Rigidity & Physiotherapy Treatment
What is a Rigidity?
- Rigidity means increased tone of muscles also called Hypertonia by many authors, is a common muscle tone disorder in which there is resistance to passive movement irrespective of posture and velocity.
- It is one of the symptoms mainly seen in Parkinson’s Disease and is usually present in extrapyramidal disorders. It affects the agonists and the antagonists equally eg. it affects the flexor group of muscles and also at the same time extensor group of muscles.
It can be present in
- Spinocerebellar Ataxia – type 43, 17, 2
- Orthostatic Hypotonia Shy-Drager Disease
- Corticobasal Degeneration
- Niemann-Pick Disease – Type A
- Multiple System Atrophy
- Seen in extrapyramidal lesions (i.e. Parkinson’s) such as the rubrospinal or vestibulospinal tracts
- Parkinson’s Syndrome
- Cerebral palsy
- Dementia
- Febrile Seizure
- Limb Syndrome
- Multiple Sclerosis
Definition of Rigidity
- Rigidity is an increase in muscle tone leading to resistance to passive movement throughout the range of motion.
- Rigidity is a hypertonic state caused by constant resistance throughout the range of motion that is independent of the velocity of movement. It is the result of excessive upper motor neuron facilitation acting on alpha motor neurons spinal reflex mechanisms are typically normal. In Parkinson’s rigidity, tendon jerks are usually normal.
Types of Rigidity
It may be characterized as either “lead pipe” or “cogwheel.”
- Cogwheel Rigidity – Refers to a hypertonic state with jerkiness and is commonly seen in upper extremity movements (e.g., wrist or elbow flexion and extension). The cogwheel type of rigidity is a combination of lead-pipe rigidity with tremor.

- Lead Pipe Rigidity – Refers to hypertonic state throughout the range of motion i.e. simultaneous co-contraction of agonists and antagonists and this is reflected in an immediate resistance to a reversal of the direction of movement about a joint.

Related Anatomy
The term “basal ganglia” describes a collection of subcortical nuclei that play a variety of tasks in the brain, including motor learning, emotions, executive processes and behaviors, and motor control.
The basal ganglia’s conventional concept shows how information leaves the basal ganglia and returns to the cortex through two channels that have opposing effects, allowing for the proper execution of movements.
Pathophysiology
When alpha motor neurons experience excessive supraspinal driving (upper motor neuron facilitation), rigidity results; spinal reflex mechanisms are usually unaffected. Normal reciprocal inhibition is not being maintained. The symptoms and indicators of stiffness and involuntary movements, as well as irregularities of posture and related movement, appear when the balance of inhibition and excitation in the basal ganglia and motor cortex is upset.
The two major hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease, rigidity, and tremor, are not sufficiently explained by the pathophysiology of the basal ganglia as it is currently understood.
Rigidity can result from a number of factors, some of which are as follows:
- incapacity of the patient to relax and totally stop using their muscles
- increased rigidity as a result of changed muscle viscoelastic characteristics
- abnormal agonist-antagonist muscle group co-activation
- increased stretch reflexes
- reduced dopamine levels
Different between Lead pipe & Cogwheel rigidity:
- Lead pipe rigidity is defined as a constant resistance to motion throughout the entire range of movement.
- Cogwheel rigidity refers to resistance that stops and starts as the limb is moved through its range of motion.
Difference Between Spasticity & Rigidity:
| SPASTICITY | RIGIDITY |
| Spasticity is a condition in which there is an abnormal increase in muscle tone or stiffness of muscle. | Clonus absent. |
| Hypertonia _ claps knife type of rigidity. | It depends upon velocity & amplitude. |
| It depends upon velocity & amplitude. | Hypertonia _ cog wheel & lead pipe type of rigidity. |
| Mainly affect anti-gravity muscles. | Both flexors & extensors are affected. |
| Clonus present. | Increased muscle tone due to damage to pyramidal tracts. |
| Clonus present . | Increase in alpha & gamma activity. |
| Increase in gamma activity. | Not stretch sensitive. |
| Ex. Chonic UMNL. | Stretch sensitive. |
| No tremors. | Static tremors. |
| Hyperreflexia. | Normal reflexia . |
| Hypertoniya _ claps knife type of rigidity. | Ex. Parkinsonism. |
SPASTICITY VS RIGIDITY
Cause of Rigidity?
- Muscle rigidity is often triggered by stress.
- Polymyalgia rheumatica is a common condition that causes pain and stiffness in older adults.
- Unexplained weight loss and fatigue.
- In parkinsonism pt. reduced dopamine levels are thought to disrupt the balance between the muscles which extend and relax for each movement.
What are the Symptoms of Rigidity?
- Stiff and/or inflexible muscles.
- Pain and muscle cramps.
- Difficulty turning when walking, turning in bed, and getting out of a chair or bed.
- The combination of tremor & increased tone is considered to be the origin of cogwheel rigidity.
- Rigidity may be associated with joint pain.
Treatment of Rigidity
Medical Treatment
Bradykinesia and rigidity are greatly reduced when levodopa (L-Dopa) is used in these different combinations to treat Parkinson’s disease.
Rigidity has been shown to be improved by deep brain stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus.
Physiotherapy Treatment
- Apply a warm compress or heating pad to the affected muscle to help relax rigid muscles.
- Gently stretch your stiff muscle to help relax it.
- Avoid strenuous activity that may trigger the muscle to become rigid again.
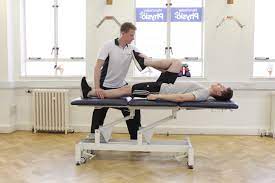
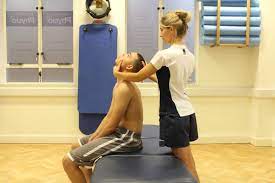


Relaxation & Stretching exercise:

- Gentle rocking exercise, rotational exercise in slow & rhythmic patterns.
- Rhythmic initiation technique in which movement progresses from passive to active assisted and active movement.
- In supine: slow side-to-side head rotation. In hook lying: lower trunk rotation.
- In side lying: upper & lower trunk rotation.
BALANCE TRAINING:

Develop high-level eccentric strength dynamic neuromuscular efficiency & reactive joint stabilization.
Balance training programs aim to:
- Strengthen balance control in everyday activities leading to improved fall-related self-efficacy, reduced fear of falling, and increased walking speed
- Improve physical function
- Improve the quality of life
Gait Training

- The exercises involve improving motion in your lower extremity joints, improving strength and balance, and mimicking the repetitive nature of your legs that occurs while walking.
- Walking on a treadmill.
- Lifting your legs.
- Sitting down.
- Standing up.
- Stepping over objects.
Home Remedies
When it comes to treating muscle stiffness caused by small injuries, tension, or overuse, home treatments typically work well. These may consist of the following:
To help relax stiff muscles, apply a warm compress or heating pad to the affected area.
To assist your stiff muscle relax, gently stretch it.
Avoid strenuous activities that could cause the muscles to stiffen up again.
Encouraging the muscles to become more relaxed through tai chi, yoga, or massage.
FAQs
What is rigidity a symptom of?
Muscle rigidity occurs when they lose their elasticity. This condition, known as a Parkinson’s mask or facial masking, affects the muscles in your face. It is among the primary signs of Parkinson’s disease.
What deficiency causes muscle rigidity?
Potassium: Potassium plays a major part in muscular contractions because of its role in conveying electrical impulses. A low potassium level prevents muscle relaxation, resulting in inflexible muscles that cause stress and reduced function.
What is the difference between spasticity and rigidity?
While rigidity is brought on by dysfunction of extrapyramidal pathways, most often the basal ganglia, but also by lesions of the mesencephalon and spinal cord, spasticity is produced by injury to the corticoreticulospinal (pyramidal) tracts.
What is muscle rigidity?
One of the most typical causes of muscle pain is muscle rigidity, which is also referred to as muscle tension, rigor, or stiffness. The incapacity of the muscles to relax normally is what defines it. Any muscle in the body may be impacted by the illness, resulting in severe discomfort that limits movement.
How to improve rigidity?
Frequent movement, and exercises throughout the day, such as clearing out a closet, hiking, strolling to the mailbox, yoga, dancing, biking, or watering your plants, might help reduce stiffness.
What disease causes rigidity?
Parkinson’s disease is a central nervous system disease that worsens over time and has no known cure. It affects the neurological system, which makes movement difficult. One of the most common signs of Parkinson’s disease is rigidity, which is typified by stiff muscles.
What does muscle rigidity indicate?
Muscles that are tight and rigid are frequently caused by trauma. Muscle soreness and rigidity can occasionally coexist with other symptoms like decreased mobility or muscle spasms. It’s usually benign and curable to have mild muscle stiffness and tightness.
What are two types of rigidity?
Lead pipe and cogwheel rigidity are the two varieties. A consistent resistance to motion across the whole range of motion is referred to as lead pipe rigidity. Resistance that fluctuates in intensity as the limb moves through its range of motion is referred to as cogwheel rigidity.




5 Comments