Vastus lateralis muscle: Origin, Insertion, Function, Exercise
The vastus lateralis is a long, powerful muscle on the front of the thigh that extends from the pelvis to the kneecap. It is one of four muscles that make up the quadriceps, which are responsible for straightening the knee. The vastus lateralis is the most superficial of the quadriceps muscles, located on the outside of the thigh. The other quadriceps muscles are the vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, and rectus femoris.
The muscle is predominantly found in the middle of the femur, and it makes up a large portion of the muscle in the quadriceps group. The Vastus Lateralis is the most powerful extensor of the knee. The Vastus Lateralis also plays a role in hip extension, which is necessary for activities such as jumping and running. It is fan-shaped and has a broad origin, including portions of the upper 1/3rd of the iliac crest; and the lower half of the iliac fossa.
Anatomy of Vastus lateralis muscle :
Origin :
following are the origins of Vastus lateralis muscle
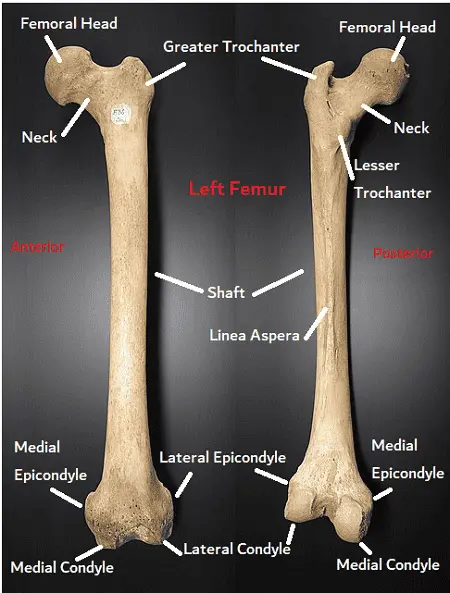
- Upper inter-trochanteric line
- the base of greater trochanter
- lateral linea aspera
- lateral supracondylar ridge
- lateral intermuscular septum
Insertion
Lateral quadriceps tendon which is finally attached over the tibial tubercle.
Nerve Supply
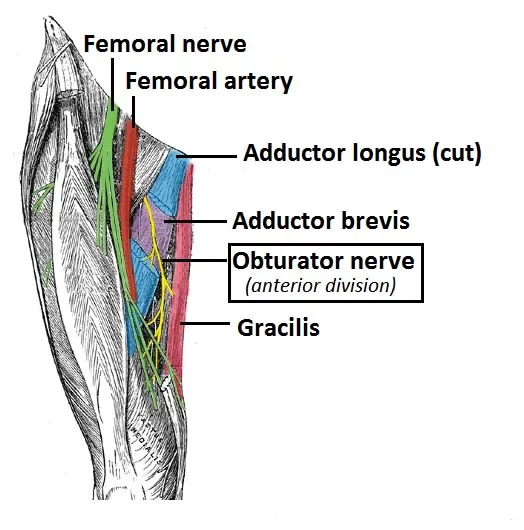
The muscle is innervated by the muscular branches of the femoral nerve (L2, L3, and L4) – (Posterior division of femoral nerve)
Blood Supply
Lateral circumflex femoral artery
Function :
The vastus lateralis muscle is the largest and most powerful part of the quadriceps muscle in the thigh. Together with the other three muscles of the quadriceps group, it serves to extend the knee joint, moving the lower leg forward.
Importance of Muscle
The vastus lateralis muscle with other quadriceps muscle groups as a whole work together to help you stand up from sitting, stair climbing, running, squatting, and walking activity.
Quadriceps muscles are relaxed during standing position with knees fully extending but become active during the heel-strike and toe-off phases of gait.
Vastus lateralis muscle exercise :
Vastus lateralis muscle exercises are mainly 2 types – Stretching exercise and strengthening exercise.
Strengthening exercise :
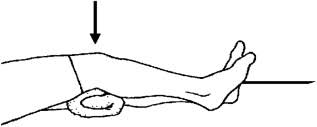
Knee extension in High sitting position :
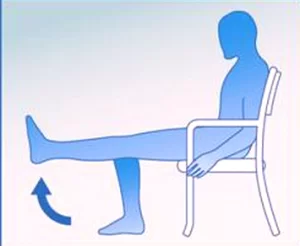
In a high sitting position, with your Hip-knee 90-degree flexed position on the Chair, gradually extend the lower leg and try to extend the knee fully, Hold for 5 to 10 seconds and return to the starting position, Do 10 do this exercise 10 times. As you progress you can start with a weight cuff of 1kg.
Static Quadriceps exercise (SQE)
To do This exercise, Take a long sitting position on a soft mat with the Knee Fully extended position and keep a folded towel beneath the knee press the towel and Hold for 5-8 seconds and relax and do this exercise 10 times.
Stretching exercise

Side-Lying Quadriceps Stretch
This stretching exercise is an easy-to-perform home exercise to keep you flexible. Take a side-lying position on the floor in a soft mat–a supported position can help you focus on the stretch in your quadriceps muscle.
- Take a Side-lying position on your side.
- Bend the knee fully of your top leg as far as possible.
- Maintain position for 5-12 seconds, Then relax
- Repeat the exercise 4 to 5 more times with the other leg.
Clinical Importance
Patellofemoral pain syndrome
Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) is the most common cause of anterior knee pain. It is also one of the main causes of non-traumatic knee pain during sports over-activities mainly vastus lateralis contracts. PFPS is diagnosed by physical examination, but sometimes an imaging test, such as an X-ray or MRI, may be done to rule out other causes of knee pain.
In recent medical studies vastus lateralis/medialis co-ordination timing has been shown to be uneven in healthy test subjects. However, this study is not clinically proven.

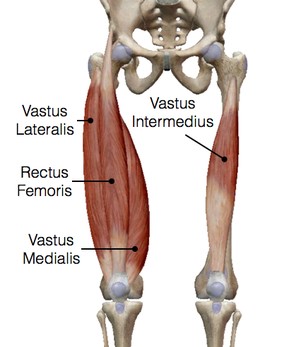

Vastus lateralis is the most powerful muscle of the Quadriceps group and we use it highly in day-to-day activities like sit to stand, walking, stair climbing, and also the bulkiest muscle as compared to other quadriceps muscles.