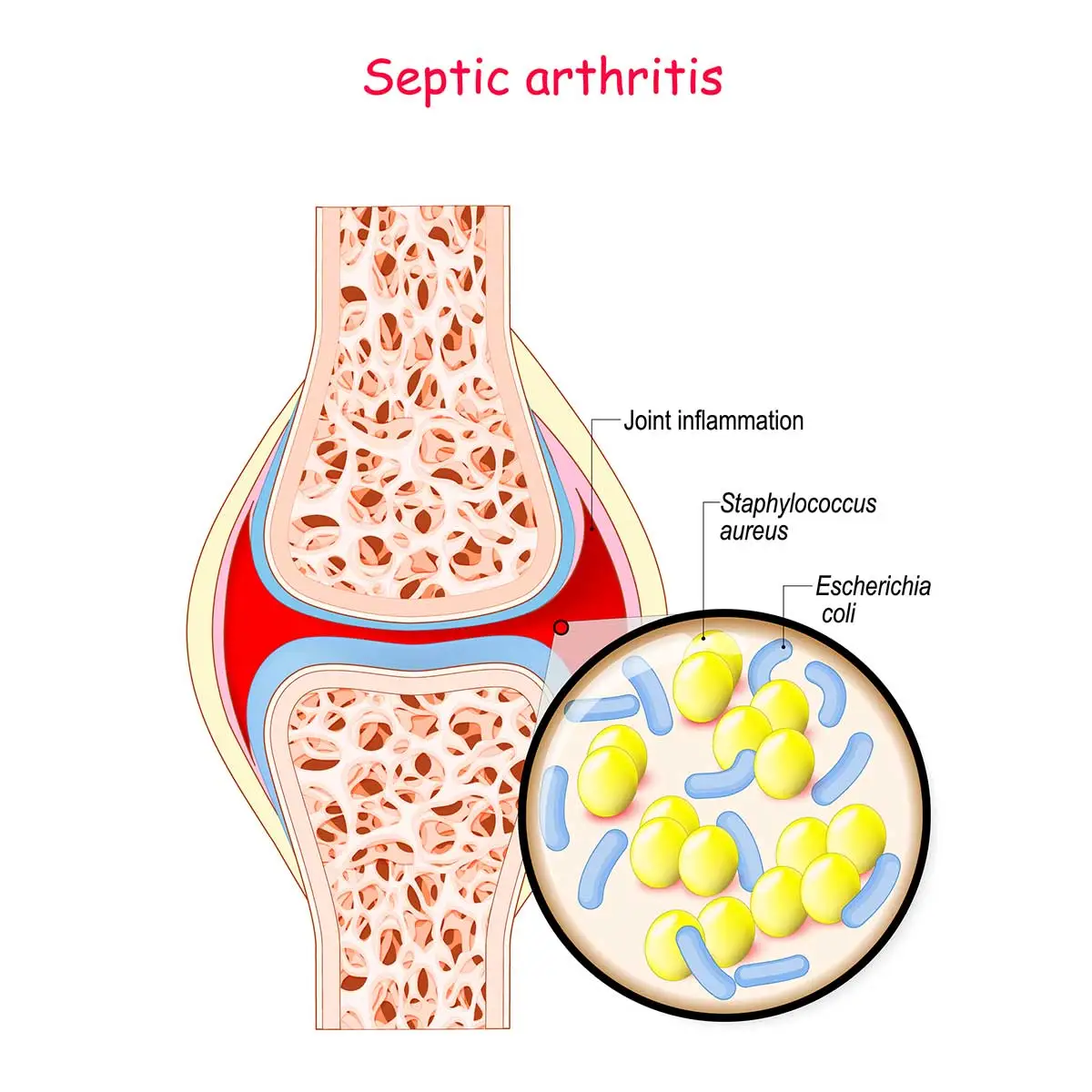
Septic arthritis
What is Septic arthritis?
Septic arthritis is an infection within the joint (synovial) fluid and the tissues. It occurs further consistently in children than in adults. The infection generally reaches the joints via the bloodstream. Septic arthritis (also referred to as contagious arthritis) happens when an infection spreads to one or further of your joints and causes inflammation.
Epidemiology
- The prevalence of septic arthritis is between 2 to six cases per,100000 people still, rates vary supported by the presence of threat factors.
- Septic arthritis is more usual in children than in grown-ups.
- The prevalence of septic arthritis peaks between periods 2 and three times and has a manly ascendance.
- Groups of youths at high threat include babes, hemophiliacs with hemarthroses, immunocompromised(e.g., red blood cell anemia, mortal immunodeficiency contagion infection), and people treated with chemotherapy.
- Threat factors in grown-ups include age aged than 80, DM ( Diabetes Mellitus ), atrophic arthritis, recent common surgery, common prosthesis, intra-articular injection, skin infections, cutaneous ulcers, mortal immunodeficiency contagion, osteoarthritis, sexual intercourse( especially in cases of presumed gonococcal septic arthritis), and other causes of sepsis.
- A large population-grounded study in the UK showed that septic arthritis is adding. Rates are growing most fleetly within the> 75 times age group, which is presumably going the result of adding co-morbidities.
What are the Causes of Septic Arthritis?
Different types of bacteria, contagions, and fungi can infect a joint. the kinds that can beget septic arthritis include :
- Staphylococci – These are common bacteria that always beget skin infections.
- Haemophilus influenza – larynx, trachea, and bronchi infected by these bacteria
- Gram-negative bacilli – this is frequently a group of bacteria that includes E. coli.
- Streptococci – this is frequently a group of bacteria that can lead to a wide variety of conditions.
- Gonococci – this is frequently the bacterium that causes gonorrhea.
- Contagions – Contagions like HIV can infect the joints of people of all periods.
- Staphylococcus aureus is also known as s. aureus.
- The bacteria can enter the body in several ways, similar as :
- A broken bone that goes through the surface of the skin( open fracture)
- An infection that spreads from another place to the body, like the skin or genitals
- An infected crack ( Wound )
- Foreign object that goes through the skin
- An injury that breaks the skin
Risk factor
Two of the foremost important factors that put a case at threat are a pre-existing common pathology, especially atrophic arthritis, or recent prosthetic joint surgery. Other threat factors to be considered are :
- adding age
- History of infection of any kind
- Autoimmune conditions like Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Scleroderma
- Diabetes
- Sarcoidosis
- mortal bite or tick bite
- Fracture
- Central line placement
- Indwelling catheter
- Immunocompromised condition eg mortal Immunodeficiency Contagion( HIV)
- habitual common damage( RA, OA)
- Sexually transmitted infection
- Injection substance abuser
- Drunkenness
- Recent immunization
- Malnutrition
- Skin breakdown
- Infrequently seen may be a case of contagious Arthritis as a complication from ACL reconstruction due to defiled bone-tendon-bone allografts.
Symptoms of Septic arthritis
- Acute, rapid-fire- the onset of pain
- Unfit to initiative the joint through an active and unresistant range of stir
- generally just one joint( can be bilateral or further than one joint depending on the type of infection)
- unfit to touch any weight on the common
- Effusion
- Common warmth
- Skin rash
- Low-grade fever
- Lymphadenopathy
- The joints of the arms and legs are the foremost generally affected in grown-ups( especially the knees)
- The hip is most generally affected in children
Symptoms in Newborns/Infants:
- Cries when the infected joint is moved
- Fever
- Unable to maneuver the limb
- Irritability
Differential Diagnosis
- Infection: Bacterial, fungal, viral, spirochete, mycoplasma
- Crystal-induced arthropathies: calcium oxalate, hydroxyapatite crystals
- Osteoarthritis, pseudogout, cholesterol, Acute gout
- Intra-articular damage: Fracture, meniscal tear, osteonecrosis, nonnative, plant thorn synovitis
- Inflammatory arthritis: seronegative spondyloarthropathies like ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease-related arthritis; Sarcoid, systemic LE, Still disease, Bechet syndrome, reactive arthritis, atrophic arthritis
- Systemic infection: human immunodeficiency virus, Lyme disease, Bacterial endocarditis
- Tumor: Metastasis, pigmented villonodular synovitis
- Other: neuropathic arthropathy, dialysis-related amyloidosis, avascular necrosis, clotting disorders or anticoagulant therapy, Hemarthrosis
Diagnosis of Septic arthritis
- Joint fluid analysis – Infections can alter the shad, thickness, amount, and makeup of the fluid within your joints. A selection of this fluid is frequently withdrawn from your affected joint with a needle – Laboratory tests can determine what organism is causing your infection, so your doctor will know which medications to prescribe.
- Blood tests – These can determine if there are gestures of infection in your blood. A sample of your blood is far down from a vein with a syringe.
- Imaging tests – X-rays and different imaging tests of the affected joint can assess injury to the joint or the loosening of a man-made joint.
- Phlegm, cerebrospinal fluid, and urine tests – These are gone to seem for bacteria and find the origin of infection.
Prognosis
Despite antibiotic use, there’s a 7% to 15% mortality rate for in-hospital septic arthritis. Morbidity from septic arthritis occurs in one-third of cases. Both morbidity and mortality increase with patient age, comorbid conditions carrying pre-existing common complaints, and prior synthetic intra-articular material. Hence the necessity for a high indicator of suspicion, early diagnosis, and prompt treatment for septic arthritis particularly in cases with known predisposing threat factors and co-morbid conditions.
Treatment of Septic arthritis
Joint drainage
Drainage methods include:
Syringe – In some cases, your doctor can withdraw the infected fluid with a needle fitted into the joint space.
Scope procedure – In arthroscopy, a versatile tube with a videotape camera at its tip is placed in your joint through a small incision.
Suction and drainage tubes are also fitted through small incisions around your joint.
Open surgery – Some junctions, like the hip, are difficult to drain with a needle or arthroscopy, so an open surgery might be required.
Antibiotics
To select the most effective drug, your doctor must identify the microbe causing your infection. Antibiotics are generally given through a vein in your arm initially. Later, you’ll be suitable to switch to oral antibiotics.
Typically, treatment lasts from two to 6 weeks. Antibiotics carry a danger of side effects, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. allergies also can occur. Ask your doctor about what side effects to anticipate from your drug.
Below may be a non-exhaustive list of antibiotics generally utilized in the treatment of septic arthritis:
- Ceftriaxone (Rocephin)- Effective against gram-negative enteric rods
- Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) – Use to treat N gonorrhea and gram-negative enteric rods.
- Cefixime (Suprax) –Wide activity against gram-negative bacteria, by chaining to at least one or further of the penicillin-binding proteins. Arrests bacterial cell membrane mixer and inhibits bacterial growth.
- Oxacillin – Oxacillin is good against methicillin-sensitive S aureus (MSSA).
- Vancomycin (Vancocin) – An anti-infective medium used against methicillin-sensitive S aureus (MSSA), methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative S aureus (CONS), and ampicillin-resistant enterococci in patients antipathetic to penicillin.
- Linezolid (Zyvox) – an optional antibiotic that is applied in patients allergic to vancomycin and for the treatment of vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Removal of the replacement joint
If a man-made joint is infected, treatment frequently involves removing the joint and temporarily replacing it with a joint spacer — a device made with antibiotic cement. A replacement joint is implanted after several months.
If a replacement joint cannot be removed, a doctor may clean the joint and take down damaged tissue but keep the artificial joint in place.
Intravenous antibiotics are followed by oral antibiotics for several months to break off the infection from coming back.
Physical Therapy Treatment
- physical therapist to recognize the signs and symptoms of the infection and relate out to other medical treatments. Subjective history, together with the physical therapist’s objective findings, is vital to recognize the risk factors that make septic arthritis the likely opinion. it’s significant to immobilize the joint in this stage to best manage the patient’s pain and to drop the likelihood of doing further damage to the joint until proper treatment can occur.
- Once the patient receives a round of antibiotic treatment simultaneously with either joint aspiration, debridement, or arthroscopy, the patient may also be referred back to physiotherapy including Crutches Walking and how to properly protect the affected joint.
- Gentle mobilization of the infected joint can begin if the patient is reacting well following 5 days of medical treatment.
- Once the infection is well-handled, current proof states the patient will generally respond best to aggressive physiotherapy to allow maximum post-infection functioning.
- Physical therapy needs to correspond with allowing the joint to be in its functional position and positioning the joint to allow a passive range of motion activities.
Key points
- Septic arthritis is an infection within the junction (synovial) fluid and joint tissues.
- Different types of bacteria, contagions, and fungi can infect a joint.
- Symptoms include fever, swelling, heat, joint pain, redness
- Quick treatment with antibiotics is needed to decrease the risk of joint damage.
- Other treatments include medicines for drainage of the joint, physiotherapy, pain and fever, and a splint.
FAQ
How does septic arthritis start?
Septic arthritis (also referred to as contagious arthritis) happens when an infection spreads to one or further of your joints and causes inflammation. The inflammation is within the surface of the cartilage (a type of connective tissue) that lines your joints and the synovial fluid that lubricates your junction. A contagion, Bacteria, or fungus may cause the infection, which generally comes from another part of your body and spreads to your joint through your blood.
Can you live a full life with arthritis?
You can’t predict this complaint. But while some people experience serious difficulties, others carry on living long, healthy lives without complications. Indeed though there’s no way to predict the progression of rheumatoid arthritis, treatments have bettered over the years. this enables numerous diagnosed with the condition to live long, healthy lives into their 80s or 90s, with smaller complications of the disease. With an early diagnosis and treatment, it’s possible to realize remission and enjoy life to the fullest.
What is the last stage of arthritis?
Stage IV: Bony Ankylosis
As the name suggests, stage IV is when the bones fuse along with actual bone tissue rather than just connective fibrous tissue. At this stage, the pain actually goes down, but so does the power to move. The joint is truly gone, so you can’t bend or flex the world. Once someone has stage IV atrophic arthritis, they’ll have problems doing the tasks and hobbies that they normally would.
What drinks are good for arthritis?
Tea is one of the best beverages for arthritis cases due to its numerous health benefits. Green, black and white teas are all rich in anti-inflammatory components like polyphenols. Coffee has proven to possess thick antioxidant profiles along with a generous concentration of anti-inflammatory polyphenols. Coffee attacks dangerous free radicals within the body, which may cause all types of severe cell damage. Coffee also provides a defensive shield that forestalls the symptoms of gout. Orange, pineapple, tomato, and carrot juices are all fulfilling with vitamin C, meaning they contain antioxidant properties to fight free radicals that cause inflammation. Tart cherry juice has also helped to prevent gout flare-ups and decrease osteoarthritis symptoms. There’s one drink to focus on, it is water! Keeping your body hydrated is significant for flushing out poisons, thereby helping fight inflammation. Drinking enough water can keep your joints oiled and help prevent gout attacks.
Can septic arthritis travel?
Infectious arthritis, also called septic arthritis, involves an abrupt, severe infection of a joint. Swelling, pain, and tissue damage it’s a types of inflammatory arthritis. Infectious arthritis generally affects only one joint, but it can spread.

10 Comments