MYOTONIC MUSCULAR DYSTROPY
Introduction:
→ Myotonic muscular dystrophy is a long term genetic disorder that affects muscle function.Myotonic dystrophy is an autosomal-dominant disorder which is typically inherited from a person’s parents.There are two main types: type 1 (DM1) due to mutations in the DMPK gene and type 2 (DM2) due to mutations in the CNBP gene.
Causes of Myotonic muscular dystrophy:
MMD is divided into two types.
→ Type 1 MMD (MMD1) occurs when a gene on chromosome 19 called DMPK contains an abnormally expanded section.
→ Type 2 MMD (MMD2) is caused by an abnormally expanded section in a gene on chromosome 3 called ZNF9.
Symptoms:
→ DM1 symptoms for DM2 include problems with executive function (e.g., organization, concentration, word-finding) and hypersomnia.
→ Both types are also associated with insulin resistance.
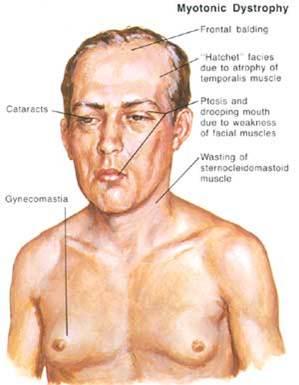
→ Myotonic dystrophy may have a cortical cataract with a blue dot appearance, or a posterior subcapsular cataract.
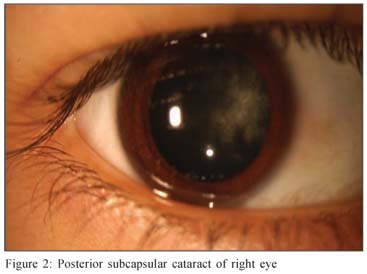
→ Symptoms may appear at any time from infancy to adulthood.
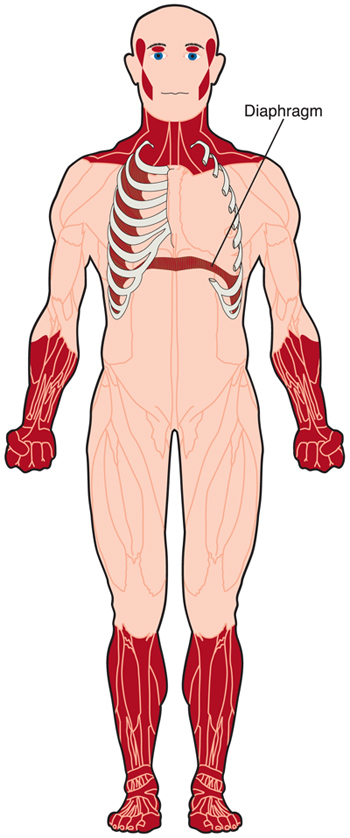
→ DM causes general weakness, usually beginning in the muscles of the hands, feet, neck, or face. It slowly progresses to involve other muscle groups, including the heart. DM affects a wide variety of other organ systems as well.
→ In affected men, hormonal changes may lead to early balding and an inability to father a child (infertility).
Diagnosis:
→ Genetic tests, including prenatal testing, are available for both confirmed forms. Molecular testing is considered the gold standard of diagnosis.
Treatment of Myotonic muscular dystrophy:
→ There is currently no cure for or treatment specific to myotonic dystrophy.
→ Medication – Mexiletine, carbamazepine, tricyclic antidepressants, nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs
→ Pacemakers, Non invasive positive pressure ventilation.
Physical Therapy treatment in Myotonic muscular dystrophy:
→ Combined strengthening and aerobic training at moderate intensity was deemed safe for individuals with neuromuscular diseases.

→ Specifically, aerobic exercise via stationary bicycle with an ergometer was found to be safe and effective in improving fitness in people with DM1.
→ The strength training or aerobic exercise may promote muscle and cardiorespiratory function, while preventing further disuse atrophy.
→ Cardiovascular impairments and myotonic sensitivities to exercise and temperature necessitate close monitoring of people and educating people in self-monitoring during exercise via the Borg scale, heart rate monitors, and other physical exertion measurements.
→ Orthotics – Muscular weakness of dorsiflexors (dorsiflexion) hinders the ability to clear the floor during the swing phase of gait and people may adopt a steppage gait pattern or ankle-foot-orthotics may be indicated.
→ Factors such as hand function, skin integrity, and comfort must be assessed prior to prescription. Neck braces can also be prescribed for neck muscle weakness.