your full potential.
Strength in the Forearms:
The antebrachial muscles, often known as the forearm muscles, are essential for many exercises that take place inside and outside of the gym. Forearm power is important for the following reasons:
- Strengthened Grip: Grip strength is considerably increased by strong forearms. A solid grasp is necessary whether you’re lifting weights, transporting large objects, or taking part in sports.
- Injury Prevention: By stabilizing the wrist and easing the strain on the tendons, strengthening the forearm muscles can help prevent ailments like tennis elbow and carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Improved Athletic Performance: Swinging a tennis racket, throwing a baseball, or climbing all require forearm strength. Your performance in these activities can be improved by having strong forearms.
- Functional Daily Tasks: Strong forearms make daily tasks easier and less tiring on your wrists and hands, from opening jars to carrying groceries.
Forearms with good definition can add to your overall muscular appearance, which helps to create a balanced body.
Anatomy of a forearm
It’s crucial to comprehend the structure of the forearm before beginning any activities. There are 2 primary muscle groups in the forearm:
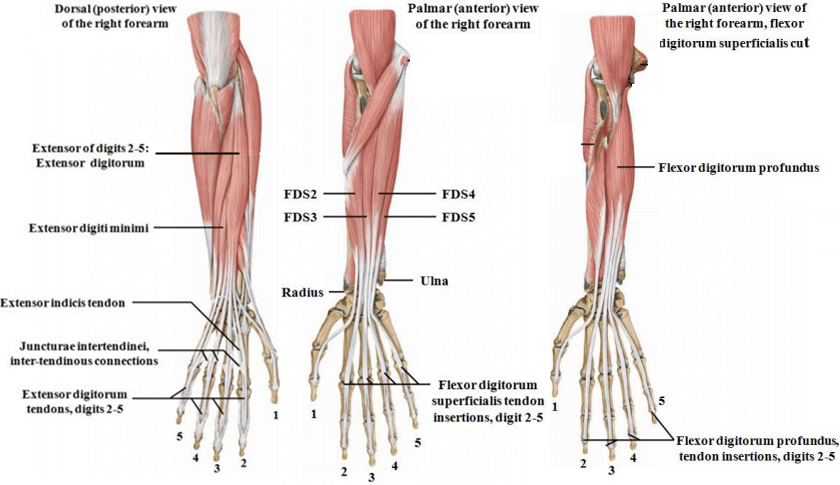
- Wrist Flexors: These muscles, which are found on the forearm’s palm side, are in charge of bending the wrist. The flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, and palmaris longus are the main wrist flexors.
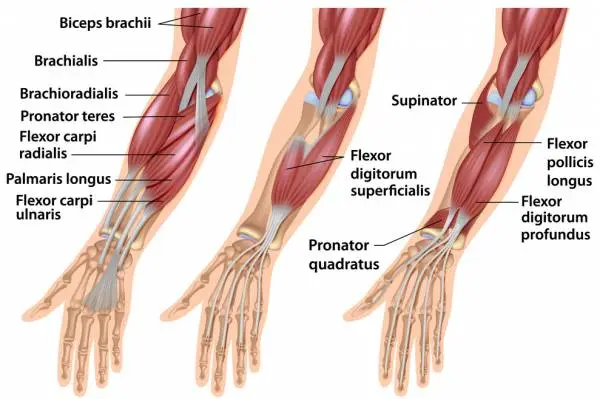
- Wrist Extensors: Located on the back of the forearm, these muscles are in charge of extending the wrist. The extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, and extensor carpi ulnaris are the three primary wrist extensors.
Arterial Supply:
The forearm is nourished by two major arteries: the radial and ulnar arteries. These vital vessels are responsible for delivering oxygenated blood to the forearm. They course along the anterior aspect of the radius and ulna, traversing the entire forearm.
Nerve Supply:
The posterior compartment of the forearm receives its nerve supply from the radial nerve, while the anterior compartment is under the jurisdiction of the median nerve.
Now that we’ve familiarized ourselves with the forearm’s anatomical components, it’s time to delve into effective forearm workouts, such as the Deadlift Pro. Engage those muscles, boost blood circulation, and let those extensors do their work.
Forearm Muscle-Strengthening Exercises
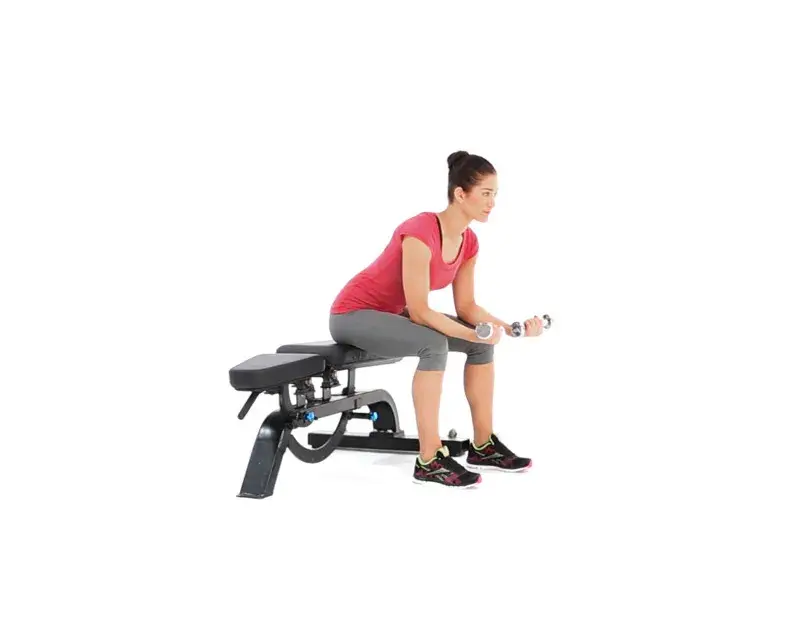
- Dumbbell Wrist Flexion
- How to Perform:
- To effectively engage your forearm muscles, consider adding Dumbbell Wrist Flexion to your routine. This movement targets and strengthens your wrist flexors, crucial for improving grip strength.
- Begin by sitting on the edge of a bench or table, holding a dumbbell in your left hand.
- Place your left forearm on your left thigh, with the back of your wrist atop your kneecap.
- Isolating the hand, slowly lower the weight while maintaining a firm grip.
- Without moving your arm, curl the dumbbell toward your bicep.
- Gently decrease the dumbbell back to the starting place.
- Repeat this on your right side.
- Aim for 10-12 repetitions across 3-4 sets per session, and do two sessions per day.
- How to Perform:
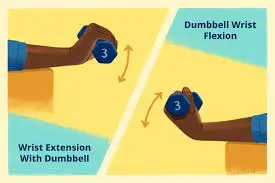
- Dumbbell Wrist Extension
- How to Perform:
- This exercise complements Dumbbell Wrist Flexion by targeting the wrist extensor muscles, aiding in forearm muscle development and strength.
- Sit on the edge of a bench or table, holding a dumbbell in your left hand.
- Place your left forearm on your left thigh, palm facing down, with your left wrist atop your kneecap.
- Concentrating on isolating the hand, curl the weight upward, maintaining a firm grip throughout the motion.
- Slowly return the weight to a neutral position.
- Repeat this on your right side.
- Perform 10-12 repetitions over 3-4 sets per session, with two sessions per day.
- How to Perform:

- Reverse Curl
- How to Perform:
- Elevate your forearm workout with the Reverse Curl, a powerful exercise that increases blood flow and strengthens often underutilized muscle groups.
- Grip the barbell with an overhand grip at shoulder width, palms facing downward.
- Keep your upper arms close to your sides and curl the barbell.
- Squeeze at the top of the movement when your hands reach your anterior deltoids.
- Slowly lower the barbell, maintaining tension.
- Complete 10-12 repetitions across 3-4 sets in one session, and do two sessions per day.
- How to Perform:
- Hammer Curl
- How to Perform:
- While primarily a bicep exercise, the Hammer Curl is a compound movement that engages lower forearm muscles during contraction.
- Stand upright and hold two dumbbells at your sides with straight arms and palms facing your body.
- Raise your right hand until your forearm is vertical, and your thumb faces your shoulder.
- Hold this position for 2-3 seconds and squeeze your biceps.
- Gradually lower the dumbbell to the initial position and repeat with your left arm.
- Aim for 10-12 repetitions in 3-4 sets per session and do two sessions per day.
- How to Perform:

- Zottman Curl
- How to Perform:
- The Zottman Curl is a compound motion that effectively strengthens forearm muscles.
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding dumbbells in both hands with palms facing your sides.
- Curl the dumbbells, keeping your upper arms stationary.
- While raising the weights, turn your palms toward your face, placing your biceps in the top position.
- Rotate your palms to face downward. Slowly lower the dumbbells, akin to a reverse curl.
- Complete 2-4 sets of 8-10 reps per arm in one session, and do two sessions per day.
- How to Perform:

- Farmer’s Walk
- How to Perform:
- The Farmer’s Walk is a fundamental forearm exercise that targets wrist and finger flexors while engaging multiple muscle groups.
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and grab a pair of heavy dumbbells at your sides, palms facing inward.
- Walk forward with engaged shoulders, a tight core, and a straight spine. Take 15-20 steps in one go.
- How to Perform:

- Chin-Up
- How to Perform:
- Chin-Up is a multi-faceted exercise that sequentially engages various muscle groups, emphasizing flexors and effectively working your forearms.
- Grab a barbell with hands shoulder-width apart and palms facing you.
- Contract your shoulder blades by pulling yourself up. Maintain stretching until your chin is over the bar.
- Hold for 2-3 seconds at the top.
- Slowly lower yourself to the starting position.
- Aim for 2-3 sets of 10 chin-ups per session, and do this for one session per day.
- How to Perform:

- Pull-Up Bar Hang
- How to Perform:
- The Pull-Up Bar Hang is a straightforward yet effective forearm exercise that engages core muscles and enhances lower forearm strength.
- Stand beneath the pull-up bar, reach up, and grasp the bar with a shoulder-width grip, palms facing forward.
- Elevate your legs off the ground.
- Hang at arm’s length for 30-40 seconds with your arms straight and your ankles crossed behind you.
- How to Perform:
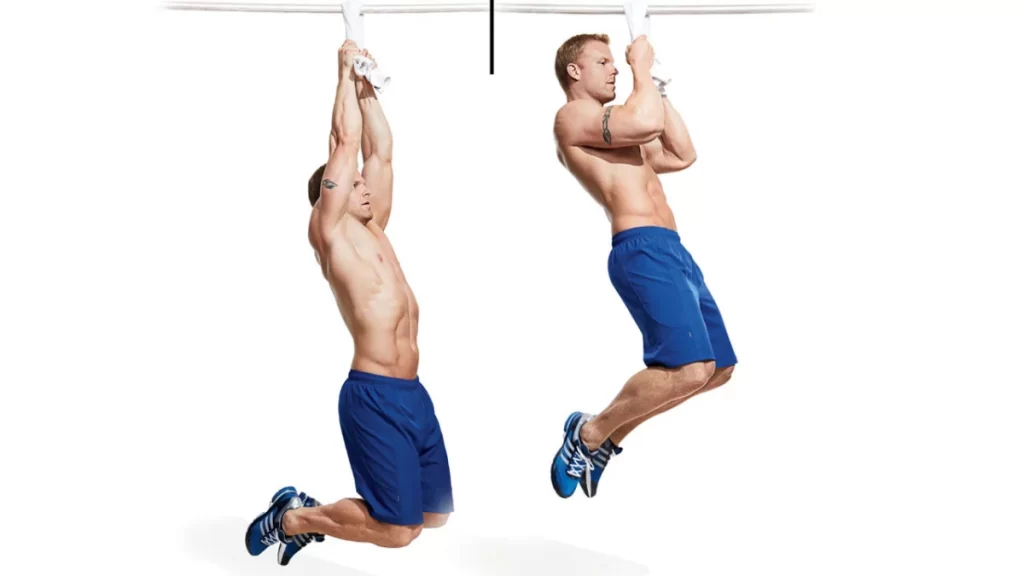

- Towel Pull-Up Bar Hang
- How to Perform:
- Similar to the Pull-Up Bar Hang, this variation targets wrist adductors while enhancing forearm strength.
- Drape 2 towels shoulder-width separated over the bar.
- Reach up and grab the towels with both hands, maintaining a tight grip.
- Engage your core and lift your feet off the floor, hanging with your ankles crossed behind you for as long as possible.
- Hold for 30-40 seconds.
- How to Perform:
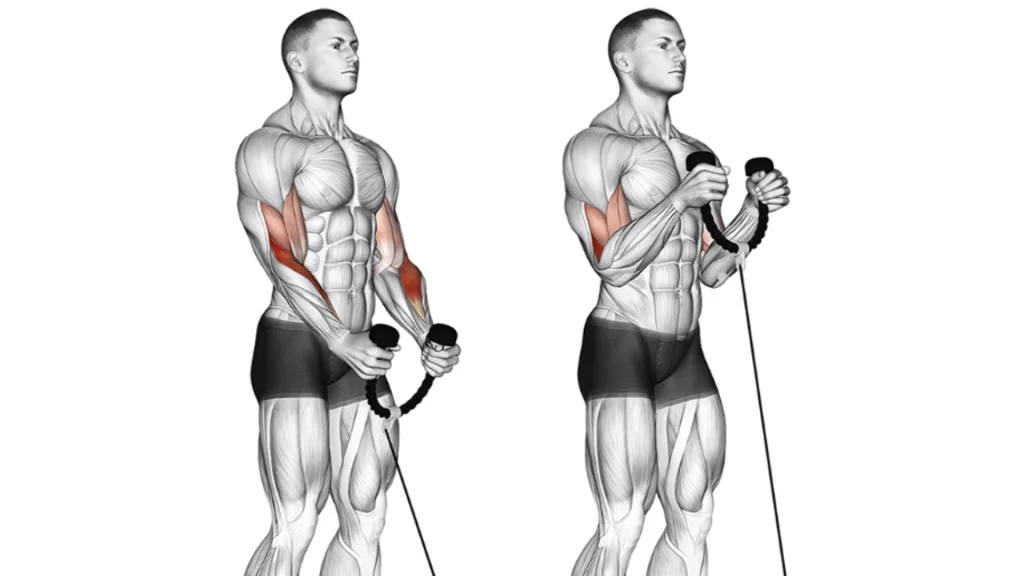
- Behind-the-Back Cable Curl
- How to Perform:
- The Behind-the-Back Cable Curl emphasizes elbow contraction and forearm engagement, enhancing blood flow through brachioradialis contraction.
- Connect a D-handle to the inferior pulley of a rope apparatus.
- Hold the handle in your right hand.
- Take a large step forward to create tension in the cable, positioning your arm slightly behind your body.
- Curl the handle, ensuring your elbow doesn’t move forward.
- Complete 4-5 sets of 10-12 repetitions in one session, and do two sessions per day.
- How to Perform:
- Parallel Bar Hand Walk
- How to Perform:
- The Parallel Bar Hand Walk involves walking forward and backward on parallel bars or a jungle gym to build wrist and finger flexors.
- Hang from the jungle gym or parallel bars.
- Walk forward with your hands to the end of the row and then walk back.
- Do this exercise for 40-60 seconds, repeating 3-4 times in one session, and perform two sessions per day.
- How to Perform:
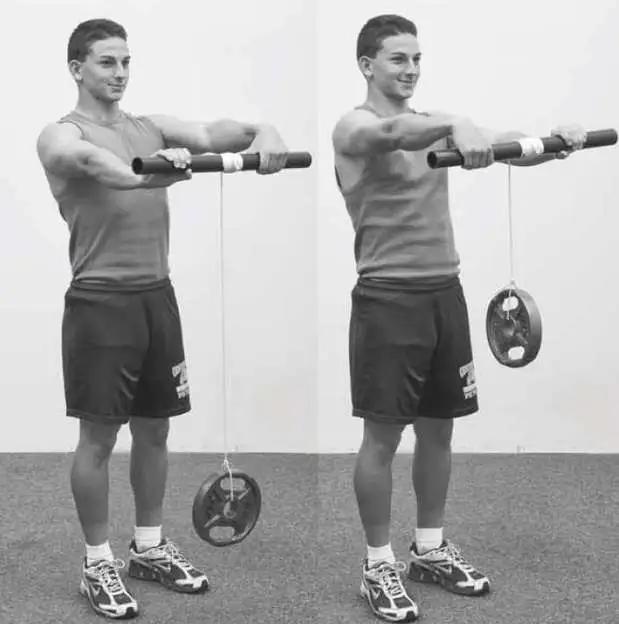

- Wrist Roller
- How to Perform:
- The Wrist Roller exercise strengthens forearm muscles and increases blood flow through brachioradialis contraction.
- Hold the wrist roller with each hand and extend your arms straight in front of you.
- Attach a 3-5 lb weight plate (or kettlebell) to the bottom of a cable.
- With palms facing down, turn your wrists toward your body and roll the apparatus between your hands to lift the weight.
- Slowly lower the plate by reversing the movement.
- Maintain extended arms throughout the exercise.
- Do 10-20 repetitions for 2-3 sets in one session, and perform three sessions per day.
- How to Perform:
- Rope Climbs
- How to Perform:
- Securely fasten a rope to a sturdy anchor point and perform rope climbs to engage forearm muscles, in addition to core, back, and upper arm muscles.
- Reach up and hold the rope with both hands.
- Pull your body up while using your legs to pinch the rope between your feet.
- Repeat this motion while keeping the rope between your feet at all times, and reverse to lower yourself back down.
- Rest for 3-4 minutes between climbs as this exercise taxes the forearms, core, back, and upper arms.
- How to Perform:
- Plate Pinch Hold
- How to Perform:
- The Plate Pinch Hold involves gripping a heavy-weight plate between your thumb and fingers, making it an excellent exercise for enhancing grip strength and forearm endurance.
- Hold a heavy-weight plate in each hand (or stack multiple 10-15 pound plates together with the smooth side facing out).
- Squeeze the weight plate as tightly as possible between your thumb and fingers, then let your arms hang at your sides.
- Hold for as long as you can, resting for 60-70 seconds between repetitions.
- You can also incorporate plate pinch rows and carries to further fatigue your forearms.
- How to Perform:

- Crab Walk
- How to Perform:
- Though it may appear unusual, the Crab Walk is an effective forearm exercise that promotes muscle growth.
- Sit on the ground, facing upward.
- Bridge up with your hips so that you’re on all fours.
- Walk forward on your hands and feet as quickly as possible.
- Perform 10 steps forward and 10 steps backward.
- How to Perform:
- Dead Hangs
- How to Perform:
- Dead Hangs involve gripping a bar and holding your body’s weight for as long as possible, making it an excellent exercise for developing grip strength.
- Hold a bar with slightly flexed elbows.
- Squeeze your shoulder blades together and down to engage the longissimus muscles.
- Keep your core tight throughout the exercise.
- Complete 2-3 sets, holding for 20-60 seconds in one session, and perform two sessions per day.
- How to Perform:
- Forearm Pull
- How to Perform:
- The Forearm Pull exercise involves using a weighted barbell on a pulley machine to strengthen forearm muscles.
- Hold the weighted barbell at shoulder level with your palms facing down.
- Pull the upper arms toward the sides of your trunk.
- Push the barbell all the way down.
- Pause, then return to the starting position.
- Perform 2-3 sets of 8-12 repetitions in one session, and do two sessions per day.
- How to Perform:
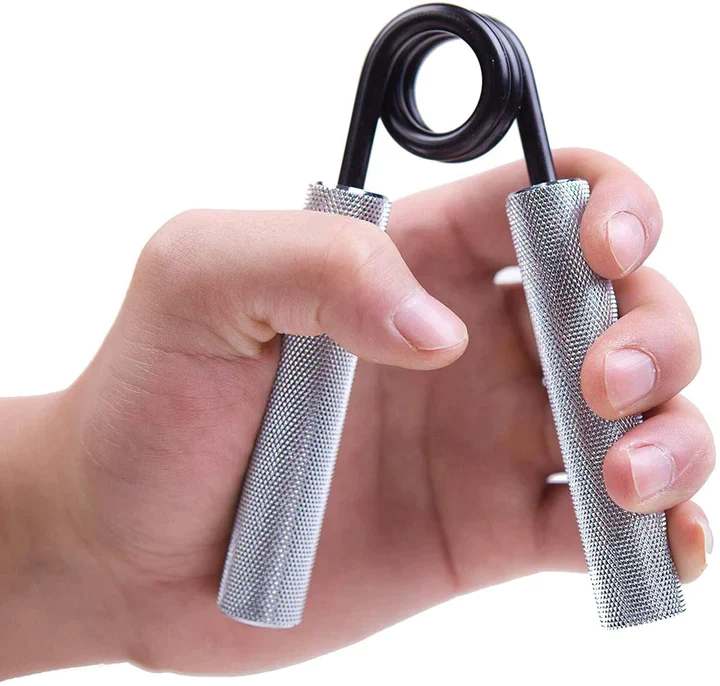

- Forearm Squeeze
- How to Perform:
- The Forearm Squeeze exercise can be done using forearm grips or any object that can be squeezed, such as a tennis ball or a sock.
- Flex and then extend your fingers to squeeze the object.
- Hold for 5-8 seconds, then release the grip for a few seconds.
- Repeat for 10-20 repetitions.
- How to Perform:
- Fingertip Pushups
- How to Perform:
- Fingertip Pushups require you to kneel on a bench or sturdy object and place your fingertips on a surface. This exercise challenges forearm muscles as well as upper body strength.
- Kneel on a bench or stable surface, placing your fingertips on the surface.
- Slowly and with control, lower your chest to the surface, bending your elbows to a 90-95 degree angle.
- Return to the starting position.
- Aim for 2-3 sets of 8-10 repetitions.
- How to Perform:
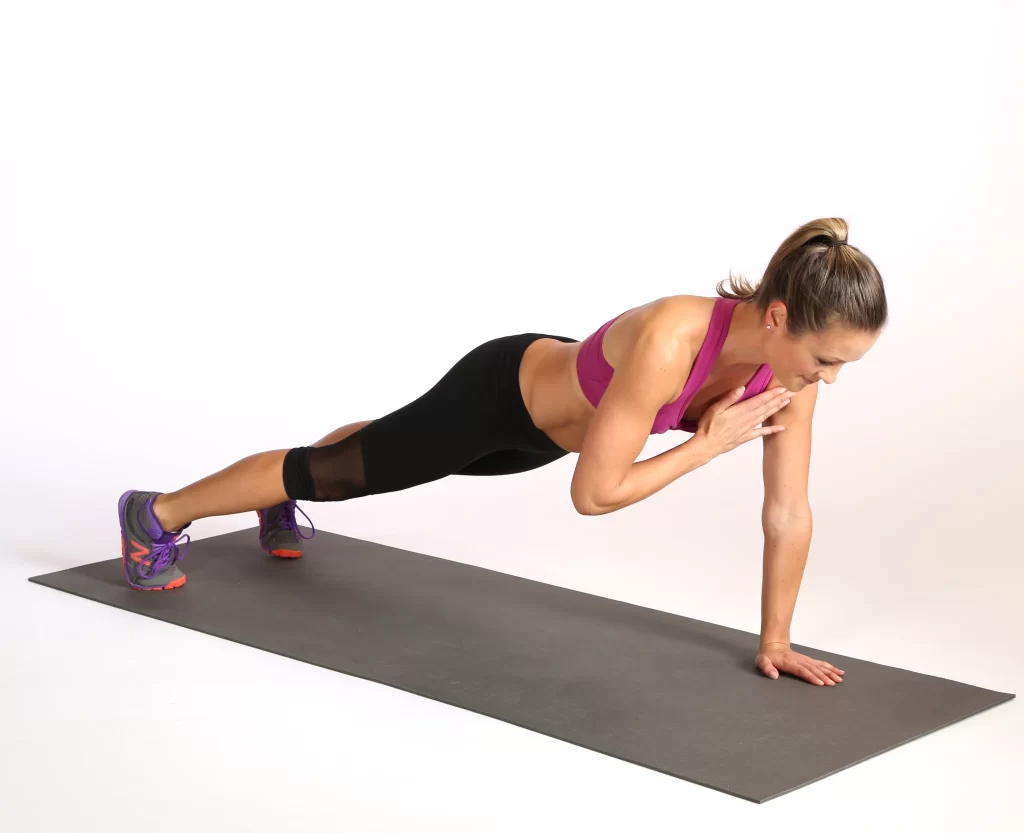

- Plank with Shoulder Taps
- How to Perform:
- Plank with Shoulder Taps is a bodyweight exercise that engages core muscles and forearm muscles by incorporating shoulder taps.
- Kneel on the floor/a yoga mat.
- Place your hands directly under your shoulders, as if you are about to do a pushup.
- Curl your toes under and raise your body into a plank position, engaging your core.
- Lift your left hand from the ground and touch the opposite shoulder.
- Return the hand to the floor.
- Lift your right hand from the ground, touch the opposite shoulder, and return the hand to the floor.
- Perform this exercise for 40-60 seconds, repeating 3-4 times in one session.
- How to Perform:
- Drag Curl Exercise
- How to Perform:
- The Drag Curl exercise is a variation of the traditional dumbbell curl, emphasizing elbow contraction for increased forearm engagement.
- Perform the curl as you would a standard dumbbell curl but maintain an upright posture.
- Move your elbows back during the curl so that the dumbbell heads touch the front of your body throughout the exercise.
- Maintain your hand facing up the whole duration.
- Complete 2-4 sets of 10-18 repetitions in one session, and do two sessions per day.
- How to Perform:
These diverse forearm exercises offer a comprehensive approach to strengthening and toning your forearm muscles, helping you achieve your fitness goals while promoting overall arm strength and stability. Incorporate them into your workout routine according to your fitness level and goals.
You may improve your forearm strength, endurance, and flexibility by including a range of these exercises in your fitness regimen. Keep in mind to gradually increase the resistance and intensity as your forearm muscles get used to the exercises. Be persistent in your exercise and patient as building strong forearms takes time and consistency.
Home Exercises
Here are a few forearm workouts you can do at home with very little gear:
- Hand Grippers
- Steps:
- Visit a fitness shop or order one online to enhance your grip.
- Your fingers should be around the handles as you hold the gripper in one hand.
- The gripper should be squeezed as firmly as possible before being progressively released.
- Once you’ve completed the required amount of reps, switch hands.
- Benefits:
- Portable and practical for use at home.
- Specifically focuses on grip power.
- Can be carried out during commercial breaks or while watching TV.
- Steps:

- Wrist Flexor Stretch
- Steps:
- Arms straight in front of you, comfortably seated or standing.
- Your right arm should be extended with the palm downward.
- Pull the fingers of your right hand down using your left hand.
- For 20-30 seconds, hold the stretch.
- On the opposite side, repeat.
- Benefits:
- Enhances the range of motion and flexibility of the wrist.
- Helps loosen up the wrists.
- Steps:

- Isometric Wrist Exercises
- Steps:
- With your arms out in front of you, either stand or sit.
- With your palms facing one another, extend your hands.
- Spend 10 to 15 seconds using all of your force to push your hands against one another.
- For numerous sets, release and repeat.
- Benefits:
- Enhances wrist and forearm muscular strength.
- Increases isometric endurance and strength.
- Steps:
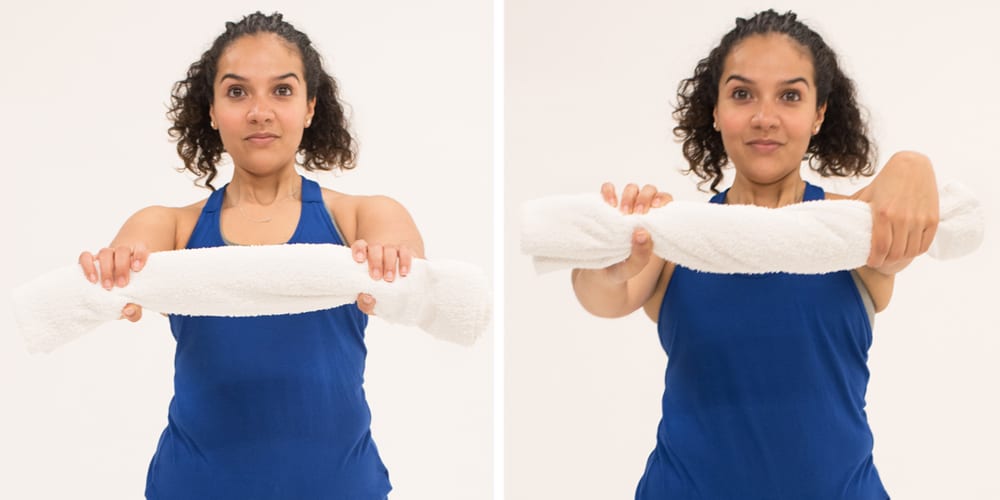

- Towel Twists
- Steps:
- Grab a tiny hand towel.
- The towel should be securely rolled into a cylinder.
- With both hands spread out to shoulder width, hold the towel.
- Utilizing your wrists to produce resistance, twist the towel in different directions.
- Twist for one to two minutes.
- Benefits:
- Strengthens the forearm and wrist.
- Low space and equipment requirements.
- Steps:
- Rice Bucket Exercise
- Steps:
- Put uncooked rice in a bucket.
- Spread your fingers widely and place your hands into the rice.
- Flexing and stretching your fingers, squeeze and release the rice.
- Repeat for one to two minutes.
- Benefits:
- gives the hand and finger muscles resistance.
- increases finger dexterity and strength.
- Steps:
For those who would want to improve their forearm strength without access to a gym or specialized equipment, these at-home workouts are perfect. Add these exercises to your at-home workout regimen, and don’t forget to progressively up the difficulty as your forearm strength develops. For maximum outcomes, consistency and perfect form are essential.
Categorized forearm exercises
The degree of intensity for forearm workouts can range from low grade to high grade. The level of intensity you choose will depend on your preferences, fitness level, and goals. Here are forearm exercises broken down by level of difficulty:
Forearm exercises that are low-intensity:
- Wrist Circles: To improve joint mobility and warm up the forearms, perform this exercise by rotating your wrists in circles in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions.
- Put a rubber band around your fingers and thumb, then extend and contract your hand against resistance to increase the flexibility and strength of your fingers and forearm.
- Finger Taps: To increase finger dexterity, lightly tap your fingers on a table or other flat surface, concentrating on one finger at a time.
Moderate-Intensity Forearm Exercises:
- Wrist curls: Place your forearms on your thighs while holding a dumbbell with your palms facing up and curl your wrists upward. The wrist flexors are the focus of this workout.
- Wrist curls in reverse: Perform wrist curls with your palms facing down. It concentrates on the wrist flexors.
- Twist a towel in different directions while holding it in both hands to create resistance. This exercise strengthens and rotates the forearms.
- Squeeze stress balls or grip strengtheners to increase your grip power and forearm stamina.
High-Intensity Forearm Exercises:
- Lifting big weights off the ground when performing a compound exercise known as a deadlift heavily works the forearm muscles, particularly the grip.
- Pull-Ups: By hanging from a bar and raising your torso, you put a lot of strain on your grip and forearms.
- Farmers’ Walk: Walk a set distance or for a set amount of time while holding hefty dumbbells or kettlebells in each hand. Grip power and forearm endurance are put to the test in this exercise.
- Rock climbing and indoor bouldering both demand strong forearms to grasp and climb walls or rocks, respectively.
- Plate Pinch: To strengthen your pinch grasp, hold two weight plates together with their smooth sides facing out. Then, pinch them between your fingers.
Very High-Intensity Forearm Exercises:
- Rows with heavy barbells or dumbbells: Rowing with high weights requires a firm grip and heavily utilizes the forearm muscles.
- Olympic weightlifting: To control the barbell during quick movements, exercises like the clean and snatch call for outstanding forearm strength.
- Grip challenges: Sophisticated grip challenges, including employing grip trainers made for expert users or training with thick barbells, will exhaust your forearm’s power.
- Build forearm strength and endurance by rolling a weighted rope or bar up and down.
Your fitness objectives and current level of fitness should guide your choice of forearm workouts. While elite athletes can add high and very high-intensity workouts for more substantial strength improvements, beginners should start with low to moderate-intensity exercises to lay a strong foundation. To prevent overuse problems and guarantee steady improvement in forearm strength, keep in mind to utilize appropriate form and gradually raise the intensity.
Cautions and Modifications
If you’re unsure where to begin or seek professional guidance, consider visiting a physical therapist or fitness expert. They can address specific concerns, create a tailored routine, and ensure you perform exercises correctly.
When engaging in these exercises, prioritize your body’s comfort and safety. Practice gentleness, maintain controlled breathing, and execute smooth, fluid movements, avoiding any jerky motions.
Cease exercising if you experience pain or any discomfort beyond a mild sensation. If post-exercise soreness arises, apply ice to the affected area and incorporate light stretching to alleviate muscle tension.
For individuals with recent injuries or underlying medical concerns that could be impacted by forearm exercises, it’s advisable to either avoid them or perform them under the supervision of a physician or physiotherapist.
Avoid these exercises if:
You’ve recently sustained a forearm or wrist fracture.
You’re currently experiencing wrist pain.
If you encounter any pain or discomfort during the exercises; stop immediately and consult a physical therapist.
Your doctor has advised you to rest.
You sense a muscle pull or experience an undiagnosed muscle contraction.
Prioritizing caution and heeding your body’s signals ensures that your forearm exercises are both safe and effective.
FAQ
Are forearms fast growing?
Be patient as it may take some time to increase forearm strength and growth. However, if you work hard, you should start to see some progress within a month or two. the elbows, wrists, and hands. You need a variety of workouts that cover the full range of motion and forearm flexion in the wrist and forearm.
Are forearms hard to grow?
Many tiny muscles with different fiber kinds make up the forearms. However, like the soleus muscle, the majority of the forearm muscles are predominately slow twitch. Since slow-twitch muscle fibers depend on myoglobin, which is a significant source of oxygenated blood, they are challenging to grow.
What makes forearms bigger?
Barbell holds farmer’s walks, plate pinchers, and hand grips are all forearm-building exercises that will improve wrist flexibility, stability, and control in other lifts. Effective forearm growth requires good form, gradual overload, and sufficient recuperation.
Can I train my forearms every day?
Similar to calves and abs, forearms are a muscle area that needs regular exercise virtually every day. This implies that you don’t need to train your forearms on a “rest” day.
Why are my forearms so weak?
Trauma from an injury, repetitive strain injury, nerve damage or compression in the neck or upper back, or blockages in the bloodstream are some of the causes of weakness in the arms. You could need emergency medical care if you have left arm weakness and chest pain.
Do hand grippers increase forearm size?
Even though utilizing hand grippers by themselves can result in a growth in forearm size, using them in conjunction with other workouts and methods will enable you to achieve even better results.
Do forearms grow with age?
Your forearms’ size and definition might alter as your body ages, just like any other muscle. Aside from throughout childhood and puberty, aging does not naturally result in the growth of muscle mass without exercise.
How many push-ups a day?
A lot of residents accomplish over 300 pushups/day. Regardless, if done accurately, even 50-100 push-ups should be acceptable for the average person to retain a powerful upper body. Begin with 20 pushups, but do not restrict yourself to that digit.
Are forearms genetic?
Many factors can affect a person’s forearm size. Given that some people are born with naturally larger or smaller forearms, genetics play a crucial impact. Regular exercise, particularly those that work the forearm muscles, can also affect size.
How many hand grips per day?
The best method to use hand grippers is in sets & repetitions; a good example is 5 sets of 10 repetitions, with a pause of about 30 seconds to 1 minute in between sets. You will begin to see an impact after doing this a few times per day for almost a week.
Reference
- Prajapati, N. (2022, December 20). Forearm muscle strengthening exercise – Benefits, How to do? Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/forearm-muscle-strengthening-exercise/
- Forearms. (n.d.). Muscle & Strength. https://www.muscleandstrength.com/exercises/forearms
- Romine, S. (2020, April 23). Are You Working Your Forearms? Because You Should Be. Greatist. https://greatist.com/health/forearm-exercises
- ExRx.net : Forearm Exercises. (n.d.). https://exrx.net/Lists/ExList/ForeArmWt