Thomas Test for contracture of the hip
- This test is performed in the clinic to check the contracture of the hip.
- This clinical test is performed by the therapist the test.
- Impaired range of motion[ ROM ] of the hip is an underlying cause of other conditions like patellofemoral pain syndrome psoas syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, lower back pain osteoarthritis.
- Often associated with the runners, dancers & gymnasts which is complained of the hip stiffness & reported of snapping sound feeling when flexing at to the waist.
Purpose of the Thomas Test :
- This Thomas test is used to for measure the flexibility of the flexors of hip .
- It is used to assess a hip flexion contracture.
- Mostly most common contracture is hip.
What is the Technique of the Thomas Test?
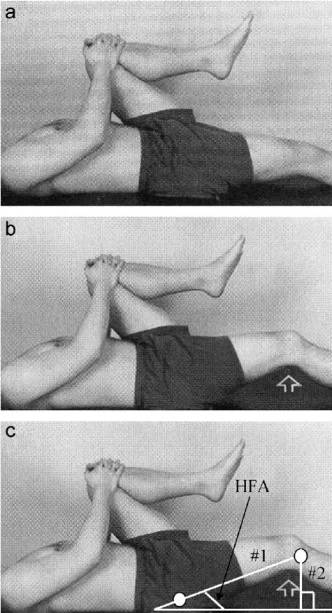
- Starting position is supine with the lower gluteal folds at the end of the table & hips & knees are flexed.
- The patient is holding the legs inflection with the hands.
- The therapist is must be sure to check the patient’s lower back into a neutral pelvic tilt.
- Then Patient is keep the unaffected leg flexed, & slowly lowers to the affected leg & lets its legs extend as far as possible.
Interpretation of the Thomas Test :
- When this test is positive following structures are considered to affect.
| Sign | Structures affected |
| Abducted hip | Iliotibial band, Tensor fascia lata |
| Flexed hip | Psoas muscles |
| Tibia lateral rotation | Biceps femoris |
| Extended knee | Extended knee Quadriceps, rectus femoris |
- If a contracture is present, the patient’s straight leg rises off the table & a muscle stretch end feel will be left.
- The angle of contracture can be measured.
- If the lower limb is pushed down onto the table, the patient may exhibit an increased lordosis, again, this result indicates a positive test.
- When doing the test, if measurements are taken, the examiner must be sure the restriction is in the hip & not the pelvis/lumbar spine.
- If the leg does not lift off the table but abducts as the other leg is flexed to the chest, it is called the J sign/stroke & is indicative of a tight IT band [ iliotibial band ] on the extended leg side.
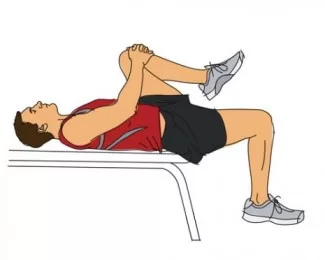
Modification of the Thomas Test :
- The modified version of this test is patient is lies down on the back,
- At the very edge of the table, with both legs are hanging freely.
- The patient is then to flex their knee & pull it back to the chest as close as to can, using both arms while doing.
- Another leg is hanging the lumbar spine remains flat & in contact with the table during the test.
Reliability of the Thomas Test:
- Reliability of the Thomas test are very limited.
- One study is demonstrated to the modified Thomas test a very good inter-rater reliability.
- Another study is demonstrated that the modified Thomas test to the average of only moderate levels of reliability.
- Further research is required to prove/refute the reliability of the Thomas test.
- Peeler & Anderson has conducted a study in 2006 examining the reliability of the Thomas test for assessing hip range.
- Their study calls into question the reliability of the technique when to used to score of range of motion & iliopsoas muscle flexibility about the hip joint use both goniometer & pass/fail scoring methods.




2 Comments