LIMB GIRDLE MUSCULAR DYSTROPY
INTRODUCTION:-
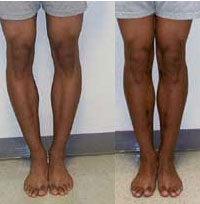
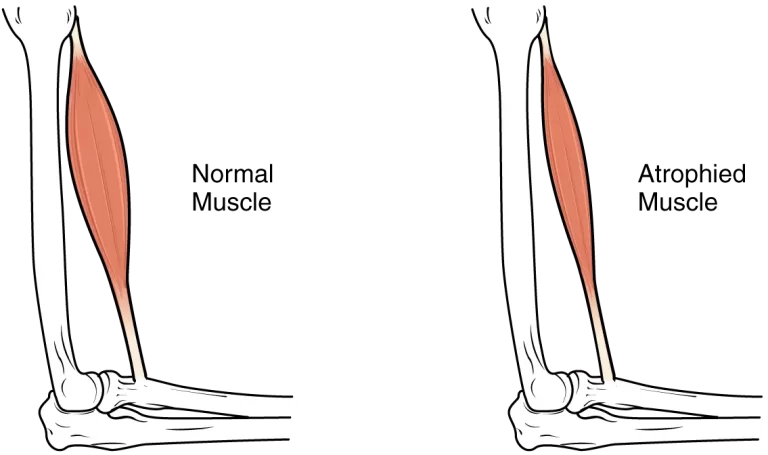
Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) is a diverse group of disorders with many sub types categorized by disease gene and inheritance. LGMD usually manifests in the proximal muscles around the hips and shoulders. (The proximal muscles are those closest to the center of the body; distal muscles are farther away from the center — for example, in the hands and feet).
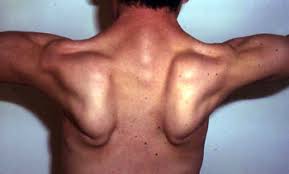
SYMPTOMS :-
→ Individuals may first notice a problem when they begin to walk with a “waddling” gait because of weakness of the hip and leg muscles. They may have trouble getting out of chairs, rising from a toilet seat or climbing stairs. As this weakness progresses, the person may require the use of assistive mobility devices.
→ Weakness in the shoulder area may make reaching over the head, holding the arms outstretched or carrying heavy objects difficult. It may become increasingly hard to keep the arms above the head for such activities as combing one’s hair or arranging things on a high shelf. Some people find it harder to type on a computer or other keyboard and may even have trouble feeding themselves.
→ Some of the various LGMD sub types also are characterized by additional symptoms. For example, the heart can be affected in some types of LGMD, with weakness of the heart muscle (cardiomyopathy) and/or abnormal transmission of signals that regulate the heartbeat (conduction abnormalities or arrhythmia’s).
→ Some disease sub types also involve the muscles used for breathing, and for that reason, respiratory function, along with cardiac function, should be monitored regularly.
Causes of Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy:-
→ In most cases, both parents must pass on the non-working (defective) gene for a child to have the disease (autosomal recessive inheritance).
→ In some rare types, only one parent needs to pass on the non-working gene to affect the child. This is called autosomal dominant inheritance.
What is the progression of Limb-girdle muscular Dystrophy?
LGMD progression in each type cannot be predicted with certainty, However knowing the underlying genetic mutation can be helpful. Few types of the LGMD progress to loss of walking ability within a few years and cause serious disability, while others types very gradually over many years and cause minimal disability.
LGMD can started in childhood, adolescence, young adulthood, or even later. Both genders are affected equally.
When LGMD starts in childhood, some Doctors say, the progression is usually faster and the disease have more disabling symptoms. When the LGMD starts in adolescence or adulthood, they say, it is generally not as severe and progresses more slowly. The course is usually one of slowly progressive, mostly symmetric weakness, with the exception of a few types with rapid progression or asymmetric weakness.
What is the latest research on LGMD?
MDA-supported scientists are showing several exciting treatment strategies in muscular dystrophy research that have also implications for LGMD. These treatment are gene therapy, exon skipping, stop codon read through, and myostatin blocking.
DIAGNOSIS:-
→ High CK levels(x10-150 times normal)
→ MRI can indicate different types of LGMD.
→ EMG can confirm the myopathic characteristic of the disease.
→ Electrocardiography (cardiac arrhythmia in LGMD1B can occur)
Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy treatment
There are no cures for LGMD, but there are treatments to manage the symptoms and slow its progression. treatments to manage the symptoms and slow its progression.
LGMD is a progressive disease, Regular Physiotherapy exercise helps maintain muscle strength and overall slowdown progression. Balance Diet and Fitness also helpful some extent.
PHYSIOTHERAPY:-
Physiotherapy treatment are depends mainly on Manual muscle testing chart, accordingly muscle strengthening exercise and stretching exercise of tight muscle and related Rehabilitation exercise.
Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy exercise :
limb-girdle muscular dystrophy exercise are planned according to muscle chart, focus on strengthening of weak muscles, stretching of tight muscle with Balancing exercise and Breathing exercise.
→ Simple devices like a cane or a long-handled reacher can make things easier as weakness progresses.

→ A power wheelchair or scooter becomes convenient when weakness in the pelvic girdle and upper legs causes frequent falls.

→ Occupational therapy focuses on specific activities and functions, particularly use of the hands, while physical therapy emphasizes mobility and (where possible) strengthening of large muscle groups.
→ The primary goals of physical therapy are to allow greater motion in the joints and to prevent contractures (freezing of the joints).
→ In occupational therapy, the focus is on improving abilities related to your job, recreation or daily living. For example, arm supports can make tasks such as using a computer or fixing your hair less tiring.
→ Some experts recommend swimming and water exercises as a good way to keep muscles as toned as possible without causing undue stress on them.